The death receptor DR5 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10B (TNFRSF10B), also known as tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2 (TRAILR2). It is expressed on the cell surface of primary osteosarcoma and soft tissue sarcoma cells, and its activation primarily induces cell death through apoptosis. Modulating DR5 expression and intervening with DR5 activators or antagonists have demonstrated significant therapeutic potential in the treatment of tumors, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, severe viral infections, and radiation injury.

(Data source: Qiao X, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2025)
Expression distribution of DR5
DR5 is expressed in many normal human tissues, such as the heart, lung, thymus, liver, kidney, colon, small intestine, ovary, prostate, testis, and skeletal muscle, but at very low levels. DR5 expression is generally elevated in several tumor cell types, including breast, endometrial, cervical, ovarian, pancreatic, hepatocellular, and rectal cancers. DR5 expression is most commonly seen in bone sarcomas (such as Ewing's sarcoma, osteosarcoma, and chondrosarcoma) and hematologic malignancies, such as multiple myeloma.

(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of DR5
DR5 is a type I transmembrane protein consisting of an ECD composed of three CRDs, a TMH, and an intracellular death domain (DD). The TMH contains a GXXXG motif that mediates DR5-TMH dimerization. The DR5 transmembrane helices (TMHs) exist as a dimer-trimer network and can self-assemble into higher-order clusters independently of the extracellular domain, driving downstream signaling.


(Data from Pan L, Fu TM, Zhao W, et al. Cell. 2019)
Biological functions and signal transduction regulation of DR5
DR5 mediates the classic TRAIL apoptosis signaling pathway and may also be involved in the regulation of other cell death pathways, such as programmed necrosis and autophagy, and cell-dependent cell death. DR5 also plays a key regulatory role in various physiological and pathological processes, including promoting proliferation, inflammation, tissue regeneration, immune regulation, and anti-tumor effects.
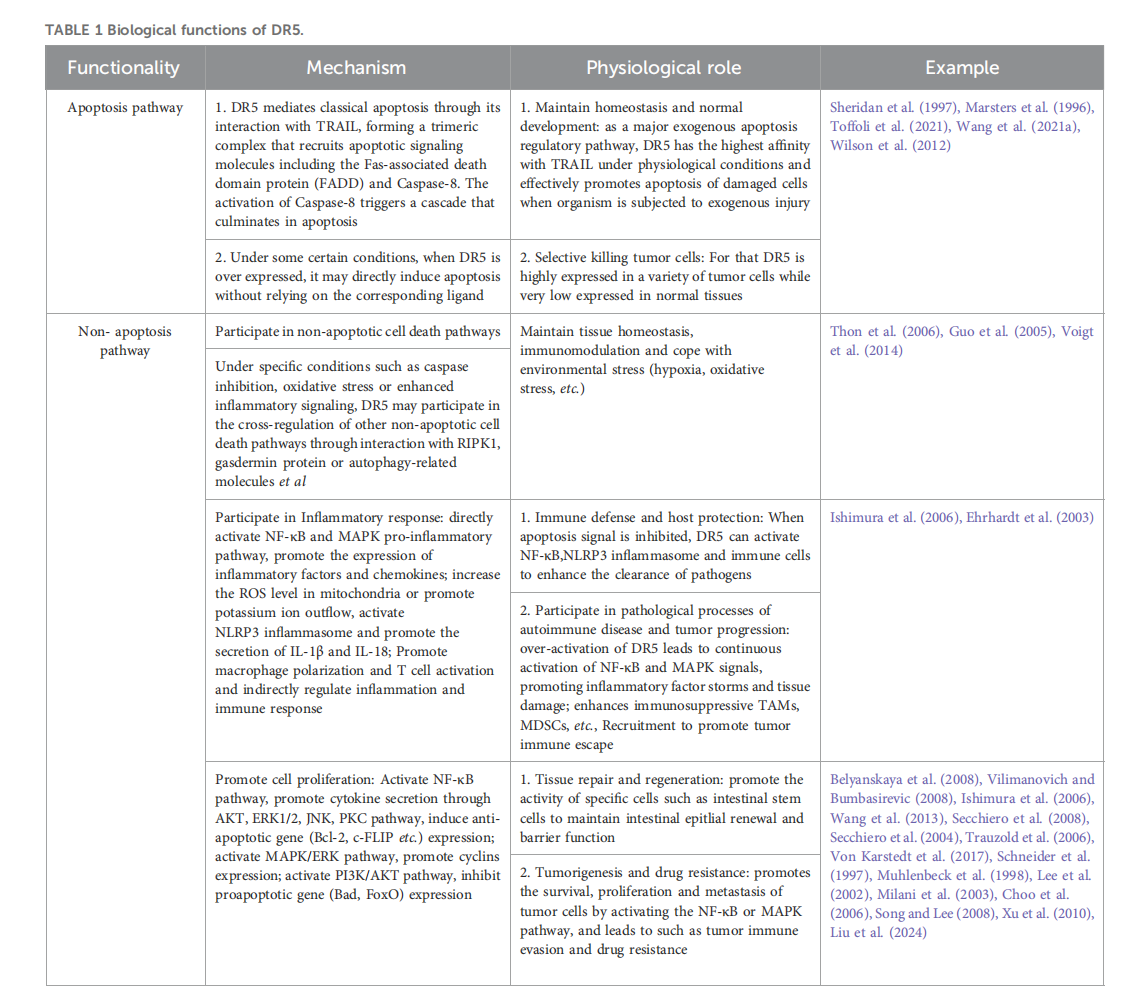
DR5 can be activated by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TNFSF10/TRAIL/APO-2L) and mediate the transmission of apoptotic signals. The apoptosis mediated by DR5 requires the participation of the adaptor protein FADD.
DR5 trimerizes upon binding to TRAIL or agonistic antibodies (such as the experimental drug Tigatuzumab). Its death domain interacts with FADD (Fas-associated death domain) to form the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC), which in turn activates Caspase 8. Caspase -8 is activated in the DISC through proximity-induced autocleavage, which can directly activate effector Caspase-3/7 or trigger the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by truncation of Bid (tBid).
Non-apoptotic pathways can also be activated. When Caspase-8 activity is inhibited (such as by drugs or the viral protein cFLIP), DR5 can trigger the ripoptosome (containing RIPK1, RIPK3, FADD, and caspase-8), thereby activating NF-κB (pro-survival/inflammation) or RIPK3-MLKL-mediated programmed necrosis.

(Data source: Qiao X, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2025)
Targeted therapy for DR5
Because DR5 is highly expressed in various tumor cells but rarely expressed in normal tissues, research on DR5 agonists has primarily focused on oncology. DR5 agonists are also being studied for autoimmune diseases, liver fibrosis, and other conditions. Antibody drugs targeting DR5 can be categorized as DR5 agonists and antagonists.
Tigatuzumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the death receptor DR5 and induces tumor cell death by activating the extrinsic apoptosis pathway. It is currently in Phase 1 clinical trials for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
TLY012 is a trimeric recombinant human TRAIL targeting DR5. It is designed to selectively induce apoptosis in activated myofibroblasts, a key driver of multiple fibrotic diseases, through a DR5-mediated apoptotic pathway. This targeted approach addresses the root cause of fibrosis and provides a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of fibrotic diseases.
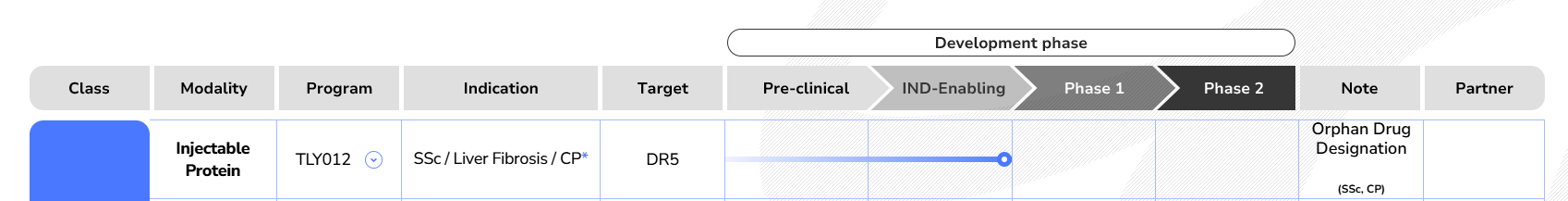
(Data source: ddpharmatech official website)
BI905711 is a tetravalent bispecific antibody developed by Boehringer Ingelheim that simultaneously targets TRAILR2 (DR5) and CDH17 on the surface of tumor cells. Through CDH17-mediated cross-linking, it induces high-order aggregation of DR5 only in tumor cells co-expressing these two molecules, thereby selectively triggering the extrinsic apoptosis pathway. On September 10, 2020, Boehringer Ingelheim announced that BI 905711 had initiated a first-in-human Phase Ia/Ib trial (NCT04137289) in patients with advanced gastrointestinal cancers. The trial is currently marked as "Completed" on ClinicalTrials.gov, but the results have not yet been disclosed.
RC248 is an antibody-drug conjugate targeting DR5 developed by Rongchang Biopharmaceuticals. It is currently in Phase I dose-escalation clinical studies for the treatment of solid tumors.
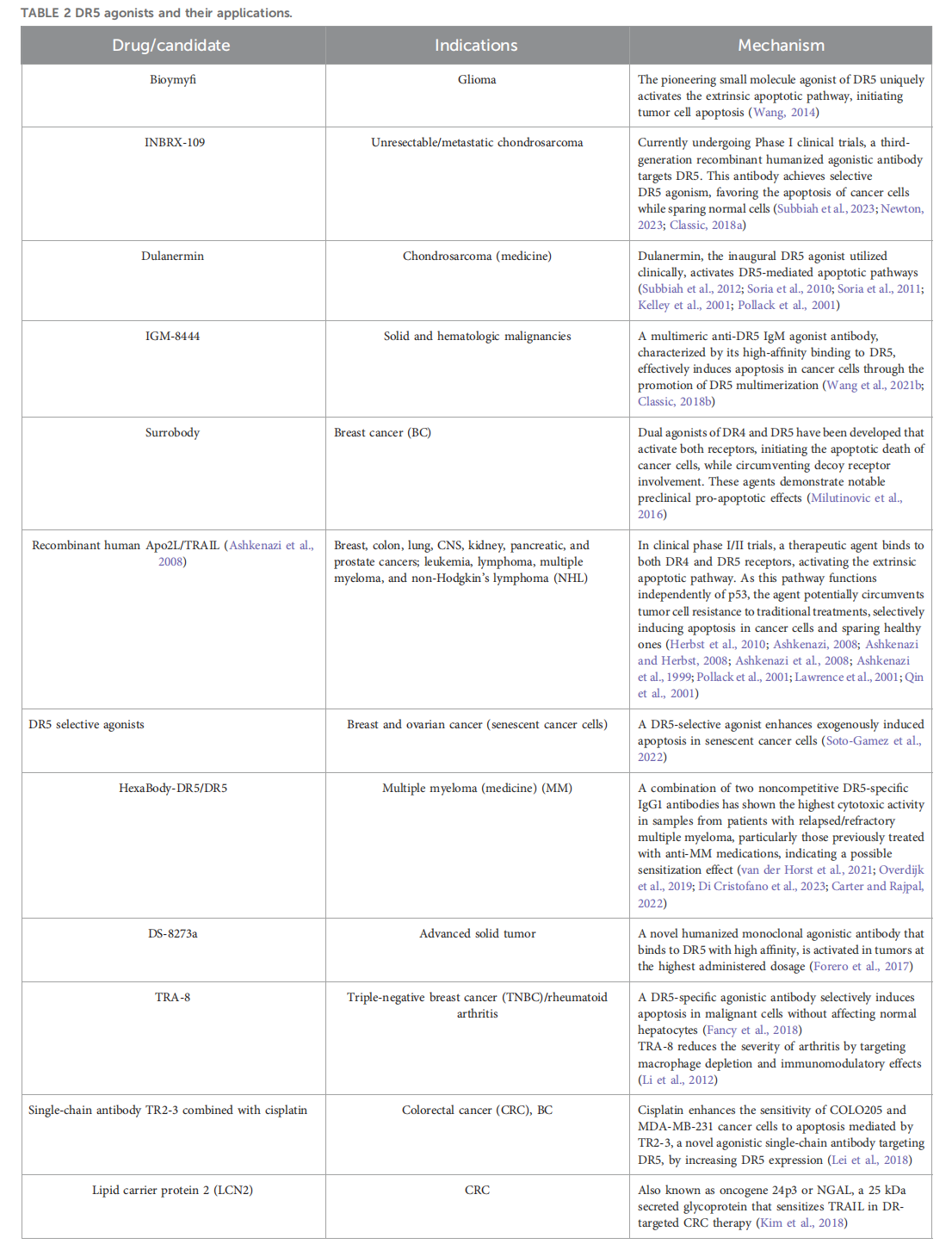
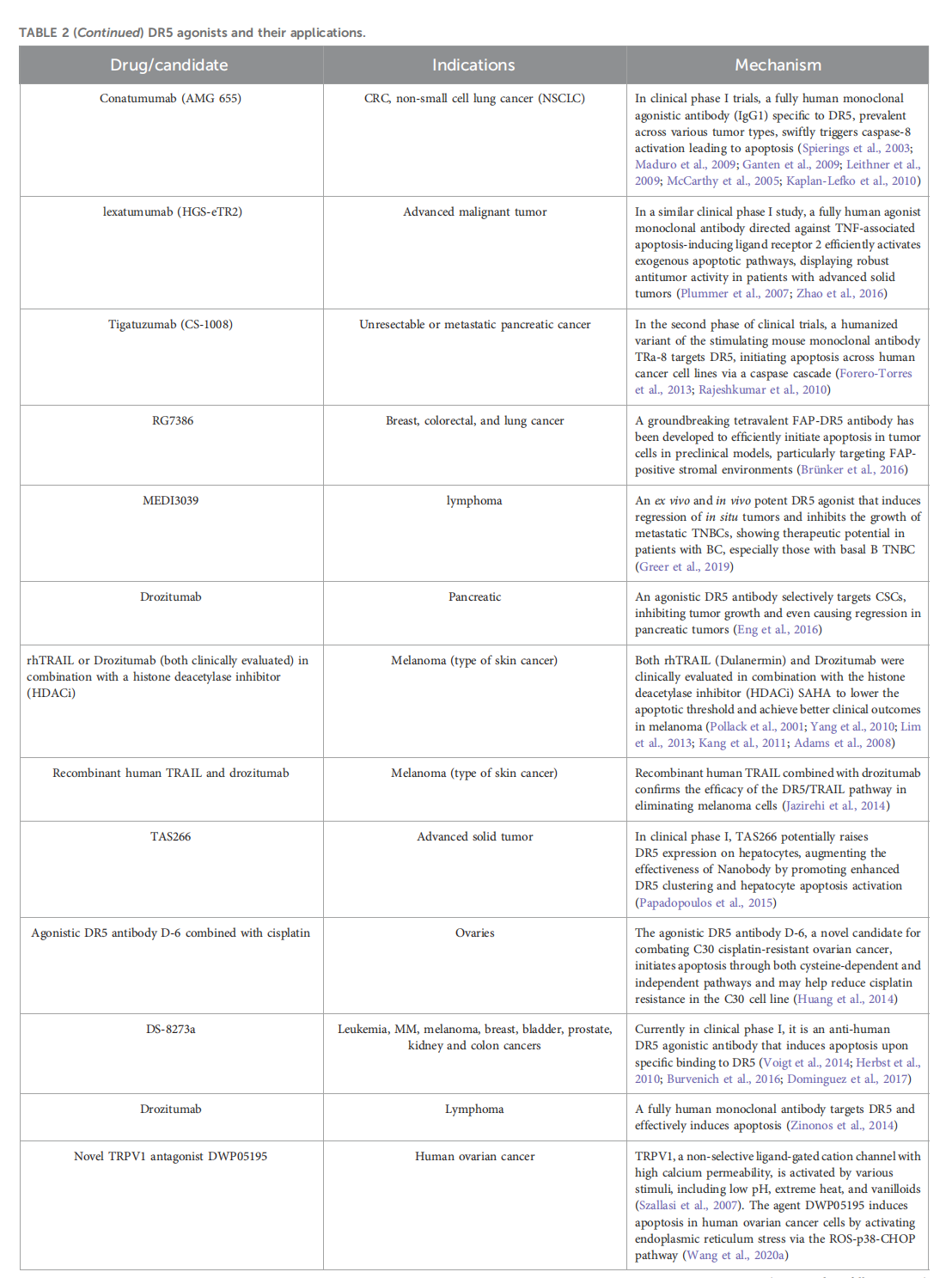
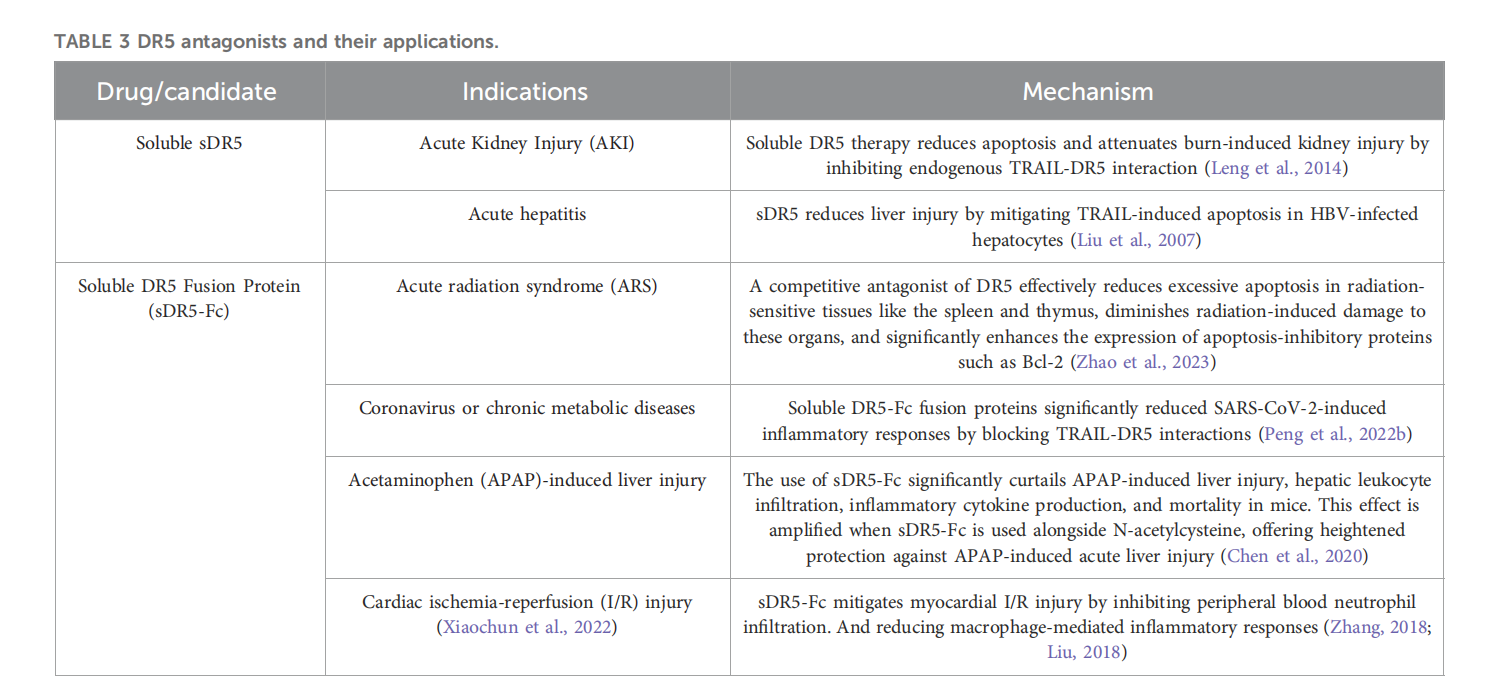
(Data source: Qiao X, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2025)
