CD14 is best known as a pattern recognition receptor of the innate immune system, where it plays an important role in sensitizing cells to Gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS; endotoxin). It is also a membrane cell surface differentiation marker for cells of the myeloid lineage.

(Data source: Wu Z, et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019)
CD14 composition distribution:
CD14 is membrane-anchored via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) tail (mCD14); and a soluble form (sCD14) that is either produced by enzymatic cleavage of mCD14 (48 kDa) or secreted directly from intracellular vesicles (56 kDa).
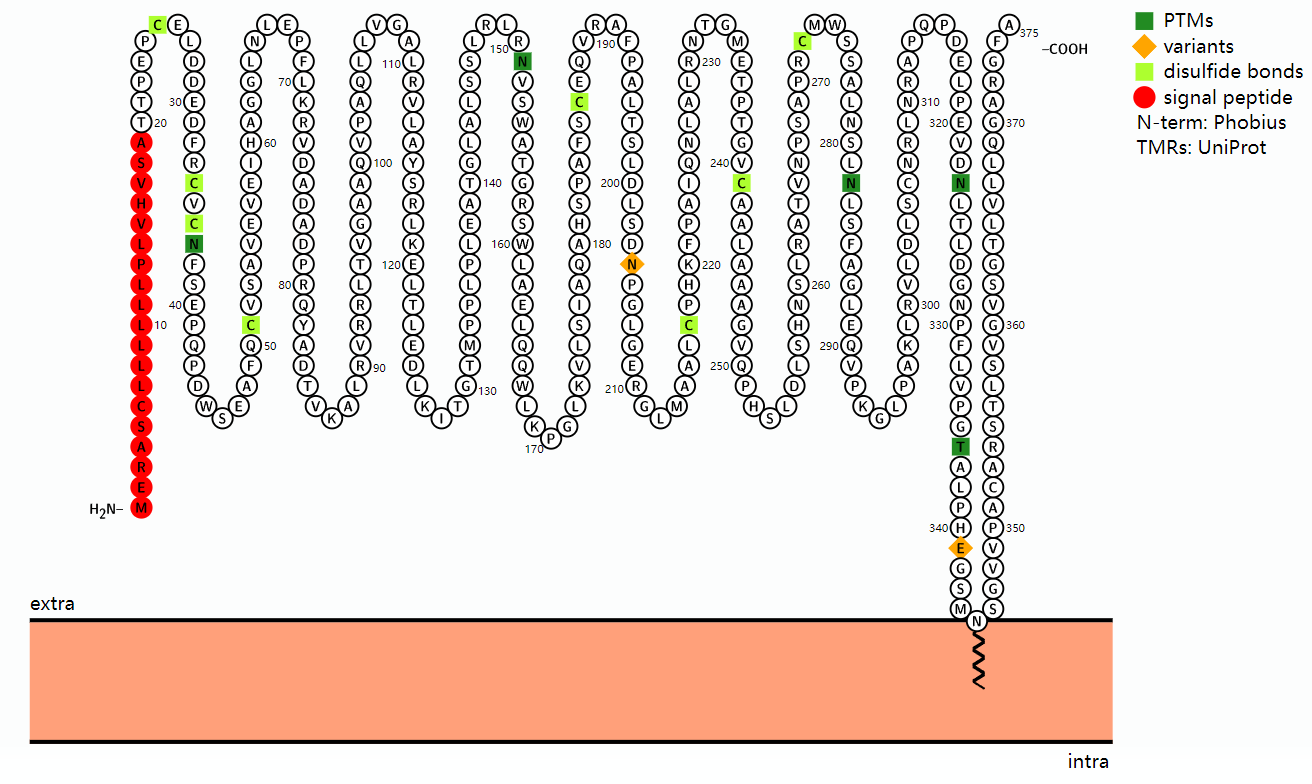
(Data source: Uniprot)
CD14 is primarily found on the cell surfaces of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, and can be used as a marker to distinguish monocytes from macrophages. Furthermore, a small amount of CD14 is also present on the surface of activated neutrophils.
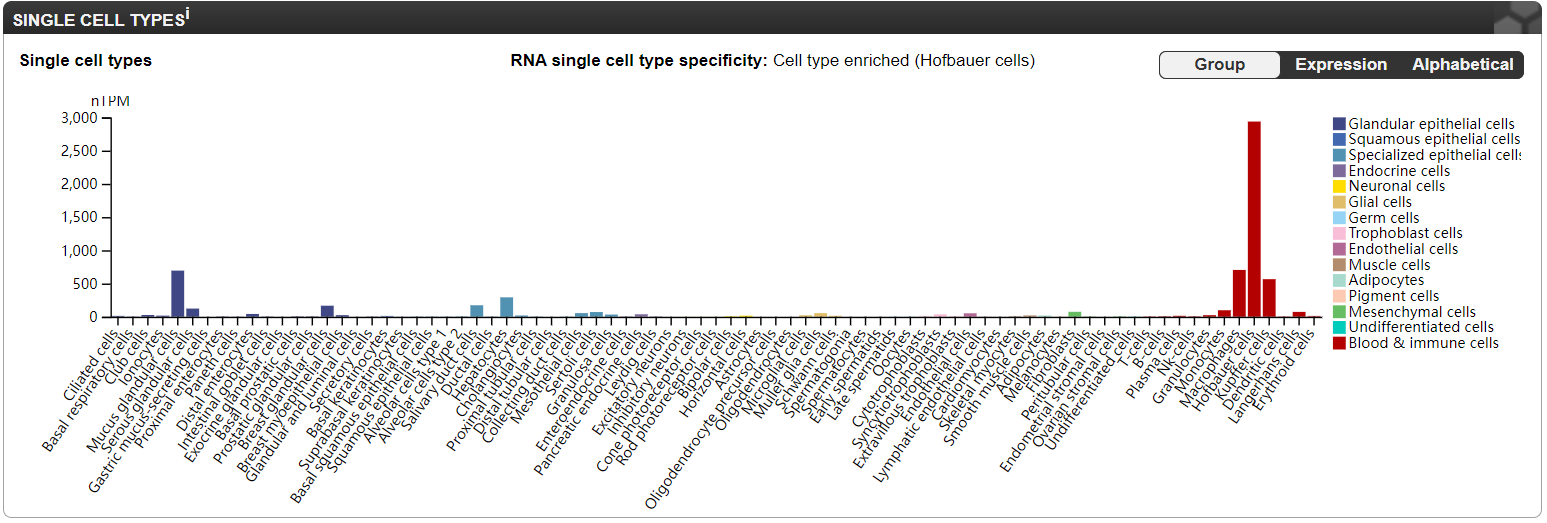
(Data source: The Human Protein Atlas)
CD14 structure:
The overall X-ray crystal structure of CD14 reveals a curved solenoid formed by 10 leucine-rich repeats, each forming a turn. Disulfide bonds are formed between pairs of cysteine residues at positions 34 and 51, 187 and 217, and 241 and 272 in the crystal structure. Both human and mouse CD14 contain a large N-terminal hydrophobic pocket, consistent with their similar roles in the binding and delivery of various lipidated molecules, including LPS.

(Data source: Kelley SL, et al. J Immunol. 2013)
CD14 signaling pathway and regulation:
CD14 activates multiple signaling pathways: (a) In human and mouse dendritic cells, the CD14-LPS complex initiates TLR4-independent activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells in a variety of inflammatory cell types; (b) LBP-dependent association of the CD14-LPS complex with TLR4-MD-2 in lipid rafts promotes the binding of TIRAP-MyD88 to the TIR domain of TLR4. The newly formed "myddosome" triggers activation of NF-κB and MAPK via TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF). As a result, large amounts of proinflammatory cytokines are secreted; (c) LPS-bound CD14 activates ITAM-containing adaptor proteins, stimulating the tyrosine kinase Syk and PLCγ2 to initiate the delivery of the TLR4/MD2 complex from the plasma membrane to the endosomal compartment ; (d) Within the endosomal vesicles, CD14 further enables LPS to stimulate the TRAM-TRIF pathway, leading to the illicit production of interferon 3 regulatory factor (IRF3) and subsequent type 1 interferon production; (e) In human monocytes, epithelial cells, and keratinocytes, when CD14 binds to LPS during tissue injury, its endocytosis enables it to bind and activate inflammasome assembly independently of TLRs.

(Data source: Sharygin D, et al. Immunology. 2023)
Clinical value of CD14:
CD14 plays a key role in the host response to sepsis, metabolism and insulin sensitivity, elevated cholesterol levels, and the promotion of autoimmunity. CD14 polymorphisms leading to increased CD14 expression are associated with an increased risk of multiple malignancies. Studies aimed at modulating CD14 expression in chronic diseases would benefit from considering the potential non-canonical roles of CD14 in various conditions.
IC14 is the only clinical-stage drug targeting CD14, and is primarily testing its efficacy against motor neuron disease (MND) , amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and all-cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).

(Data source Clinical trials)
