Since the first report in 1975 on the development of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) using hybridoma cell lines, the field has witnessed rapid and robust growth in both therapeutic and diagnostic antibodies. Antibodies have become indispensable tools in basic and translational biological research. However, the use of traditional hybridoma-generated antibodies or polyclonal antibodies derived from animals comes with several drawbacks.
(Moraes J. Z, et al. Current Research in Immunology. 2021)
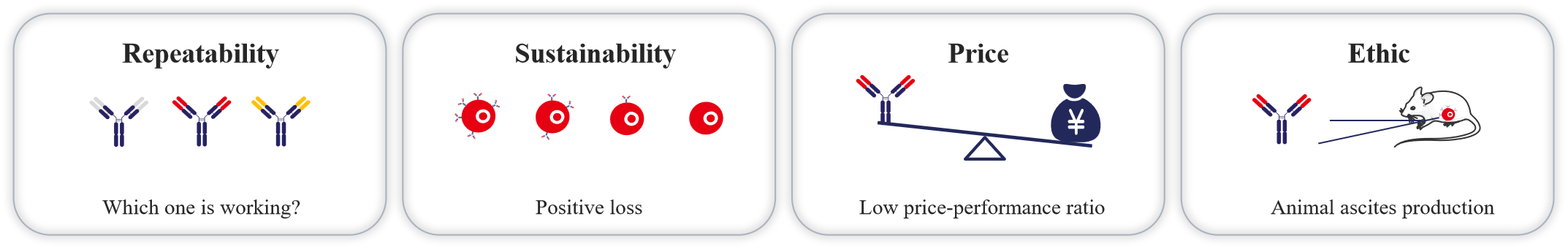
Reproducibility: Due to the lack of standardized and well-defined antibodies, their characteristics are often incomplete, not molecularly validated, and exhibit variations in performance across different batches.
Sustainability: The continuous availability of traditionally produced antibodies cannot be guaranteed, as their quality depends on the stability during maintenance, storage, or continuous production in animals.
Cost: For many researchers, the high cost of commercially available traditional antibodies severely limits research innovation.
Ethical concerns: The use of a large number of vertebrate animals to generate antibodies for biomedical research raises ethical issues.
To address these challenges, researchers have continually developed practical methods and tools. With advancements in antibody mass spectrometry and hybridoma sequencing, coupled with progress in host cell production and purification processes, the expression and manufacturing of recombinant antibodies have advanced. Improvements in expression hosts, expression vectors, cell culture media and production purification processes have elevated antibody expression levels to hundreds of milligrams or even gram-scale levels. Recombinant antibodies circumvent many of the issues associated with traditional antibodies: firstly, using recombinant antibodies produced from an unaltered amino acid sequence enhances reproducibility; secondly, recombinant antibodies can be used indefinitely once the sequence is determined; thirdly, low-cost expression and purification systems allow for the mass production of recombinant antibodies.
(Different types of antibodies)
Based on a mammalian cell recombinant expression platform, We have developed practical methods and tools to prepare diverse forms of recombinant monoclonal antibodies based on the original antibody sequences. This approach ensures low cost, high yield, and high-quality delivery.