Background
Machine learning algorithms have played a fundamental role in the development of therapeutic antibodies by training on sequence and/or structural datasets. However, structural datasets remain limited, particularly those containing antibody-antigen complexes. Furthermore, many of the available structures are not standardized, and antibody-specific databases often do not provide molecular descriptors that could enhance machine learning models.

On May 11, 2025, researchers published an article titled " AbSet: A Standardized Data Set of Antibody Structures for Machine Learning Applications " in J Chem Inf Model. AbSet is a curated dataset containing more than 800,000 antibody structures and corresponding molecular descriptors. The dataset provides a comprehensive dataset consisting of standardized experimental structures of antibody-antigen complexes extracted from the RCSB PDB and represented at the residue level by molecular descriptors. In order to better sample the data, subsets generated by computer simulations further enriched the database, providing a reliable and detailed resource for antibody-antigen interaction studies in a single curated dataset. AbSet is publicly available through the Zenodo repository, and the accompanying scripts are hosted on GitHub (https://github.com/SFBBGroup/AbSet.git).

Research Methods
Structural processing
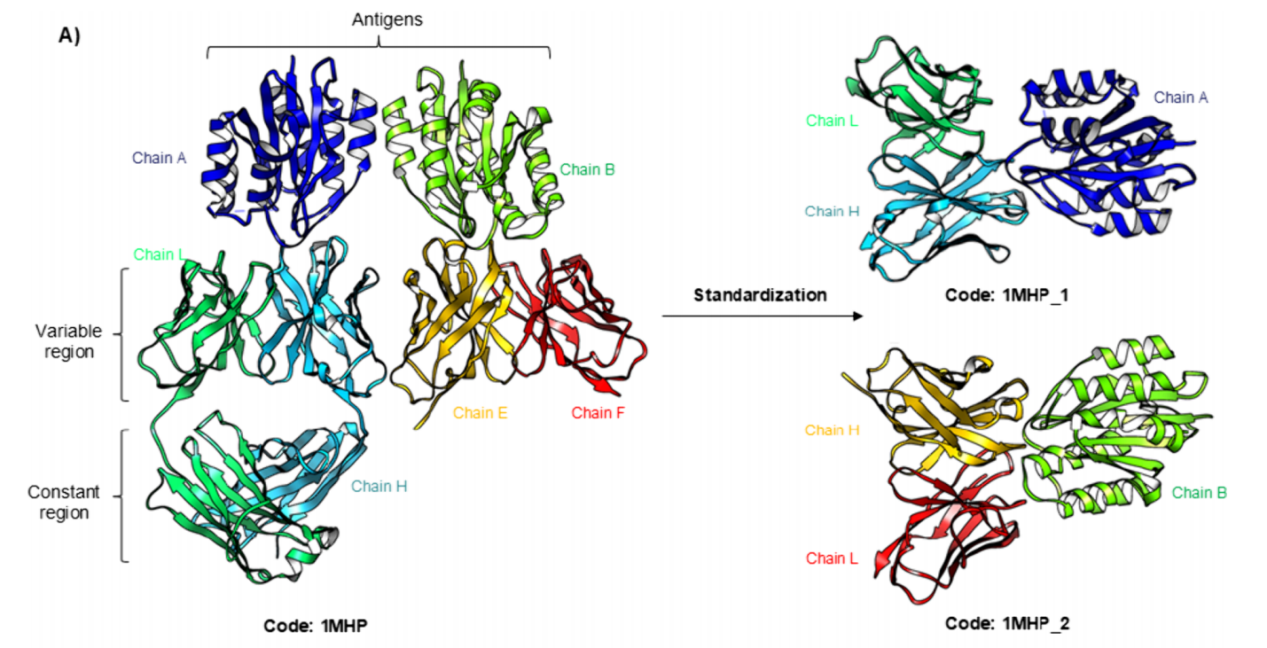
We first retrieved and identified experimental antibody structures from the RCSB PDB. Using ANARCI (a dedicated tool for numbering antibody amino acid sequences), we numbered the sequences according to the Martin scheme, limiting the analysis to antibodies only.
Construction of computer simulation subsets
To increase data diversity, in silico subsets were generated by performing molecular redocking and antibody modeling to generate variations in binding modes for each recovered complex.

Molecular descriptor calculation
Once the structures of the antibody-antigen complexes were standardized across experimentally derived and computer-generated subsets, molecular descriptors were calculated to capture the characteristics of the amino acid residues and their surrounding environment. These descriptors were carefully selected as appropriate representations of the structure, enabling them to be used as input features for the AI algorithm.
Molecular surface properties are described by using both surface and volume information. The selected descriptors include relative solvent accessible area, atomic depth, protrusion index, and hydrophobicity, which effectively capture key characteristics of amino acid residues and their environment. Other important descriptors are also considered, such as the position of Cα atoms and protein structural information. These properties are derived from hemispherical exposure calculations, Cα coordinates, φ and ψ dihedral angles, and protein secondary structure .

AbSet Advantages
The AbSet database successfully handles unusual antibody structures, including those that may not be recognized by AbNum, thereby ensuring comprehensive coverage of antibody variants. This approach complements existing algorithms by overcoming their limitations and providing a more flexible and inclusive solution for antibody structure standardization. Through a strict standardization protocol, it is ensured that each antibody structure contains only variable regions and that each file contains only one complex, improving data quality and consistency.
86% of the structures in AbSet fall within this range, with a resolution better than 4 Å. This is a critical factor in ensuring the quality and accuracy of the structural data used in AI-based model training. The dataset includes antibodies that bind to a variety of antigens, including SARS-CoV-2, reflecting a wide range of antigenic diversity. AbSet's data and scripts are publicly available to facilitate access and use by other researchers.

In conclusion
AbSet is a highly standardized dataset of antibody structures, including variable regions and interacting antigens, enriched with a wealth of data, such as molecular descriptors and decoys representing different binding modes. These structures are carefully curated to reflect key biochemical properties at the residue level. AbSet provides a valuable resource for training and optimizing machine learning models in antibody discovery. In addition, the dataset and accompanying software tools used for calculating molecular descriptors will also be publicly available to support further research in this field.
