IL5 is mainly secreted and expressed by T2 lymphocytes Th2, innate lymphocytes ILC2, mast cells and eosinophils. These cells release IL5 after being activated by various environmental stimuli such as inhaled allergens, respiratory viruses and airborne pollutants. At the same time, IL5 has multidirectional effects on eosinophils, promoting their maturation, activation, survival, migration from the blood and entry into the respiratory tract. It is a powerful pro-inflammatory cytokine.

(Data source: Pelaia C, et al. Front Physiol. 2019)
IL5 structure:
IL5 is a dimeric protein with a 4-helix motif that acts on target cells by binding to a specific IL5 receptor (IL5R). Although IL5 is a homodimer, it can only bind to one IL5R receptor molecule because the IL5R binding site on IL5 extends to both sides of the intramolecular dimer. The three FnIII domains of IL5R surround the ligand IL-5 like a wrench around a nut. This wrench-like structure increases the interaction surface area between the receptor and the ligand.

(Data source Patino E, et al. Structure. 2011)
IL5 signaling pathway and regulation:
The IL5 receptor is composed of the IL5 receptor α subunit (IL5Rα) and the co-receptor βc subunit (βc subunit is a signal transduction molecule). IL5Rα specifically binds to IL5, inducing the recruitment of βc to IL5R, which is shared with two monomeric cytokine receptors, IL3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). This subsequently activates a complex intracellular signaling network composed of the JAK1/2-STT1/3/5 module, P38 and MAP kinases, and NF-kB transcription factors, ultimately leading to the maturation, survival, and activation of eosinophils.

(Data source: Pelaia C, et al. Front Physiol. 2019)
Clinical value of IL5:
Eosinophilia is associated with a variety of type 2 inflammatory diseases that occur in different parts of the body. Given the close connection between IL5 and eosinophils, early researchers have identified IL5 as a major target for therapeutic intervention, particularly in patients with T2 asthma. In asthma, IL5 directly drives the differentiation and recruitment of eosinophils. During a type 2 inflammatory response, eosinophils undergo a process called degranulation, in which they release tissue-destroying cytotoxic proteins and more than 30 cytokines, leading to a dramatic increase in inflammation.

(Data source: Pavord ID, et al. Allergy. 2022)
In clinical practice, three monoclonal antibodies (mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab) have been approved, which can effectively interfere with and block the pathogenic IL5/IL5R eosinophilic signaling axis to treat IL5-mediated inflammatory diseases.
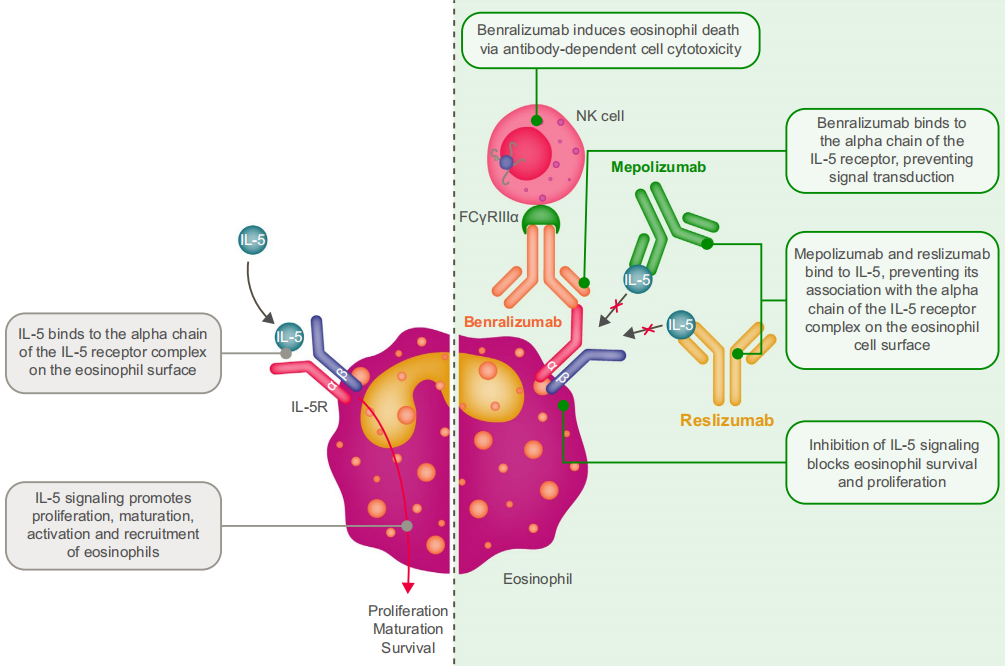
(Data source: Pavord ID, et al. Allergy. 2022)
