CD123 is the alpha chain of the interleukin-3 receptor (IL-3RA). IL-3Rs are members of the beta common (C) receptor family, which includes the IL-5R and granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) receptors. This family of membrane receptors regulates the growth, proliferation, survival, and differentiation of hematopoietic cells, as well as immune and inflammatory responses. CD123 is a therapeutic target for acute myeloid leukemia and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic neoplasm (BPDCN).
Expression distribution of CD123
CD123 is primarily expressed in dendritic cells, oocytes, endothelial cells, adipocytes, and Langerhans cells. CD123 is also expressed in a variety of hematological malignancies, particularly blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) , acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of CD123
CD123 is a type I transmembrane protein composed of 378 amino acids and includes an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain. The extracellular region is responsible for binding to the interleukin IL-3 ligand, while the intracellular domain is involved in signal transduction.
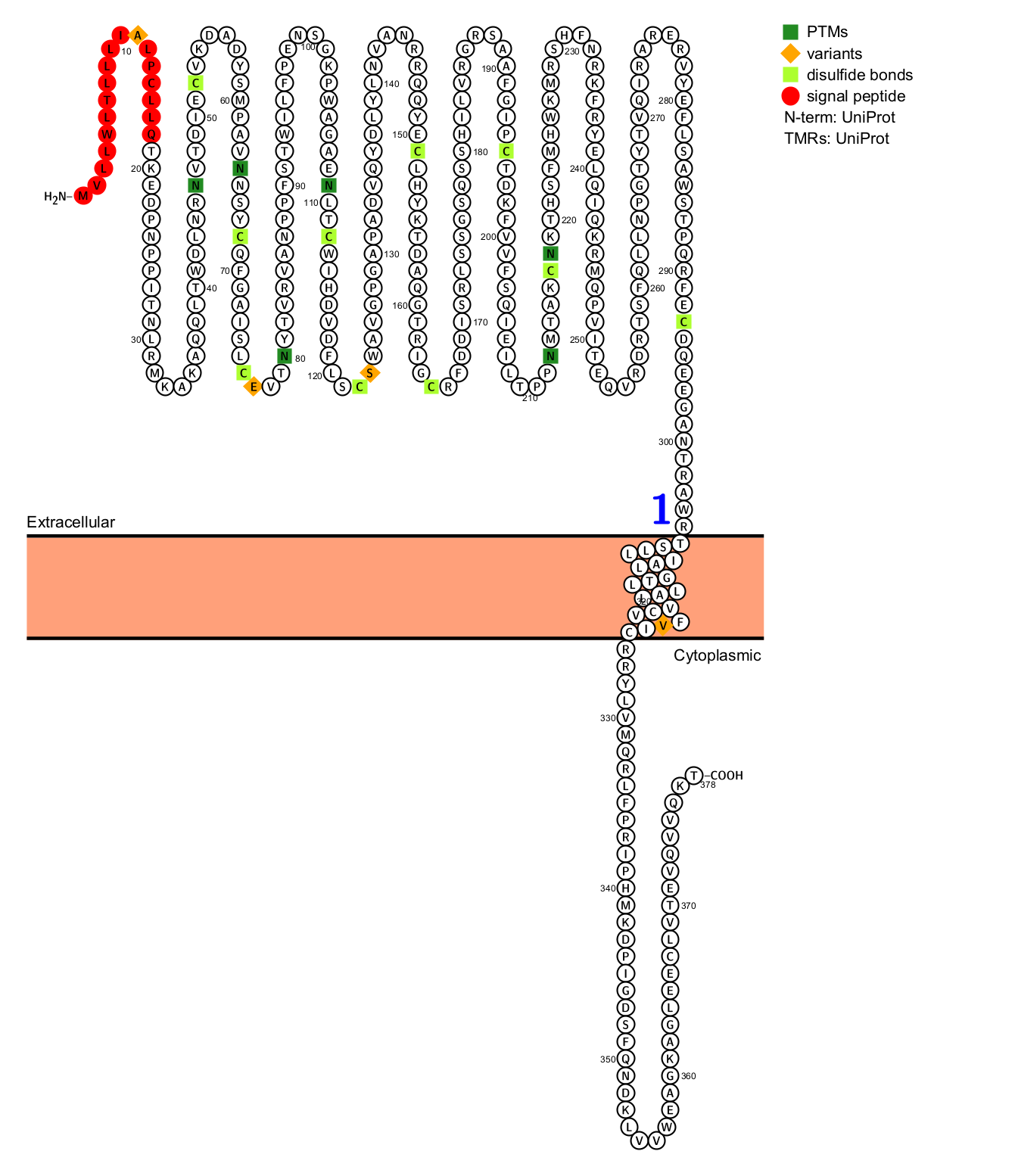
(Data source: uniprot)
CD123 signaling pathway and regulation:
CD123 can bind to IL3 ligand , induce IL3RB heterodimerization, and activate the downstream signal of intracellular receptor cascade through the cell membrane, thereby activating JAK/STAT, RAS-MAPK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways.

(Data source: Podolska MJ, Grützmann R, Pilarsky C, Bénard A. Front Immunol. 2024)
CD123-targeted therapy
Because CD123 is only overexpressed and not mutated in hematological malignancies , its therapeutic targeting must involve the use of drugs that specifically interact with this receptor, such as its natural ligand IL3, or monoclonal antibodies that deliver cytotoxic drugs to CD123+ leukemia cells and induce their death or trigger an immune response and activate the immune system. To this end, many drugs have been developed, including CD123 fusion proteins, monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).
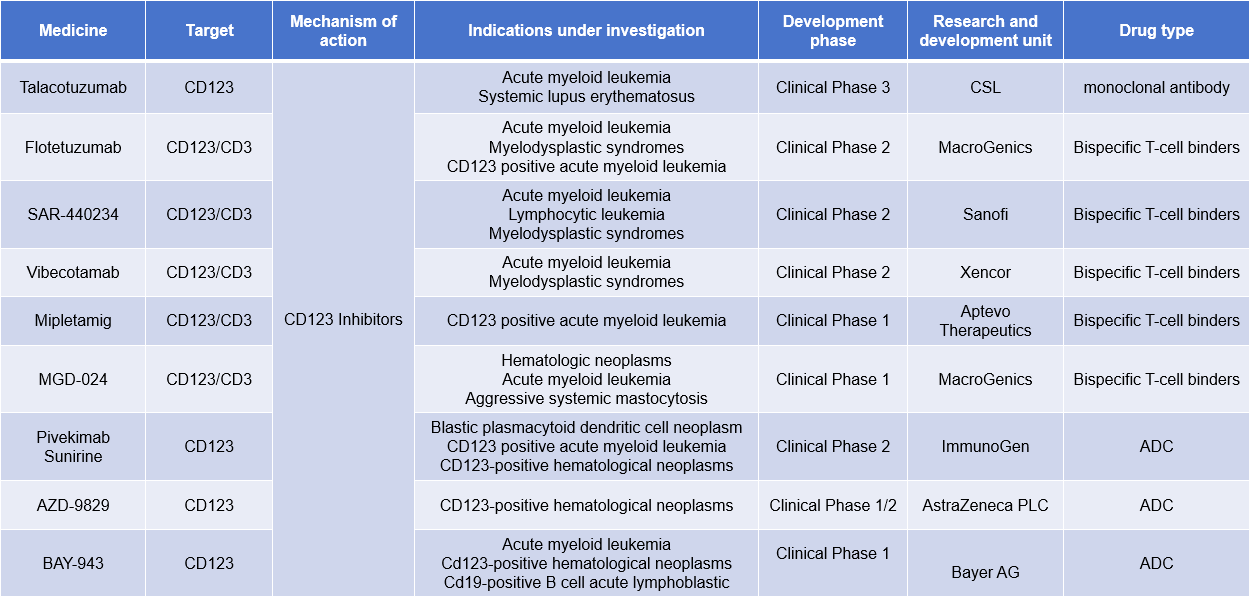
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
Tagraxofusp is the only marketed drug targeting CD123, a fusion protein used to treat BPDCN.
MGD024 is an investigational, next-generation, bispecific CD123 × CD3 DART® molecule that binds to CD3 on immune effector cells and kills CD123-expressing cancer cells in certain hematological malignancies (AML). MGD024 is designed to minimize cytokine release syndrome while maintaining anti-tumor cytolytic activity and allowing intermittent dosing to extend half-life. Currently underway in the clinical laboratory is NCT05362773 , a study in patients with relapsed or refractory hematological malignancies.

(Data source: Macrogenics official website)
