Nectin-4, also known as poliovirus receptor-associated protein 4, is closely associated with tumor growth, angiogenesis, metastasis, and recurrence. Due to its target-specific expression, nectin-4 has emerged as a potential biomarker and promising target for cancer therapy.
Nectin-4 expression distribution
Nectin-4 is expressed in the placenta and embryo, but at lower levels in healthy adult tissues (e.g., skin and bladder) and cells.

(Data source: Uniprot)
It is highly expressed in malignant tumors, including bladder cancer, bile duct cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, skin cancer and other diseases.
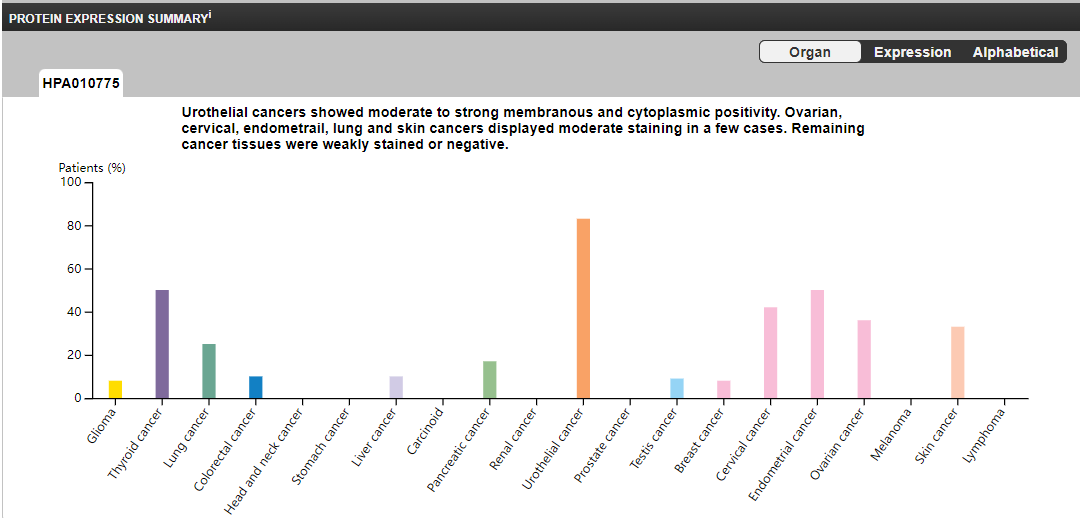
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of nectin-4
Nectin-4, encoded by the PVRL4 gene located on chromosome 1q23.3, is a 66 kDa, single-pass transmembrane type I membrane protein. Its extracellular domain, consisting of two C2-type and one V-type immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) domains, is directly involved in cell-cell adhesion. The intracellular portion interacts with the actin-binding protein afadin and participates in intracellular signaling. The C-terminus of nectin-4 contains a conserved Gly-His-Leu-Val motif, which binds to the PDZ domain of afadin.

(Data source: uniprot)
The role of nectin-4 in cancer
Nectin-4 binds to the PDZ domain of afadin. Upregulated nectin-4 can interact with afadin and activate Rac1 through the PI3K/AKT pathway, promoting tumor growth, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Under hypoxic conditions, the proteolytic enzyme ADAM-17 specifically cleaves nectin-4 into extracellular and intracellular fragments. The intracellular fragment is transported to the nucleus, where it participates in DNA repair and promotes cell survival. The extracellular fragment binds to integrin-β in vascular endothelial cells and promotes angiogenesis through the PI3K/AKT-mediated endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) pathway. Furthermore, the extracellular fragment activates lymphatic vessel endothelial receptor 1 (LYVE-1)-mediated lymphangiogenesis through interaction with CXCR4/CXCL12. Nectin-4 is a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis.

(Data source: Wang Y, et al. Breast. 2024)
Nectin-4 targeted therapy
Nectin-4-targeted therapeutics primarily utilize antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Enfortumab vedotin (EV) is an ADC targeting nectin-4 and has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of urothelial carcinoma. EVs are complexes formed by a protease-dependent linker linking the microtubule-disrupting agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) to an anti-nectin-4 monoclonal antibody (AGS-22M6). EVs bind to nectin-4 on the cell membrane, and the EV-antigen complex is internalized and transported through the endosomal pathway. During this process, EVs are first hydrolyzed by various enzymes and ultimately completely broken down into lysosomes. The released MMAE disrupts microtubules, leading to cell apoptosis due to inhibition of cell division.
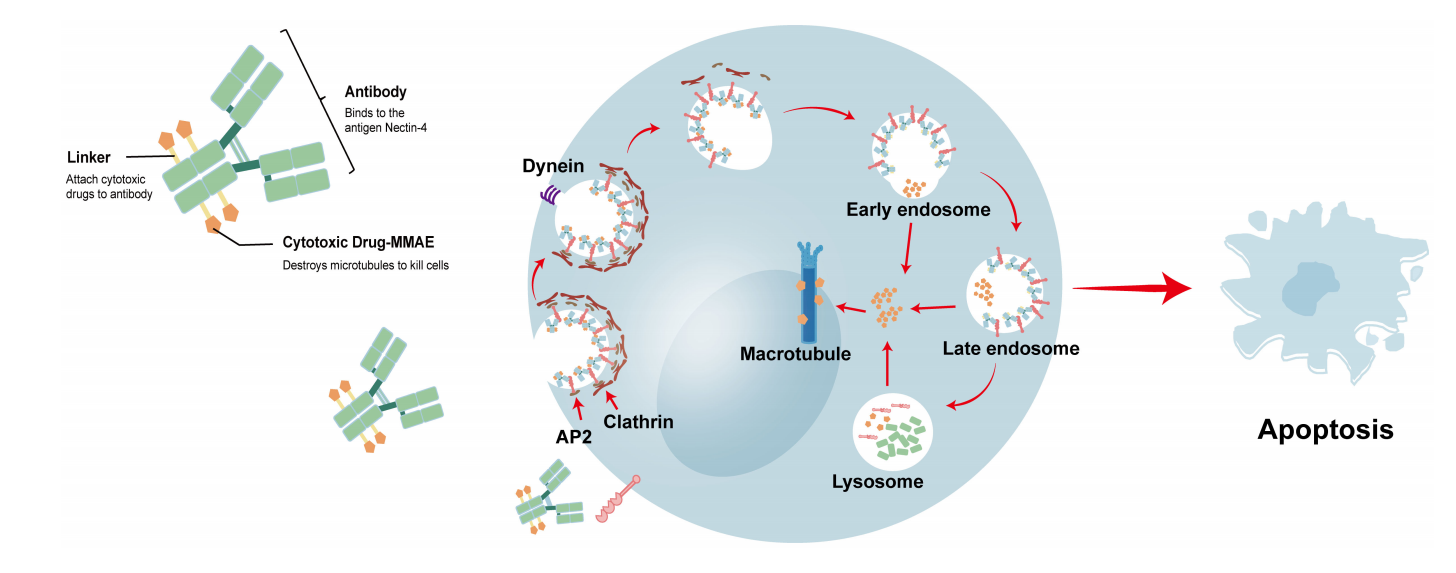
(Data source: Li K, et al. Front Oncol. 2024)
9MW2821 consists of an anti-nectin-4 antibody (MW282), a connector (IDconnect), and MMAE. IDconnect is a novel thioether connector that cross-links the Fab and hinge regions, allowing for stronger attachment of MMAE. The IDconnect design is an advantage of 9MW2821, demonstrating a reduction in the amount of non-targeted drug in circulation and reduced liver toxicity. Compared to EVs, 9MW2821 has a uniform drug-antibody ratio (DAR) and has demonstrated superior anti-tumor efficacy and fewer side effects in preclinical trials.
ADRX-0706 and BAT8007 are also ADCs targeting nectin-4. ADRX-0706 has a DAR of 8 (typical DARs for ADCs range from 2-4), resulting in significantly increased drug concentrations in the localized tumor area. Therefore, therapeutic effects achieved with high DARs deserve greater attention. Clinical trials of ADRX-0706 are ongoing in patients with specific advanced solid tumors, including urothelial carcinoma, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, breast cancer, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, NSCLC, and pancreatic cancer (NCT06036121).
Nectin-4 antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) can also be used in combination with other treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, radiotherapy, immune checkpoints, and other ADC drugs.
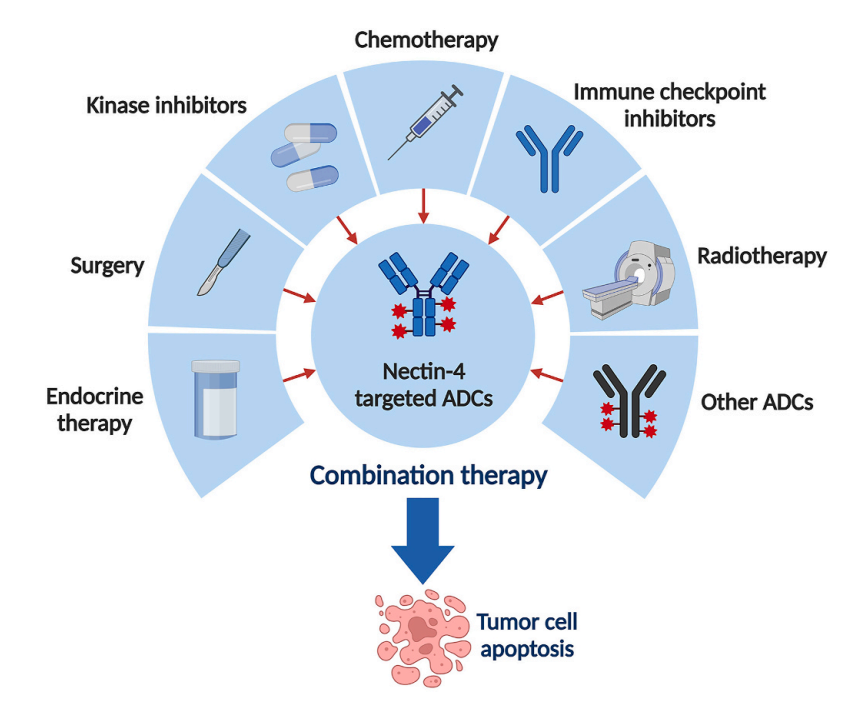
(Data source: Wang Y, et al. Breast. 2024)
