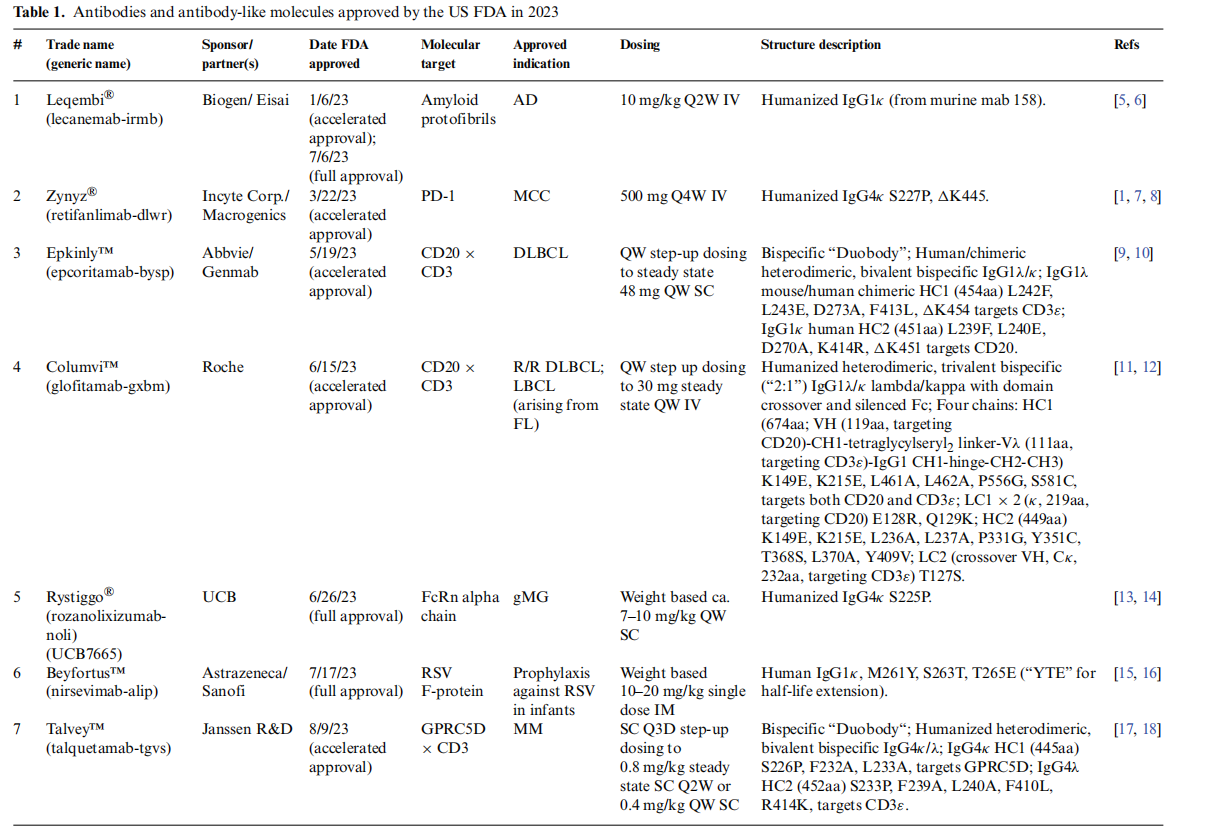
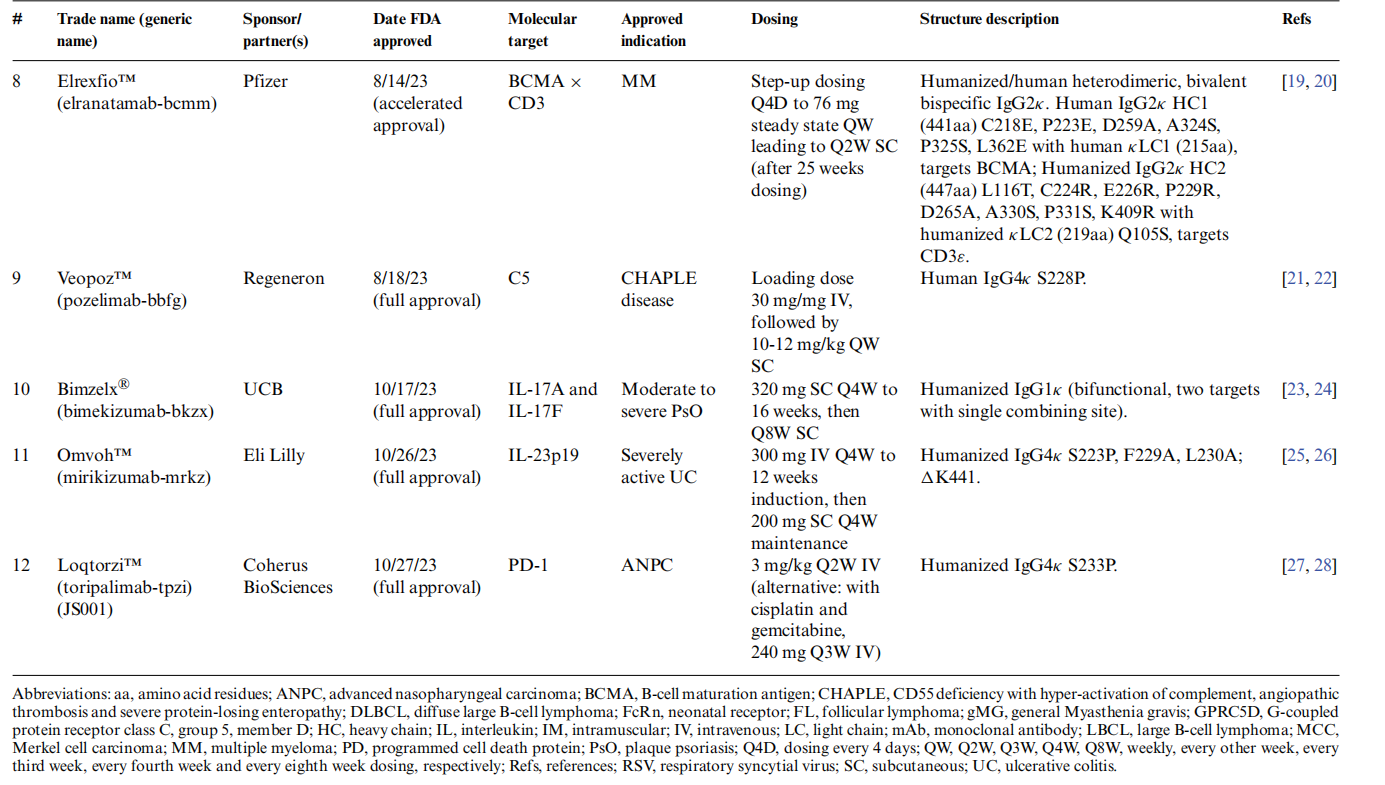
Background
Over the past decade, the number of new antibody-based biologics approved each year has increased significantly, with the FDA approving 100 new antibodies in the past decade, more than double the total number of antibodies approved previously.

In 2023, the US FDA approved 12 therapeutic antibodies, of which 8 were relatively standard IgG antibodies, 3 were bivalent bispecific antibodies, and 1 was a trivalent bispecific antibody. On March 19, 2024, William R. Strohl published an article titled "Structure and function of therapeutic antibodies" in Antibody Therapeutics.
The article "Approved by the US FDA in 2023" analyzes the structure and function of therapeutic antibodies approved by the US FDA in 2023. The approval status of these novel antibodies is described in detail, providing an important reference for further research and development of therapeutic antibodies.

Overview of the structural characteristics of 12 FDA-approved antibodies
Among the 12 antibodies approved by the US FAD in 2023, their structures also vary. Three are typical IgG1κ antibodies, one of which incorporates YTE long-half-life technology; five are hinge-stabilized IgG4κ antibodies, one of which is Fc-silenced; one is a heterodimeric IgG2κ bivalent bispecific antibody; two are heterodimeric bivalent bispecific antibodies containing κ and λ light chains; and one is a trivalent heterodimeric bispecific antibody using Roche's CrossMab technology.

These approved antibodies primarily target various indications, such as Alzheimer's disease, multiple myeloma, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, and infant respiratory syncytial virus.
Lecanemab-irmb (Leqembi®)
AD is the most common form of dementia, leading to progressive cognitive and behavioral disorders. One of the most popular explanations for the pathogenesis of AD is the "amyloid hypothesis", which can be summarized as the accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides (Aβ40 and Aβ42) to form neurotoxic senile plaques, which in turn promote the development of tau pathology, both of which lead to neuronal cell death and neurodegeneration.

(Data source: Shajahan SR, et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024)
The first antibody approved by the US FDA for the treatment of AD is Aduhelm (aducanumab), which was approved on June 7, 2021. Two antibodies for the treatment of AD have been approved by the US FDA, and others are in clinical trials.
Lecanemab-irmb (Leqembi®) is the first novel antibody approved by the U.S. FAD in 2023. It is the second antibody approved by the U.S. FAD for the treatment of AD targeting the amyloid-β (Aβ) pathway. In January of this year, Leqembi received accelerated approval from the FAD based on biomarker data from a Phase II trial.

Leqembi is a humanized IgG1κ antibody derived from Mab158 that targets residues 1-15 of Aβ 42; it preferentially binds to toxic forms of Aβ, including Aβ oligomers and soluble Aβ fibrils. Aduhelm targets residues 3-7 of the Ab and prefers to bind to more complex Aβ plaques, resulting in a reduction in plaque volume. Lecanemab binds these toxic oligomers and protofibrils 10-15 times more potently than it binds to Aβ fibrils and existing plaques, and 100-fold more potently than Aβ monomers. This differs from solanezumab, which primarily binds to monomers, and aducanumab and gantenerumab, which have a greater preference for binding to plaques and mature fibrils. The key to the success of an antibody is related to the actual Aβ epitope to which the antibody binds and the pathogenic form of Aβ to which it binds in vivo.

Leqembi is mainly used to treat patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia. During the 18-month treatment, the Leqembi treatment group showed a 47% slowdown in clinical decline in the ADAS-Cog14 scoring system, and also showed the effect of reducing the burden of amyloid protein in the brain and slowing the development of tau pathology.
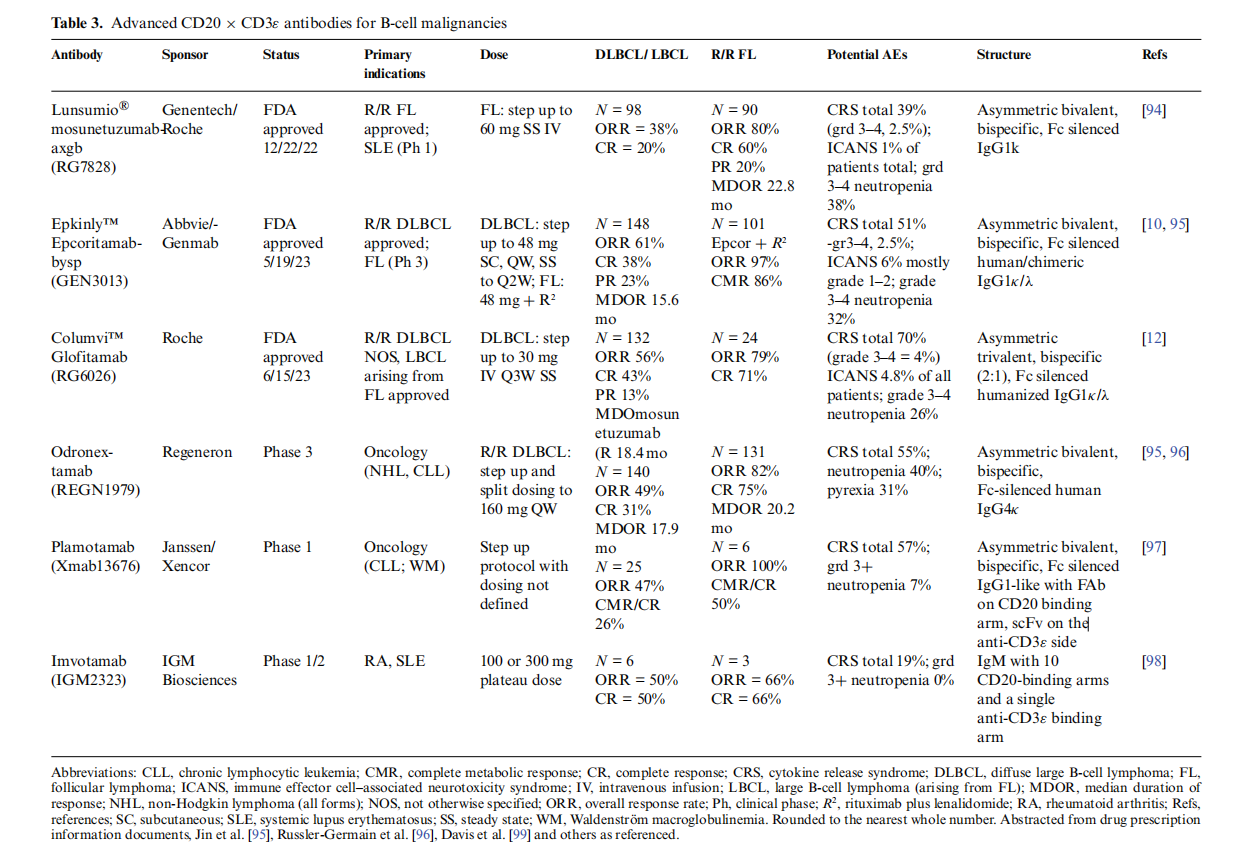
Epkinly™ (epcoritamab-bysp) and Columvi™(glofitamab-gxbm)
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) is a malignant disease of the lymphatic system that can be indolent, slowly progressive, or aggressive. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive form of NHL.
The US FDA approved two new anti-CD20 antibodies, epcoritamab and glofitamab, in 2023, and some other antibodies are in clinical trials.
Epkinly™(epcoritamab-bysp) is an asymmetric, bivalent, bispecific, Fc-silenced human/chimeric IgG1κ/λ antibody that drives the formation of a homodimeric Fc in homodimer pairing. In this antibody, the light chain pairing issue is addressed by using Duobody technology to control the Fab arm exchange process. The parental antibodies, CD20 and CD3ε, are oxidized separately, mixed, and then reduced. A CH3 (F413L) mutation is introduced on the CD3ε side, and a K414R mutation is introduced on the CD20 side. This allows for heterologous Fc formation through recombination of the parental IgGs. Epkinly™ is administered subcutaneously, has a long half-life, and a low rate of drug resistance, which offers certain therapeutic advantages.
Columvi™(glofitamab-gxbm), also known as RG6026, is a trivalent IgG1κ/λ-based bispecific antibody with two binding sites targeting CD20 and one binding site targeting CD3ε. It is used to treat relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and has demonstrated good overall response rates and durable complete remission rates in clinical trials.
Zynyz®(Retifanlimab) and Loqtorzi™(toripalimab)
PD-1 is a checkpoint receptor present on activated T and B lymphocytes. It normally binds to the PD-L1 receptor expressed on antigen-presenting cells and tumor cells. Normally, PD-1 suppresses immune responses by inhibiting the activity of inflammatory T cells, helping to prevent autoimmune reactions. However, many forms of cancer overexpress PD-L1, exploiting the PD-1/PD-L1 regulatory axis and preventing T cells from killing cancer cells.

(Data source: Zhang K, Kong X, Li Y, Wang Z, Zhang L, Xuan L. Front Pharmacol. 2022)
Retifanlimab (Zynyz®) and toripalimab (Loqtorzi™) are the fifth and sixth anti-PD-1 inhibitor monoclonal antibodies approved by the US FDA. They are both hinge-stabilized (S/P;56) IgG4κ isotype antibodies, which is currently the preferred IgG format for anti-PD-1 antibodies.
Retifanlimab (Zynyz®) binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks the interaction between its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 , thereby enhancing T cell activity. It was granted accelerated approval for the treatment of metastatic or recurrent MCC, a rare and aggressive neuroendocrine skin cancer, based on results from the POD1UM-201 trial (NCT03599713).
Toripalimab (Loqtorzi™) also binds to the PD-1 receptor, blocking its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2, thereby releasing PD-1-mediated inhibition of T cell activation. Toripalimab has an unusually long heavy chain complementarity-determining region-3 (CDR-H3) , which binds to the FG loop in a manner independent of PD-1 glycosylation. It is primarily used to treat metastatic or recurrent locally advanced NPC.
Bimzelx® (Bimekizumab)
Plaque psoriasis (PsO) is a relatively common chronic autoimmune disease of the skin, affecting approximately 2-5% of adults, of which approximately 20% have moderate to severe disease.
The IL-17 proinflammatory cytokine family consists of six structurally related members: IL-17A, IL-17B, IL-17C, IL-17D, IL-17E (also known as IL-25) , and IL-17F. They play a crucial role in combating infections, particularly fungal infections. IL-17A is primarily produced by TH17 T cells, while IL-17F is produced by T cells, innate immune cells, and epithelial cells. IL-17A and IL-17F can form homodimers and heterodimers with IL-17AF.
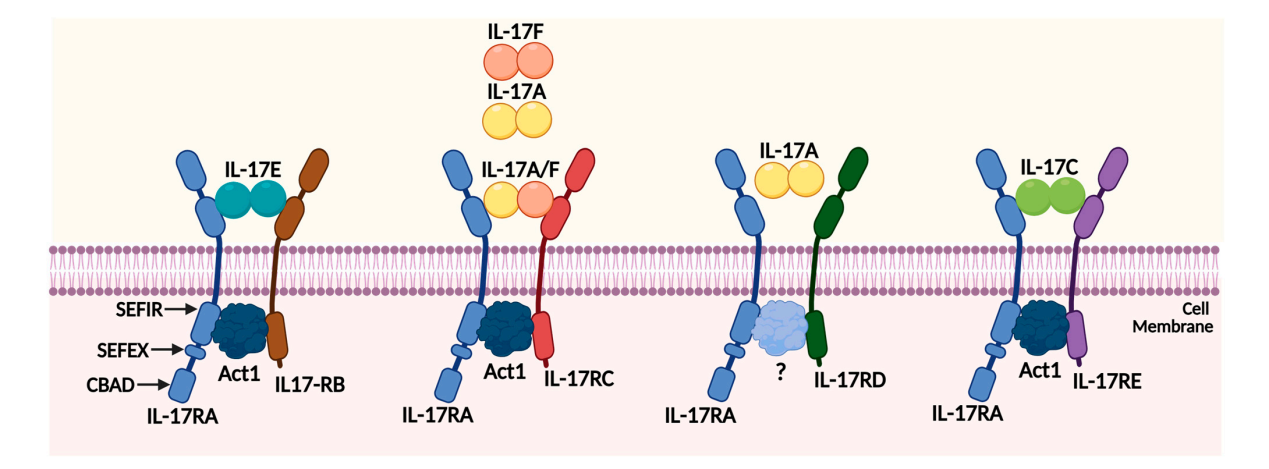
(Data source: Chen Z, Qiao S, Yang L, Sun M, Li B, Lu A, Li F. Int J Mol Sci. 2023.)
Bimekizumab (Bimzelx®) is an IgG1κ antibody with dual functionality, binding to two related cytokines, IL-17A and IL-17F, using the same binding site, thus being dual specific rather than bispecific.
Omvoh™ (Mirikizumab-mrkz)
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, autoimmune-related inflammatory bowel disease that causes gastrointestinal inflammation and ulceration. IL-23, a member of the IL-12 four-helix bundle cytokine family, is a heterodimeric cytokine. It consists of a novel p19 subunit that binds to IL-12p40, promoting the expansion of T helper type 17 (TH17) cells. IL-23 binds to a heterodimeric receptor composed of its cognate IL-23R subunit and IL-12Rβ1, the latter of which is also shared with IL-12. Studies have shown that pharmacological inhibition of IL-23p19 can ameliorate intestinal inflammation. Blockade of IL-23 has also been shown to have therapeutic effects in autoimmune diseases such as PsO, inflammatory bowel disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.
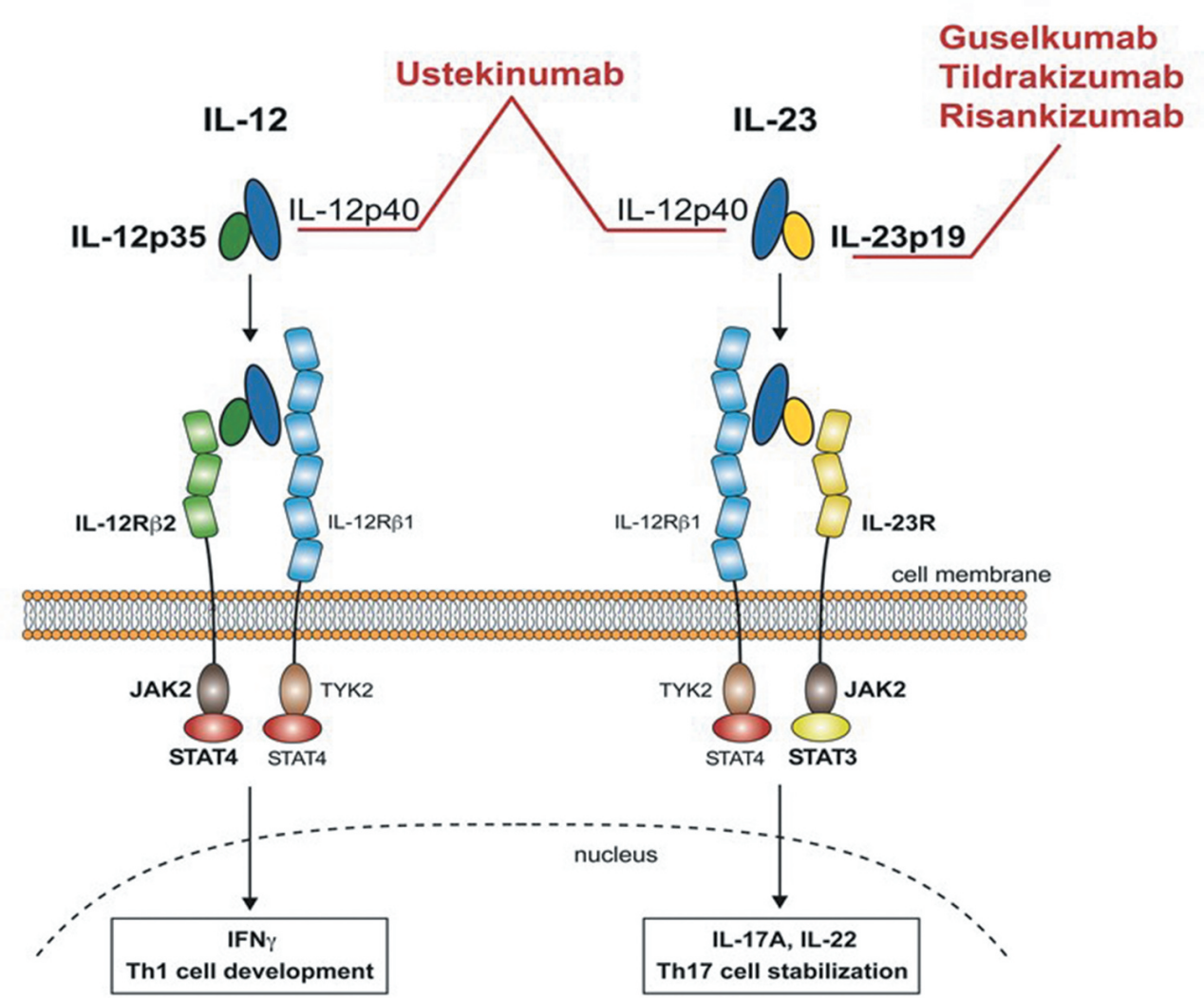
(Data source: Boehncke WH, et al. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021)
Mirikizumab-mrkz (Omvoh™) is a humanized, Fc-silenced IgG4 monoclonal antibody that targets the IL-23p19 subunit and does not bind IL-12. It is FDA-approved for the treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (SA-UC).
Elrexfio™(elranatamab-bcmm) and Talvey™ (talquetamab-tgvs)
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a B-cell malignancy with increasing incidence, caused by the uncontrolled expansion of bone marrow plasma cells.
Since its approval in 2015, daratumumab (Darzalex®) , an antibody targeting CD38 , has been the standard of care for MM. However, many patients develop resistance to it, and daratumumab can cause healthy NK cells and T cells to kill each other. New targets, such as BCMA, CD33, and GPRC5D, have emerged. In 2023, two new bispecific TCE antibodies were approved by the FDA for the treatment of MM: Elrexfio™ (elranatamab-bcmm), a BCMA TCA × CD3ε, and Talvey™ (talquetamab-tgvs), a GPRC5D × CD3ε TCE.
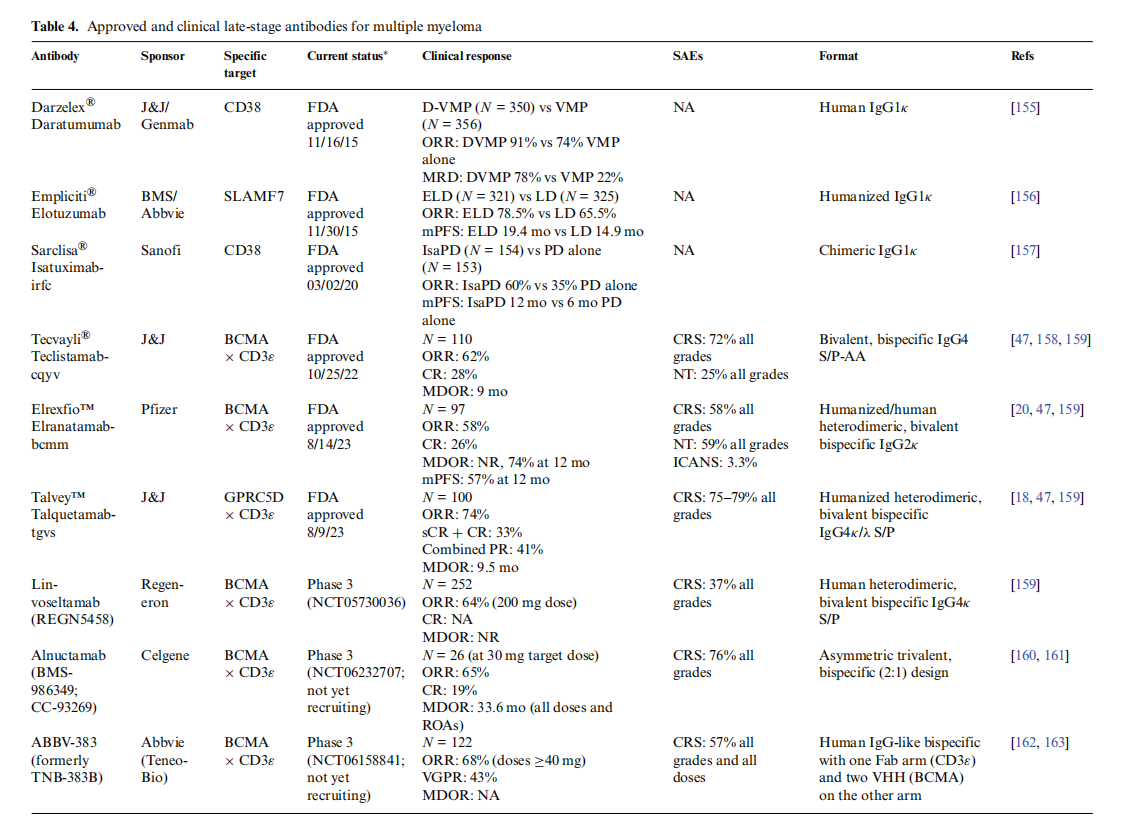
Elrexfio™(elranatamab-bcmm) is a humanized, Fc-silenced IgG2κ-based bispecific antibody derived from two parental antibodies: an anti-BCMA monoclonal antibody and an anti-CD3ε monoclonal antibody. Mutations in the CH3 domain of the Fc region promote heterodimerization rather than homodimerization, resulting in the formation of two Fc molecules with heterospecificity. Light chain specificity is enhanced by two compensatory mutations: one in the CH1 and one in the CL region of the CD3ε-binding domain. Fc mutations inhibit the antibody's ability to bind to Fc receptors and complement.
Talvey™(talquetamab-tgvs) is an IgG4κ/λ, S/P hinge-stabilized, bivalent, bispecific TCE antibody produced using a Dubody-controlled Fab exchange process. One of its Fab arms binds to the CD3ε receptor expressed on the surface of T cells, while the other binds to GPRC5D expressed on the surface of MM cells, non-malignant plasma cells, and healthy tissues such as epithelial cells in skin and tongue keratinized tissue.
Rystiggo®(rozanoliizumab-noli)
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by the presence of autoantibodies directed against specific human (self) proteins. These antibody-mediated autoimmune diseases include generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG).
FcRn maintains the homeostasis of endogenous IgG and significantly prolongs its half-life. This is achieved by pinocytosis of IgG by FcRn at acidic pH, protecting it from the lysosomal degradation pathway, and then transporting the bound IgG back to the cell surface for exocytosis back into the circulation at neutral pH.
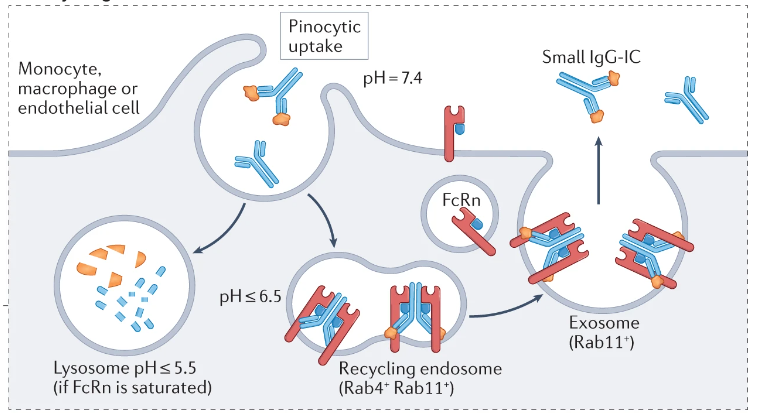
(Data source: Pyzik M, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023)
Since FcRn is the IgG recycling receptor, either antagonism of this receptor or overwhelming competition for this receptor will reduce its ability to recycle serum IgG (including pathogenic IgG) .
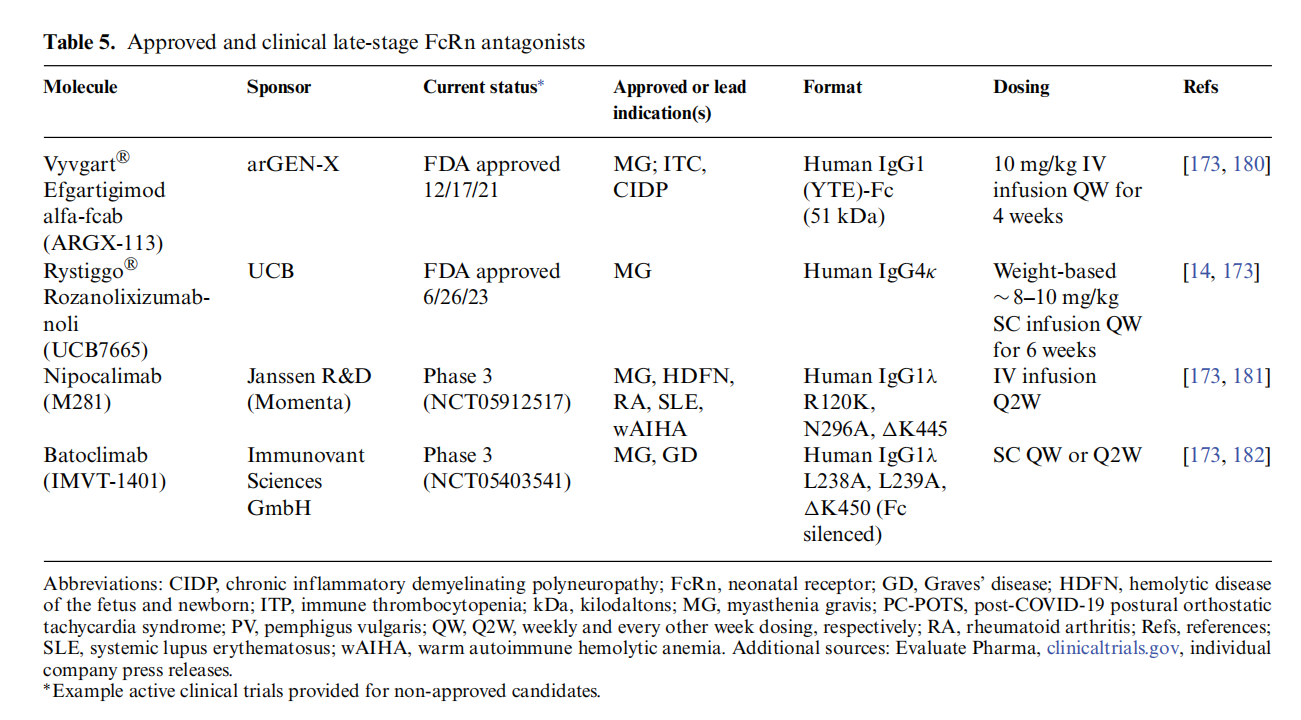
Rozanolixizumab-noli (Rystiggo®) is an IgG4κ FcRn receptor-blocking antibody approved by the US FDA for the treatment of gamma-MG in adults with autoantibodies to either AChR or muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK). Rozanolixizumab and its Fab fragment bind to the α subunit of human FcRn with high affinity at both pH 6.0 and pH 7.4, directly competing with IgG bound to the receptor. Rozanolixizumab has been shown to inhibit IgG recycling in vitro. In addition to rozanolixizumab, other FcRn antagonists are already approved or in clinical trials.
Veopoz™(Pozelimab-bbfg)
The complement system is a rapidly acting cascade of protein-protein interactions that plays a crucial role in the innate immune response to sterile and infectious insults. The complement cascade can be activated through three distinct pathways: the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway. All three pathways converge in the terminal complement pathway, which is initiated by the cleavage of complement factor C5 into C5a and C5b by the C5 convertase (C4bC2aC3b). Once formed, C5b becomes a building block that recruits C6, C7, C8, and C9 to form the membrane attack complex (MAC).

(Data source: Girardi G, Lingo JJ, Fleming SD, Regal JF. Front Immunol. 2020)
Pozelimab-bbfg (Veopoz™) is a human, hinge-stabilized IgG4k antibody targeting the terminal complement protein C5. It inhibits terminal complement activation by binding to complement factor C5 and blocking its cleavage into C5a (anaphylatoxin) and C5b, thereby blocking the formation of the membrane attack complex. It is fully approved by the US FDA for the treatment of CHAPLE disease in adults and children over one year of age. Veopoz™ is the first drug approved in the US for the treatment of CHAPLE disease.
Beyfortus™(nirsevimab-alip)
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common seasonal respiratory virus and one of the most common causes of lower respiratory tract infections. RSV is a leading cause of respiratory illness in young children, with a global morbidity rate of 9.5% and a mortality rate of 2.2%.

(Data source: De Moerlooze L. Vaccines ( Basel ) . 2023)
Nirsevimab-alip (Beyfortus®)is an IgG1κ antibody containing a YTE mutation ( M252Y/S254T/T256E ). This increases circulation half-life by modulating pH-dependent binding to the neonatal receptor (FcRn). Nirsevimab has a terminal half-life of 71 days in infants, more than three times the in vivo half-life of a typical therapeutic antibody. This allows it to be administered once at the beginning of the RSV season and remain effective throughout the season. Nirsevimab neutralizes RSV by inhibiting the conformational changes in the F protein required for fusion of the viral and cellular membranes, thereby preventing viral entry.
Summary
The 12 antibodies approved by the US FDA in 2023 are of great significance for improving the treatment of various diseases. The approval of these antibodies also reflects the rapid development of the field of antibody therapy.
