Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) is a broad-spectrum mitogen that acts as a polypeptide ligand in a paracrine or endocrine manner. FGF stimulates or maintains specific cellular functions required for metabolism, tissue homeostasis, and development through signaling axes mediated by fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs).
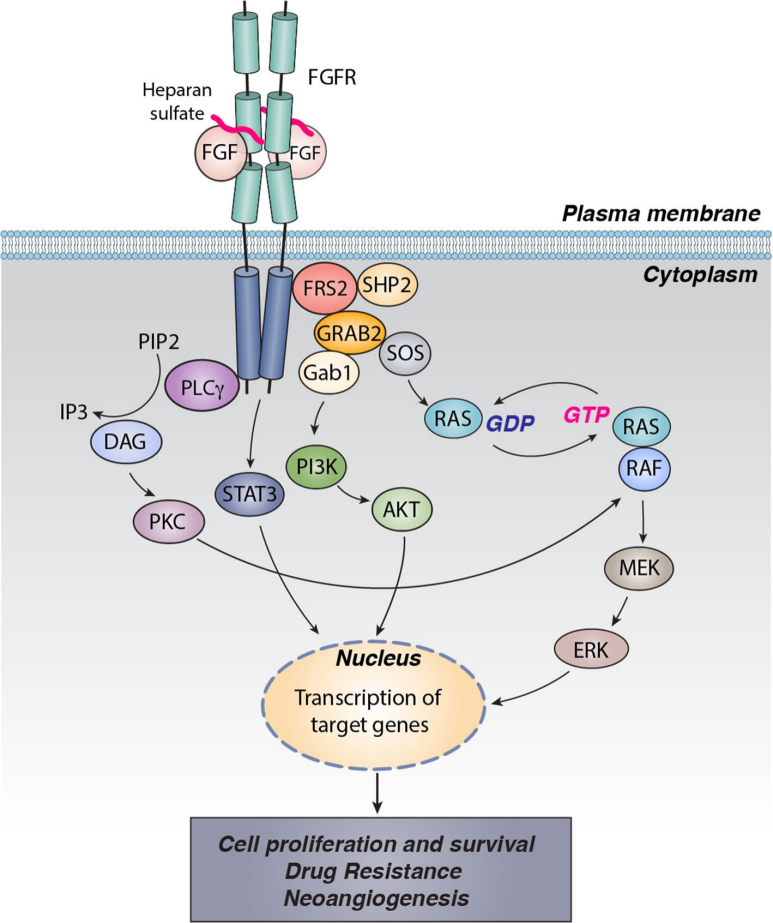
(Data source: Chen L, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021)
The mammalian FGF family consists of 22 related members, all of which have a core segment of approximately 140 amino acids. Based on amino acid sequence and structural analysis, 18 of them are divided into five paracrine action groups (FGF1, FGF4, FGF7, FGF8, FGF9 subfamilies) and one endocrine action group (FGF19 subfamily), and there is also an intracellular non-crine action group (FGF11 subfamily).
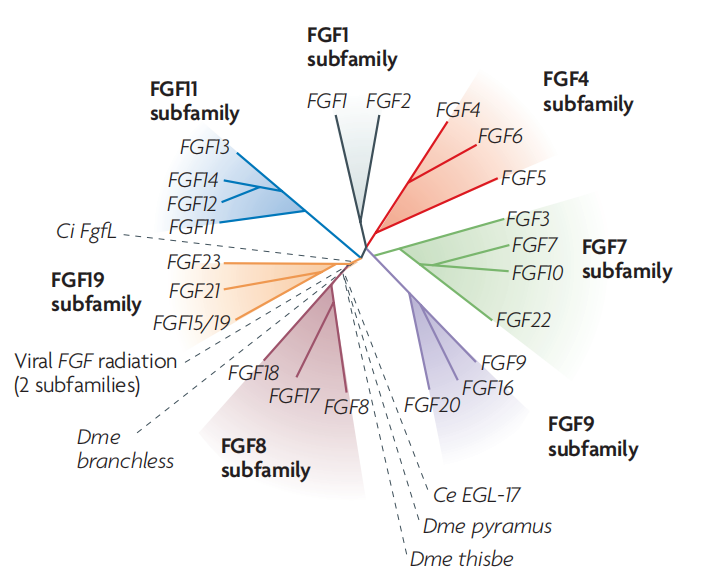
(Data source: Mason I. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007)
So far, five FGFR family members have been identified: FGFR1, FGFR 2, FGFR3, and FGFR4 are single-pass transmembrane proteins containing an extracellular domain (ECD), a transmembrane domain (TMD), and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) (wherein , ECD is composed of three immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains (1–3), an acidic region, and the heparin-binding motif of FGF. TMD anchors the receptor in the cell membrane and promotes its dimerization. In the cytoplasm, the membrane-proximal region of FGFR participates in receptor dimerization, while TKD is required for transmitting FGF-related signals.); FGFR 5/FGFRL1 is a truncated FGFR without an intracellular domain.

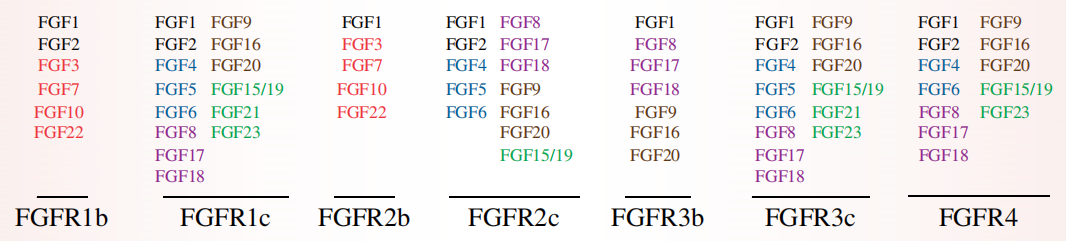
(Data source: Turner N, et al. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010)
Alternative splicing of the second half of the IgIII domain of FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 generates b (FGFR1b-3b) and c (FGFR1c-3c) isoforms, which have different FGF-binding specificities.
(Data source: Francavilla C, et al. Open Biol. 2022)
The binding of FGF ligands to FGFRs is located in the D2 and D3 domains of the extracellular domain. When FGFs bind to inactive monomeric FGFRs, they trigger conformational changes in FGFRs, phosphorylating tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic tail of FGFRs, leading to dimerization and activation of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases.
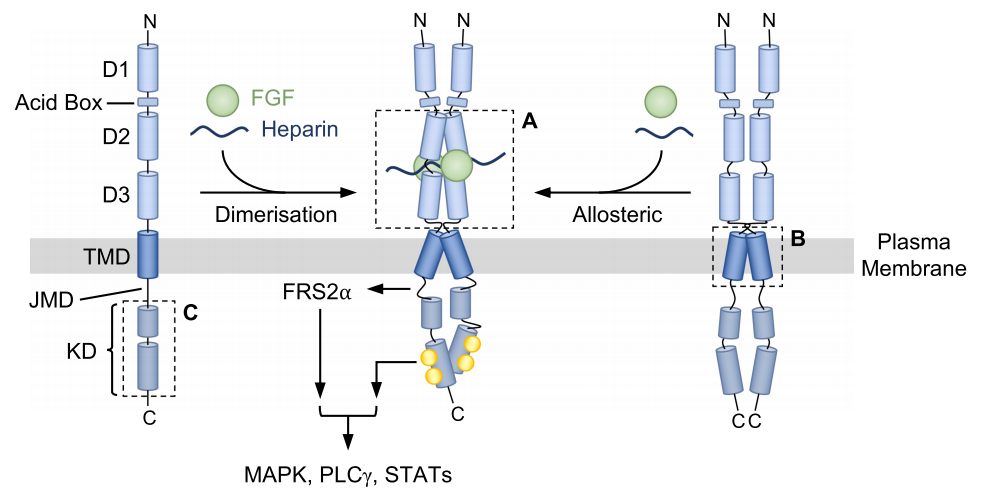
(Data source: Farrell B, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018)
The FGF & FGFR signaling axis has been observed in a variety of human diseases, such as craniosynostosis and dwarfism, as well as chronic kidney disease (CKD), obesity, insulin resistance, and various tumors. These abnormalities are primarily due to dysregulated expression of paracrine FGF family proteins and genetic alterations in FGF, FGFR, or accessory factor genes—such as mutations, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), or fusions. Furthermore, dysregulation of the FGF & FGFR axis is implicated in cellular processes during the development of drug resistance, thereby limiting the effectiveness of current treatment strategies.
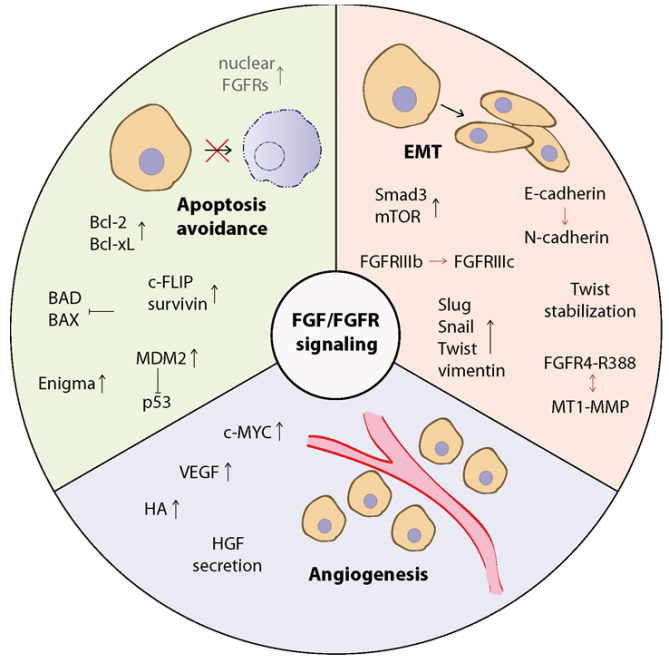
(Data source: Szymczyk J, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021)
Given the importance of FGFR signaling in a range of pathologies, numerous drugs are being developed to target this pathway. These treatments fall into four categories: (i) orthosteric binding inhibitors, which target the ligand-binding domain of the receptor, preventing FGF attachment and induction of downstream signaling; (ii) allosteric inhibitors, which bind to the extracellular portion of the receptor, preventing its internalization and signaling even upon ligand binding; (iii) ligand traps, which consist of the ligand-binding domain, such as the extracellular portion of FGFR1c fused to the Fc domain of IgG1, competing for ligand binding, leading to ligand sequestration and thus preventing receptor stimulation; and (iv) small molecule kinase inhibitors, which are the most common therapeutic approach and target the ATP-binding region of the intracellular kinase domain of the receptor.
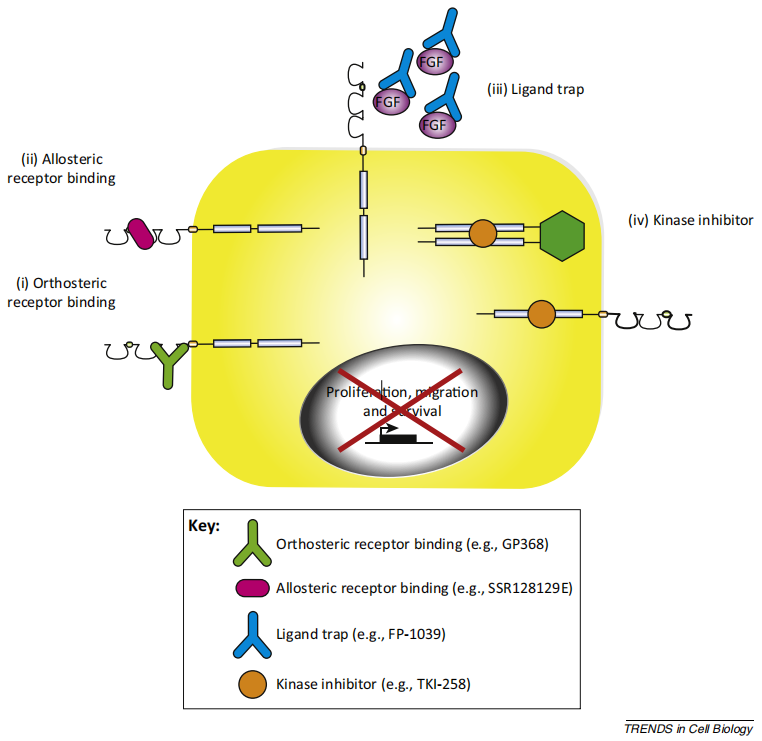
(Data source: Carter EP, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2015)
Let's take a closer look at each member of the FGF family:
FGF1 subfamily: FGF1, FGF2
FGF4 subfamily: FGF4, FGF5, FGF6
FGF7 subfamily: FGF3, FGF7, FGF10, FGF22
FGF8 subfamily: FGF8, FGF17, FGF18
FGF9 subfamily: FGF9, FGF16, FGF20
FGF11 subfamily: FGF11, FGF12, FGF13, FGF14
FGF19 subfamily: FGF19, FGF21, FGF23
