Dysregulation of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling frequently occurs in cancer and may lead to dysregulated cancer stem cell (CSC) differentiation and promote tumorigenesis. GREM1, a cell proliferation -inducing gene 2, is a BMP antagonist and a secreted member of the DAN family of cysteine knot proteins. It is a member of the TGF-β superfamily , known for its ability to bind to and inhibit the activity of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), such as BMP2 and BMP4. Gremlin1 has been shown to play an important role during embryonic development and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Gremlin1 is upregulated in multiple solid tumors.
Expression distribution of GREM1
GREM1 is mainly expressed in cardiomyocytes, with a small amount expressed in collecting duct cells, granulosa cells, mucous gland cells, and oligodendrocytes.
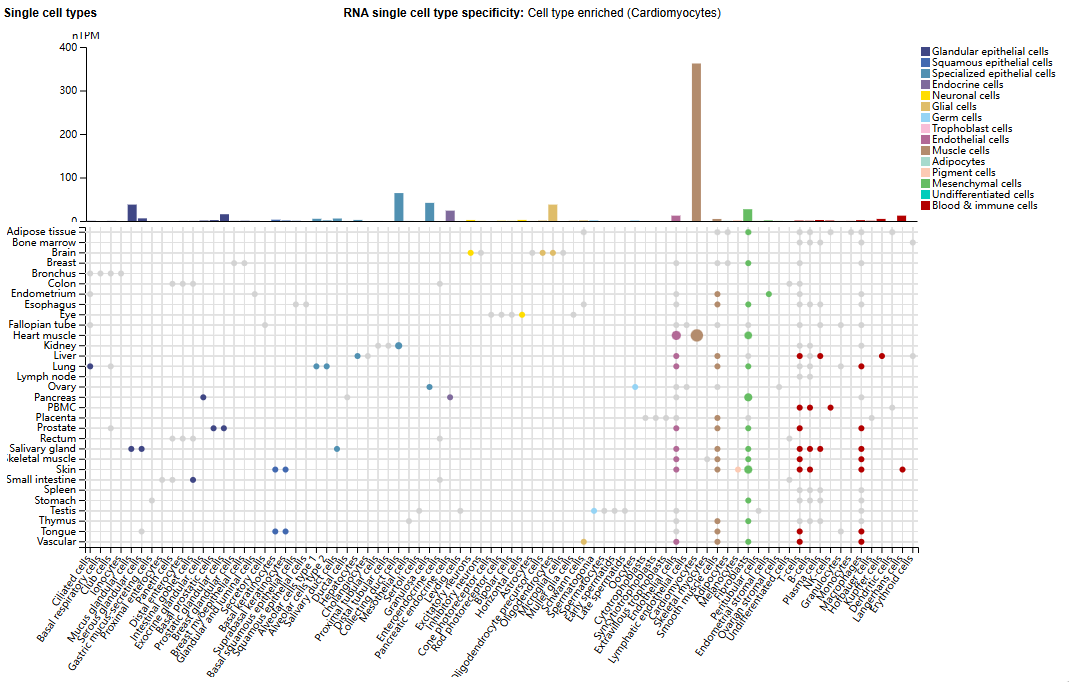
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of GREM1 and its receptor
GREM1 is a secreted bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonist. Its gene is located on chromosome 15q13.3 and consists of 184 amino acids. GREM1 contains a cysteine-rich region and a cysteine knot motif, which are essential for BMP binding. GREM1 can promote covalent homodimer formation through an intermolecular disulfide bond formed by cysteine at position 141. Similar to BMP, GREM1 has the ability to bind to heparin, a process that depends on 11 key arginine and lysine residues (such as Lys90, Arg91, and Lys145) distributed in three basic residue clusters.
Secreted GREM1 mainly binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) on the extracellular matrix and cell membrane surface, restricting its localization to the vicinity of secreting cells, thereby regulating the signal activation process and preventing proteolytic degradation.

(Data source: Jin Z, et al. Invest New Drugs. 2024)
GREM1 signaling pathway in cancer
GREM1 dimers bind to BMP dimers to prevent BMPR activation and R-SMAD1/5/8 receptor signaling. GREM1 binding to EGFR leads to phosphorylation and activation of STAT3, ERK, and AKT in breast cancer cells, promoting increased invasion . GREM1 dimer binding to FGFR1 leads to activation of RAS/ERK signaling and drives tumor progression in androgen-insensitive prostate cancer cells . GREM1 binding to VEGFR2 drives VEGFR2 activation in endothelial cells, leading to angiogenesis.
Increased GREM1 expression in specific subsets of CAFs leads to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the formation of mesenchymal cancer cells, solid tumor formation, and increased tumor cell invasion and metastasis, all of which contribute to poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer and other tumors.
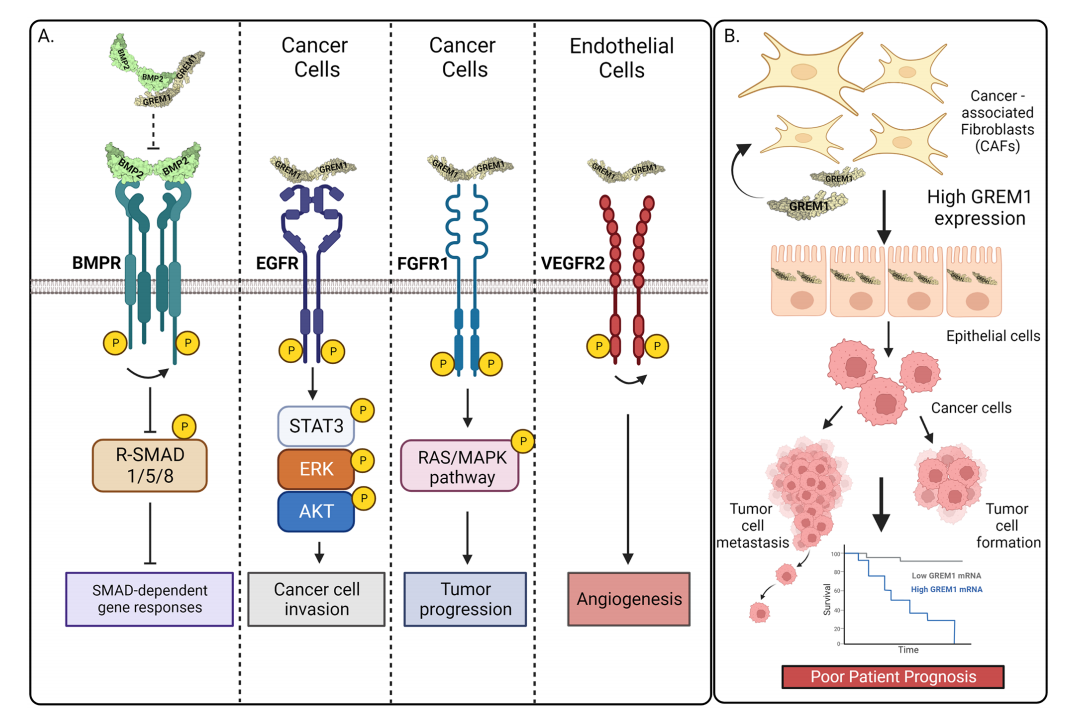
(Data source: Gao Z, et al. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023)
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) express high levels of BMP2, which drives CSC differentiation into cancer cells. CSCs also express high levels of GREM1, which binds to BMP2 and inhibits its activity, preventing differentiation and promoting CSC self-renewal and stemness.
GREM1 also regulates the Wnt signaling pathway, another important pathway in CSC regulation. The Wnt signaling pathway promotes the self-renewal and proliferation of CSCs in various cancers. Studies have shown that the Wnt-regulated TCF7L2 tightly binds to a polymorphic site within the GREM1 enhancer, thereby increasing GREM1 expression. By regulating the Wnt signaling pathway, GREM1 may further enhance the stem cell-like properties of CSCs. GREM1 has been reported to activate the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR2) signaling pathway to promote angiogenesis.

(Data source: Gao Y, et al. Cells. 2025)
Targeted therapy of GREM1
Ginisortamab (UCB6114) is a monoclonal antibody targeting GREM1 developed by UCB and is currently in Phase 1/2 clinical development. NCT04393298 is a study designed to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity of intravenous UCB6114 in patients with advanced solid tumors.
TST003 is a high-affinity humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody targeting Gremlin1 , developed by Transcenta Holding Limited, for the treatment of prostate cancer, NSCLC, CRC, ESCC, GC, PADC, and breast cancer. TST003 blocks the binding of GREM1 to BMP2/4, enhancing the BMP signaling pathway. TST003 has demonstrated promising monotherapy and combination activity in patient-derived xenograft models of checkpoint inhibitor-resistant solid tumors, including castration-resistant prostate cancer and microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer. NCT05731271 is a first-in-human Phase 1 study in patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors who have progressed during or after prior therapy and have no proven clinical benefit from standard therapies .

(Data source: Transcenta official website)
