Usually, cell lysates contain the essential components for translation, protein folding, and energy metabolism. Almost any protein encoded by an RNA template can be synthesized by adding amino acids, energy substrates, nucleotides, and salt. In the transcription-translation system, recombinant proteins can be synthesized by adding the appropriate RNA polymerase (such as T7 RNA polymerase) and a DNA template (PCR product or vector) containing the corresponding promoter. Compared to host cell-based expression systems, the cell-free expression system provides the capability to rapidly express challenging proteins, including transmembrane proteins and even toxic proteins.
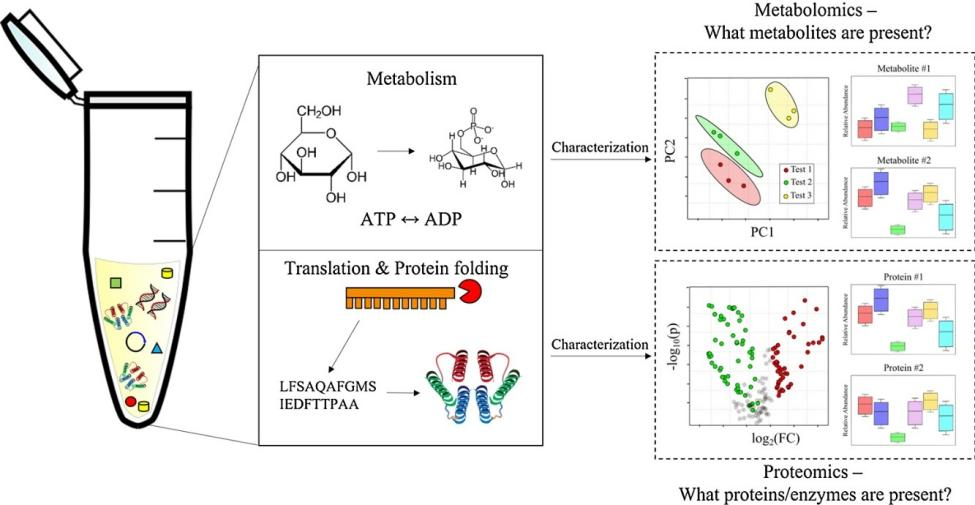
(Sridharan H, et al. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2022)
Through the lysis of selected cells, crude cell extracts are prepared, followed by multiple washing steps to remove cell debris and genomic DNA. These cell extracts can be stored for many years at -80°C and can be thawed and used before reactions. They contain all the essential components for transcription and translation, such as aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (AAS), ribosomes, and factors required for elongation, initiation, and transcription. Cell-free expression systems achieve this by combining cell extracts with necessary substrates (such as amino acids, energy substrates, DNA, cofactors, salts and nucleotides). The choice of a suitable cell-free expression system can be based on the biochemical characteristics of the protein and its ultimate application.
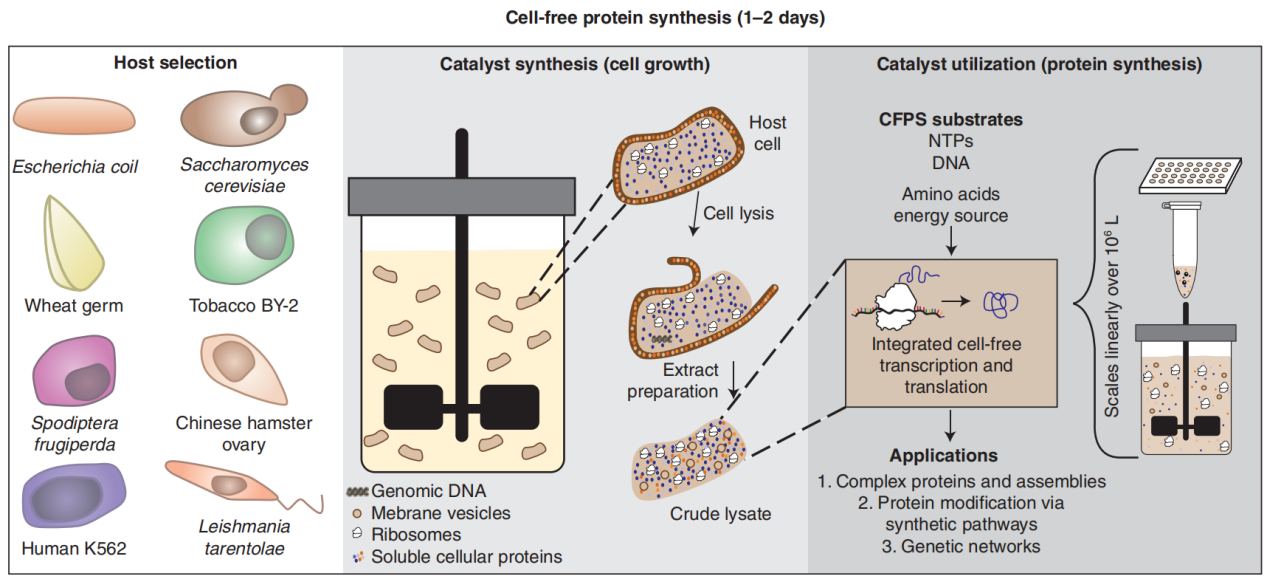
(Perez JG, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016)
The cell-free expression system is a rapid protein expression system because it doesn't require transfection or cell culture, has no cell viability limitations, and due to its open nature, offers more advantages compared to cell-based expression methods. Currently, Mabnus Biotech can provide recombinant protein expression services based on the E. coli cell-free expression system, allowing for easy detection and purification.
This system primarily includes:
Optimized E. coli cell extracts that enhance the stability of structures during DNA transcription and translation processes, increasing the yield of soluble proteins.
Optimized reaction buffer that continuously provides energy for protein synthesis through an ATP regeneration system.
Optimized amino acid concentrations to provide ample substrate supply for protein synthesis.