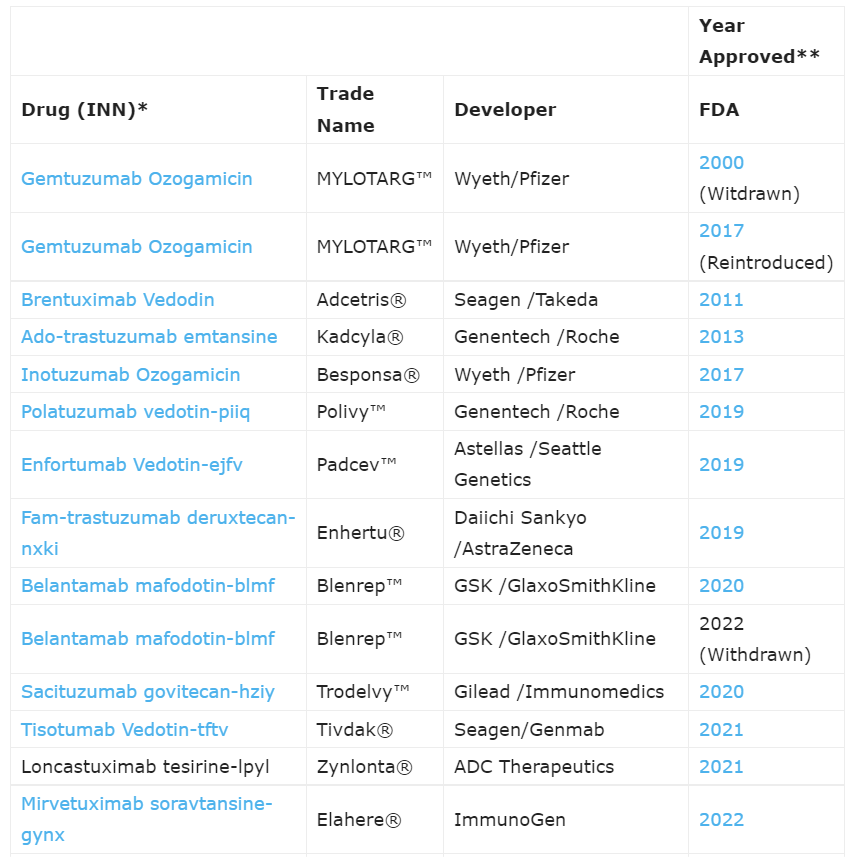
In the past over 30 years, antibody-based cancer therapy has achieved significant success. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), as a complex and continually evolving class of drugs, are specially designed to deliver anticancer drugs to cancer cells in the most precise and selective manner. Currently, there are 12 approved ADCs on the market, making them a powerful class of therapeutic drugs in the fields of oncology and hematology.
(FDA)
According to data from Pharmaprojects, there are currently 428 ADC drugs in development. The industry is currently focused on the next generation of ADCs that exhibit higher efficacy and fewer side effects. HER2 stands out as the most common target for ADC therapy, but there is also a growing utilization of other targets. Claudin 18 has emerged as a new target for ADC developers.
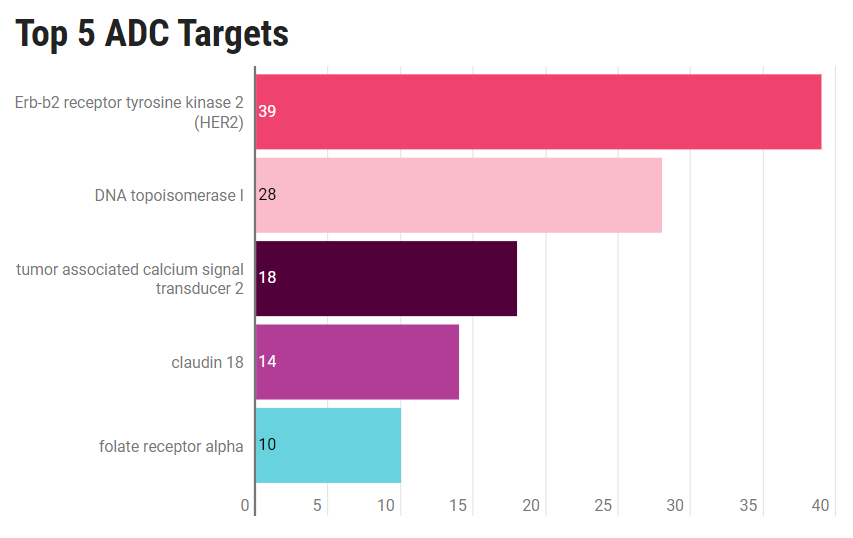
(The top 5 popular ADC targets)
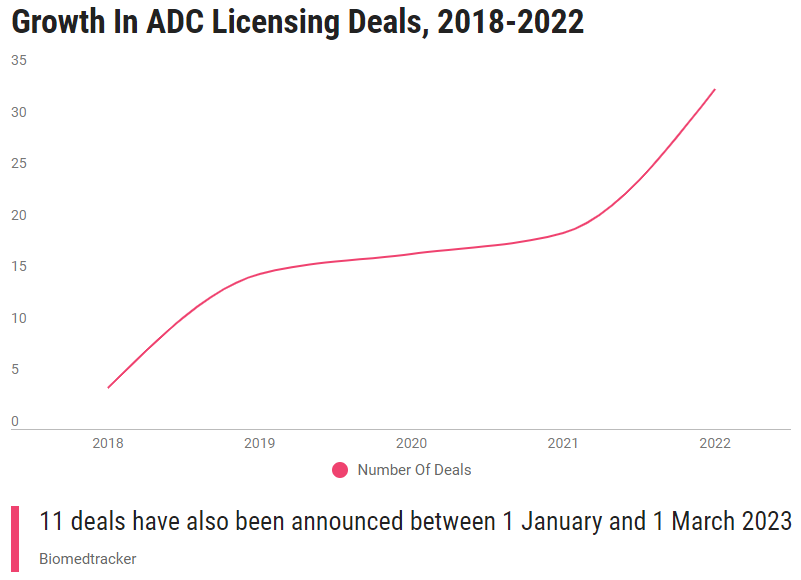
(Recent numbers of ADC licensing transactions)
ADC (Antibody-Drug Conjugate) is an enhanced antibody (mAb) designed to leverage their targeting capabilities by connecting monoclonal antibodies with cytotoxic agents. An ideal ADC possesses:
A highly selective monoclonal antibody (Antibody) targeting tumor-associated antigens, which are expressed in a limited or absent manner on normal (healthy) cells.
A potent cytotoxic drug (usually a small molecule drug with high systemic toxicity) designed to induce targeted cell death after internalization and release within tumor cells.
A linker (Linker) that is stable in circulation but releases the cytotoxic agent within the target cells.
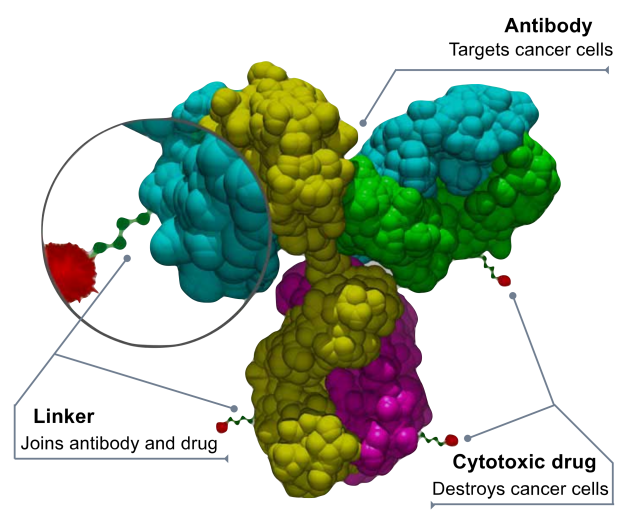
(The structure of ADC,Courtesy By Bioconjugator )
From a mechanistic perspective, ① when intravenously administered ADC binds to the target antigen on the surface of tumor cells, ② this complex is internalized into the cell. ③ After internalization, the internalized vesicle fuses with other vesicles and enters the endolysosomal pathway. ④ In the lysosome, proteinases in the weakly acidic environment digest the monoclonal antibody to release the free payload. ⑤ The released payload then traverses the lysosomal membrane to enter the cytoplasm and/or nucleus, where it binds to target molecules, ultimately leading to cell death.
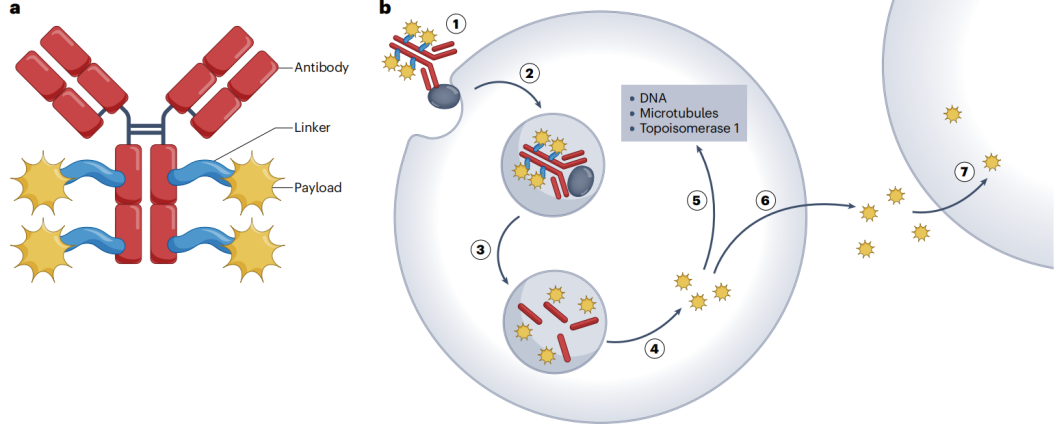
(Dumontet C, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023)
While the concept of ADC is relatively easy to understand and seemingly simple, designing a fully functional and effective ADC is highly challenging and typically requires a specialized development team. Wuhan Meisu Biotechnology is a company dedicated to the development of recombinant proteins and recombinant antibodies. We currently have an organic chemistry team capable of conducting linker chemistry conjugation and design for existing antibody drug conjugate analogs, and we offer ADC drug reference standards:

ADC purity detection ≥98%:
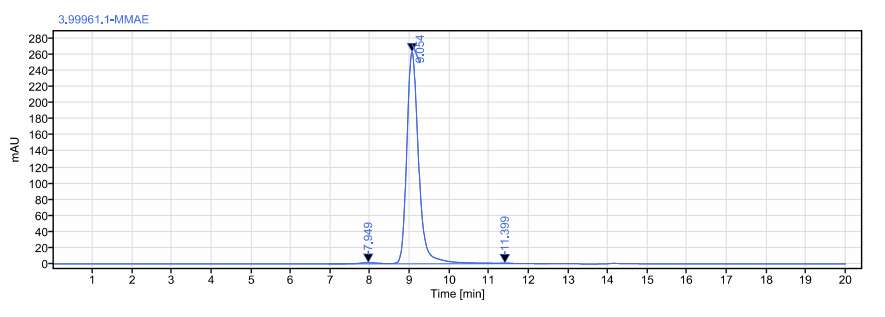
ADC drug antibody ratio (DAR) detection at 3.7:
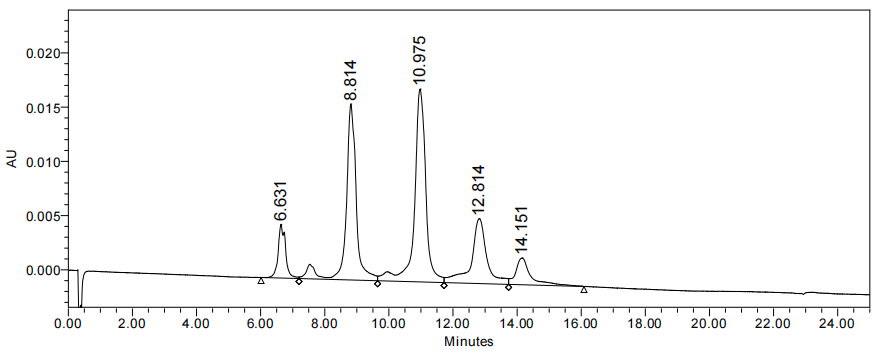
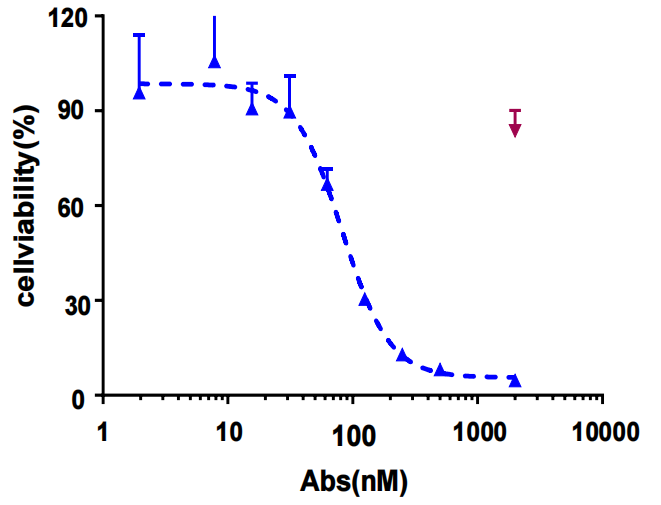
ADC intracellular uptake and toxicity assays: