Serum amyloid A (SAA) is a nonspecific acute phase protein primarily produced by liver cells. It acts as an immune preventive molecule, combating local inflammatory damage. When infected or injured, SAA levels can rapidly increase by approximately 1,000-fold within 4-6 hours. Once the antigen is cleared, SAA quickly returns to normal. It is a sensitive indicator of infection status and inflammatory recovery.
The structure of SAA
SAA is composed of a family of proteins encoded by multiple genes located on human chromosome 11. The human SAA monomer structure consists of four α-helical regions and a C-terminal amorphous tail, with no β-pleated region. SAA normally exists as a hexamer composed of two trimers.

(Data source: Lu J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014)
Function of SAA in inflammation
SAA induces the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-4, IL-8, IL-10, IL-18, COX-2, and TNF-α. SAA promotes the infiltration of distal colonic macrophages and the pathogenic differentiation of CD4+ T cells. Its binding to macrophages leads to IL-1β secretion and lipid internalization for tissue repair. Elevated SAA levels contribute to colitis-associated cancers. SAA also helps clear toxic lipids and membrane debris to accelerate tissue repair.
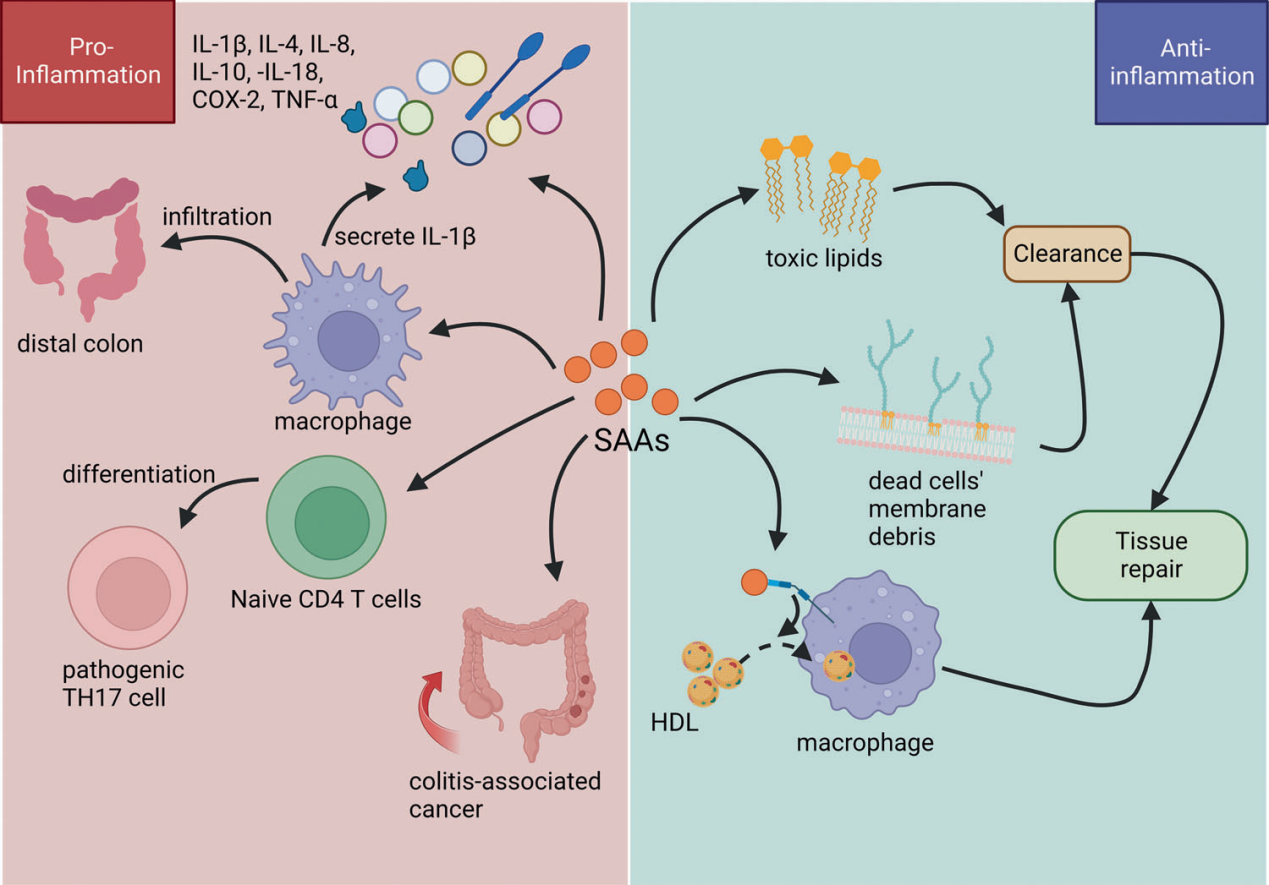
(Data source: Chen R, et al. Cell Death Discov. 2023)
Clinical value of SAA:
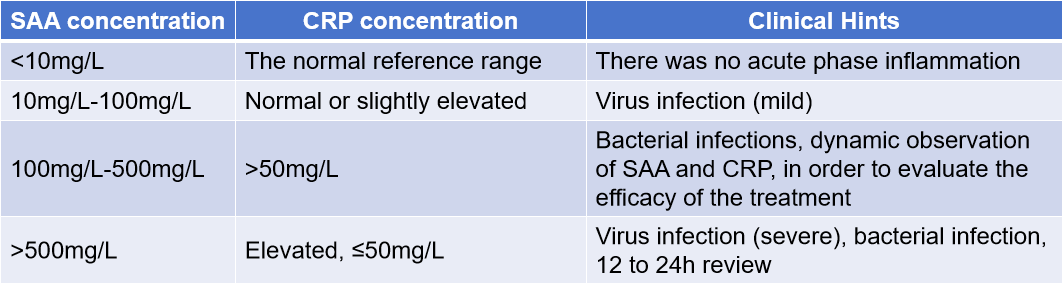
SAA combined with CRP testing: Under normal circumstances, the reference range of serum SAA is <10 mg/L. SAA can be combined with CRP to differentiate between bacterial and viral infections. When the serum SAA concentration is >100 mg/L, if the CRP concentration is >50 mg/L, it may indicate a bacterial infection; if the CRP concentration is elevated but <50 mg/mL, it may indicate a severe viral infection or a bacterial infection.
SAA combined with PCT testing: helps in the early diagnosis of systemic inflammatory reactions such as neonatal sepsis and septicemia, as well as the identification and monitoring of infection in critically ill patients.
Transplant rejection: SAA can be used as a sensitive marker for monitoring renal transplant rejection and early liver transplant rejection.
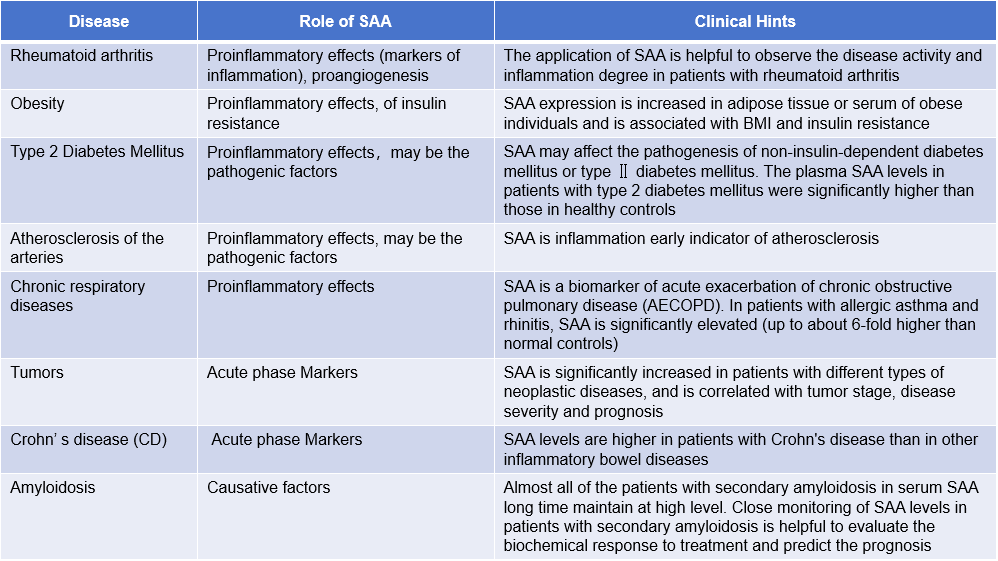
The role of SAA in non-infectious diseases: SAA also plays an important role in non-infectious diseases, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease and autoimmune diseases.

(Data source: den Hartigh LJ, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023)
SAA targeting strategy:
Inhibiting inflammatory pathways: Anakinra and canakinumab are monoclonal antibodies against IL-1β that have been used to reduce SAA levels in inflammatory conditions such as FMF and gouty arthritis.
Use of small molecule peptides: Synthetic small molecule peptides can mimic the structure and function of SAA and may help regulate its activity by competing with SAA for binding sites.
Liposomal delivery system: Use nanocarriers such as liposomes to deliver small molecule peptides or drugs to specifically target SAA and reduce its accumulation in the body.
Antagonists targeting specific receptors: Develop antagonists targeting SAA receptors (such as FPR2/ALX, RAGE, etc.) to block SAA signaling.
