IL4 is a multifunctional cytokine produced by T h2 helper T cells, fibroblasts, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, adipocytes, and a wide range of epithelial cells. IL4 acts on a wide range of cells, including keratinocytes , acting as a multipotent regulator of multiple immune and inflammatory processes.

(Data source Cormac S. Nat Biotechnol. 2018)
IL4 structure:
IL4 is stabilized by three internal disulfide bonds, with one half of the structure dominated by a bundle of α-helices with a left-handed turn. The helices are antiparallel, with two connecting in opposite directions, forming a two-stranded antiparallel β-sheet structure. IL4 and IL13 share a set of transmembrane receptors: type I receptors, composed of IL4R subunits with a common imaging chain, specifically bind IL4. Type II receptors, composed of a subunit called IL13Rα1, bind IL4 and IL13, respectively.
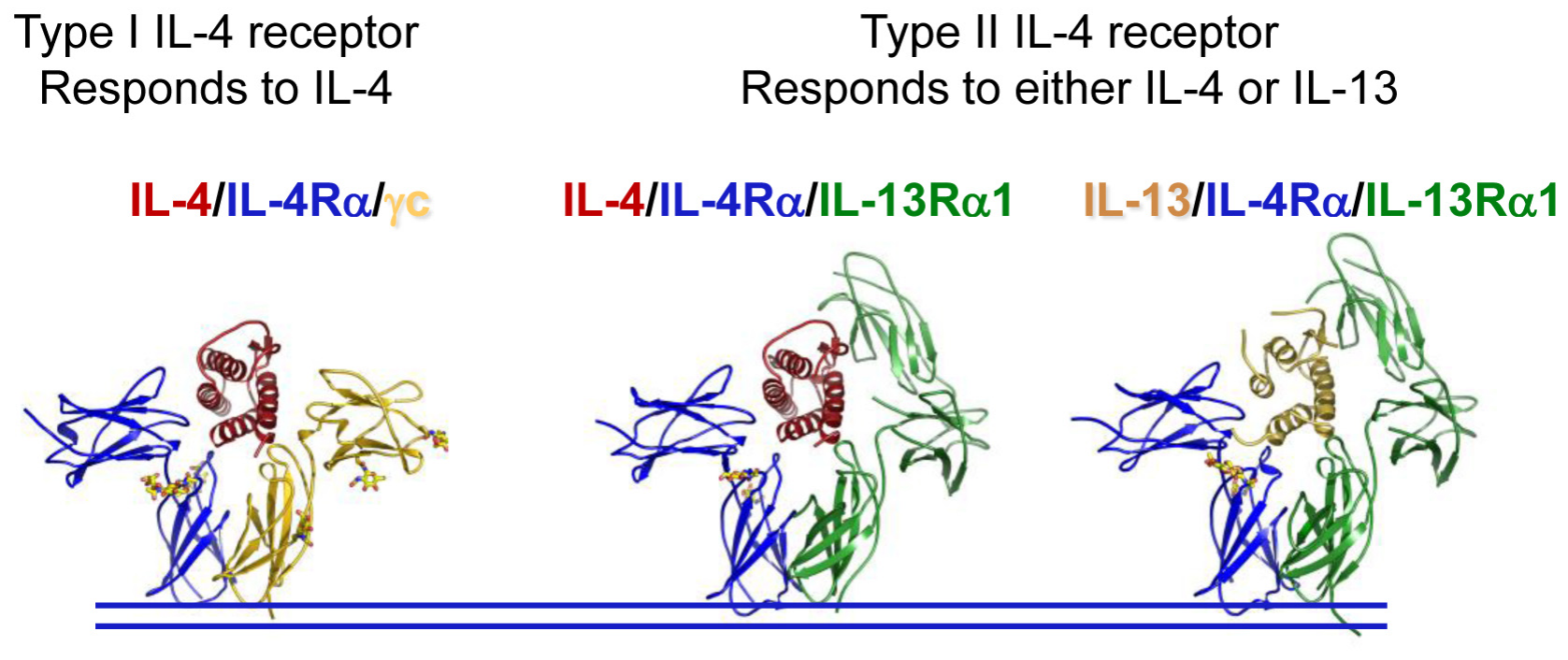
(Data source: Keegan AD, et al. Fac Rev. 2021)
IL4 signaling pathway and regulation:
IL4 binds to type I or type II receptors, activates kinases (JK1, JK2/TYK2 and JK3), and then phosphorylates signal transducers and activating transcription factors (STAT6), initiating type II inflammatory pathways and leading to Th2 cell differentiation. The signal activation of T2-type cytokines is an important survival signal for mast cells, basophils and eosinophils. The degranulation of mast cells leads to the release of inflammatory mediators such as histamine, tryptophan, folliculin, kinase (which can produce bradykinin), heparin, prostaglandins and sulfaphenate.

(Data source: Awosika O, et al. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018)
Clinical value of IL4:
IL4 and IL13 are important components of Th2-mediated immunity. They play a vital role in the pathogenesis of allergic inflammation and have effects on multiple cells such as B cells, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes and fibroblasts. They are considered to be the pathogenesis and main therapeutic targets of allergic dermatitis.

(Data source: Mitra S, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2018)
Dual inhibition of these two cytokines has been shown to improve the treatment of atopic dermatitis and currently includes numerous biotherapeutic agents that are marketed or in clinical development.
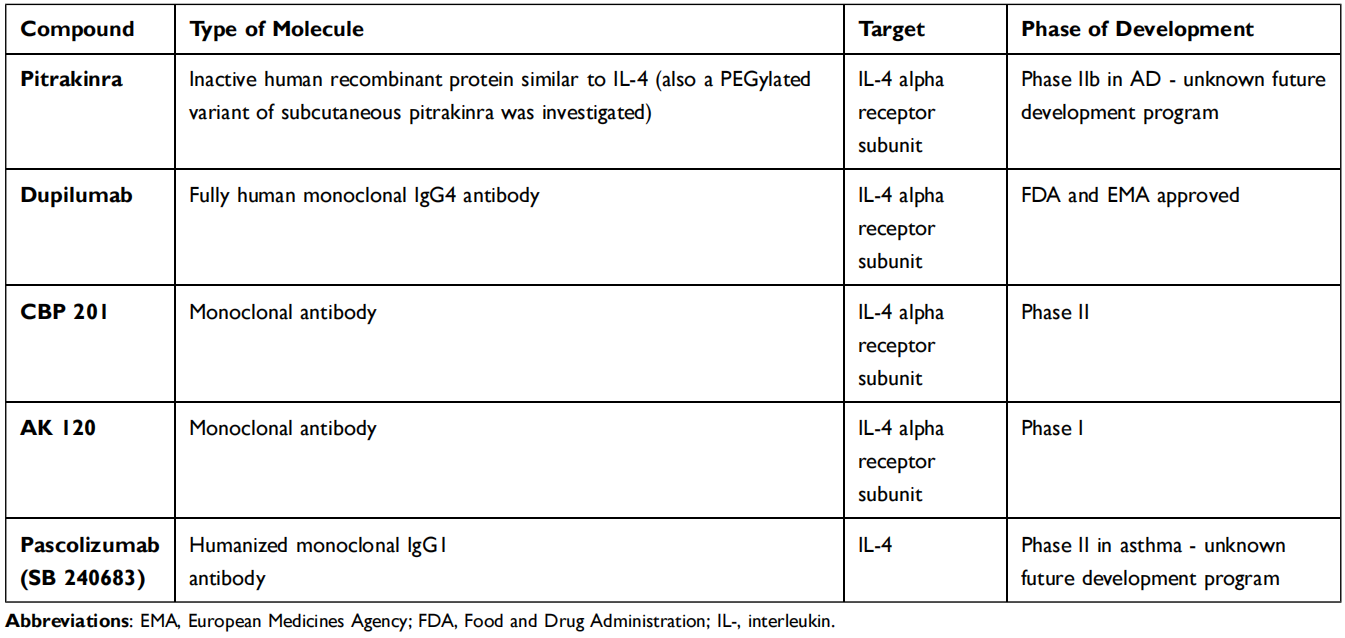
(Data source: Chiricozzi A, et al. Immunotargets Ther. 2020)
