Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 8 (TNFRSF8), also known as CD30 or Ki-1 antigen, is a receptor for TNFSF8/CD30L. It may play a role in the regulation of cell growth and transformation in activated lymphoblasts, modulating gene expression through activation of NF-kappa-B. Its expression is crucial for the diagnosis of various lymphomas. For example, CD30 is expressed in nearly 100% of tumor cells in patients with cHL and ALCL, making CD30 a diagnostic marker for these two lymphomas.
Expression distribution of CD30
CD30 is mainly expressed in monocytes, late spermatocytes, adipocytes, macrophages, Kupffer cells, and mesothelial cells; it is also expressed in small amounts in dendritic cells and endothelial cells.

(Data source: Uniprot)
The structure of CD30 and its receptor
CD30 is a type I membrane protein composed of 595 amino acids with intracellular, transmembrane, and extracellular domains. Its extracellular domain shares amino acid sequence homology with other TNFRSF members and contains six cysteine repeats. In inflammatory diseases and CD30+ lymphomas, the extracellular portion of CD30 is readily cleaved by proteases into a soluble fragment (sCD30), which is secreted into plasma and detected by CD30 antibodies. The intracellular domain of CD30 shares no homology with other members but comprises three subdomains, D1, D2, and D3, which have independent functions. The D2 and D3 subdomains contain binding sites for TNFR-associated factors (TRAFs) 1, 2, 3, and 5, which mediate the activation of multiple signaling pathways, whereas the D1 subdomain does not require binding to activate these pathways. This conformation provides the structural basis for CD30 to exert its biological functions.
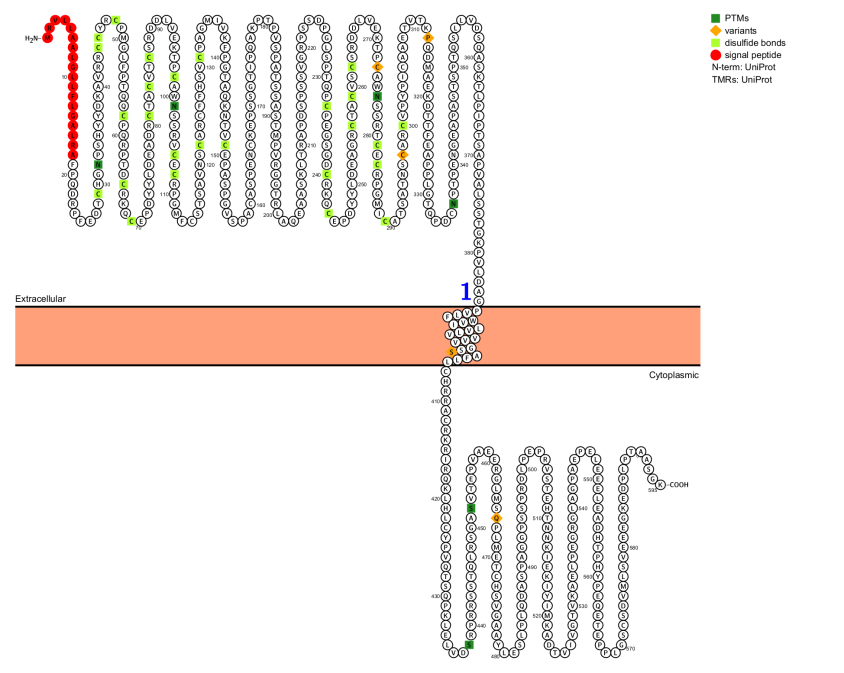
(Data source: uniprot)
CD30 signaling pathway and regulation
CD30 can activate NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, including canonical and non-canonical NF-κB pathways, ERK MAPK, JNK MAPK, and p38 MAPK, through interaction with CD30 ligand (CD30L) or overexpression of CD30 itself. CD30 binds to CD30L to form a trimer, which recruits TRAF-1, 2, 3, and 5 to its intracellular domain. TRAF members act as key signal transducers, transmitting signals between surface receptors and transcriptional regulators, thereby inducing activation of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways.
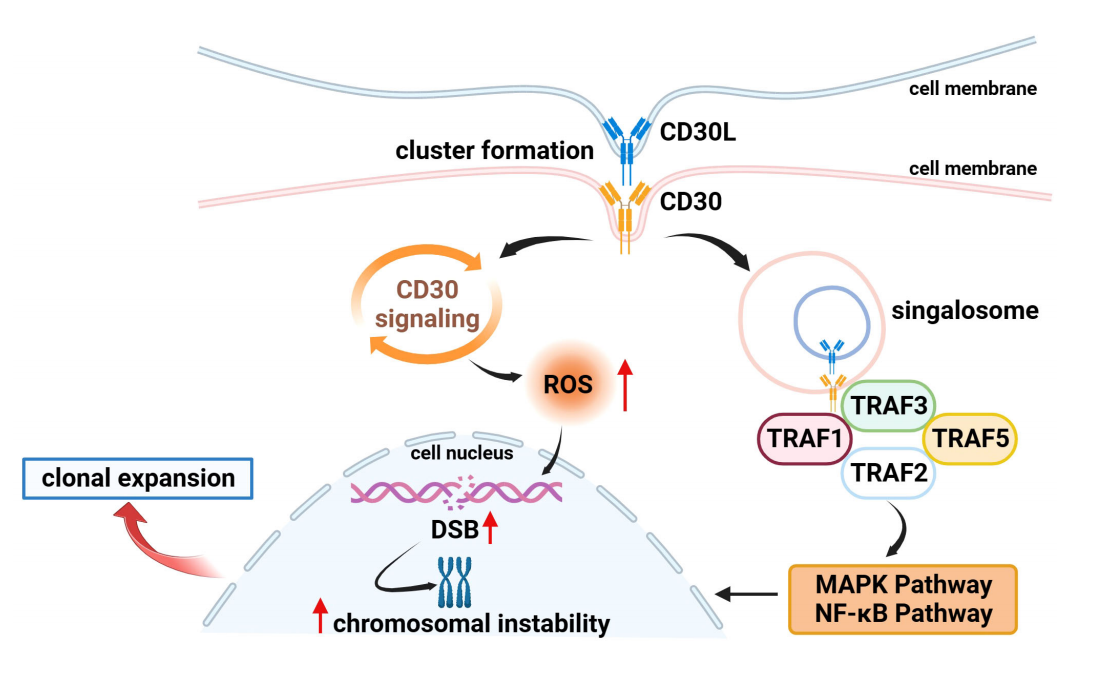
(Data source: Li Z, et al. Front Oncol. 2023)
The role of CD30 in cancer
CD30 is associated with the TME in lymphoma. It promotes chemokine secretion to recruit immune cells to the TME. It upregulates cytokine levels associated with the Th1/Th2 balance, thereby indirectly regulating the TME immune network. It downregulates perforin, granzyme B, Fas-L, and c-myc, inhibiting the proliferation and cytotoxicity of NK cells and CTLs in the TME.
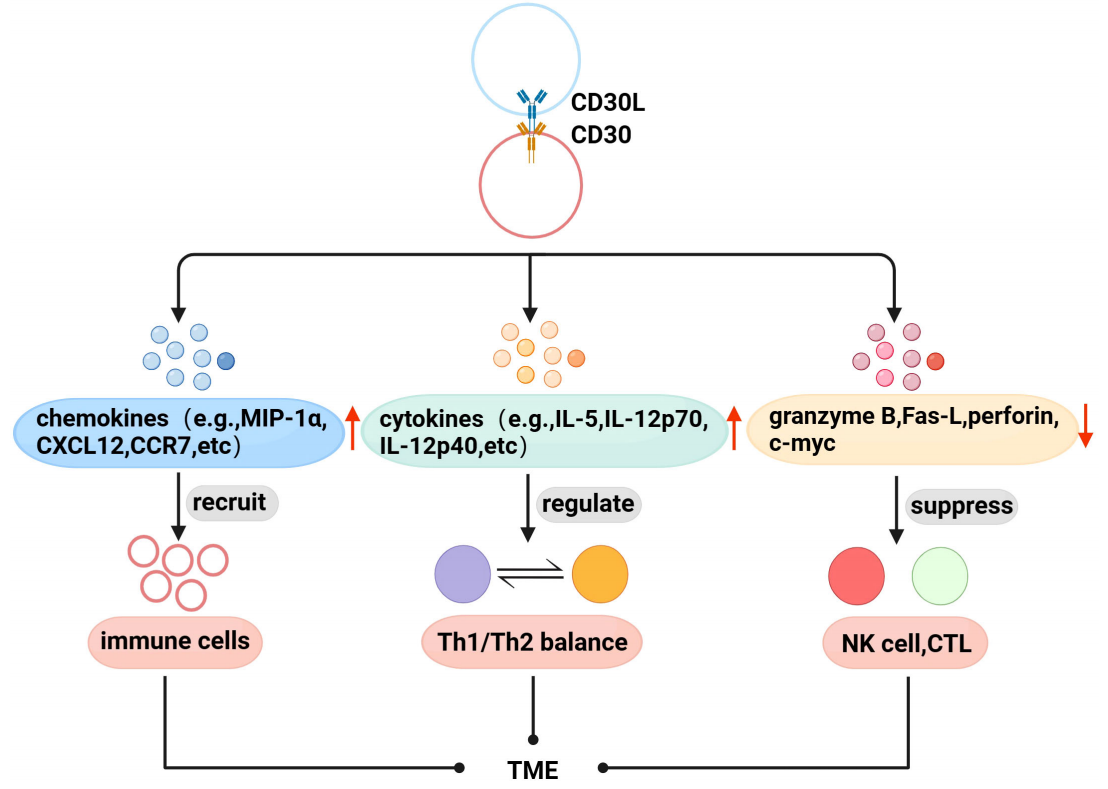
(Data source: Li Z, et al. Front Oncol. 2023)
CD30-targeted therapy
Brentuximab vedotin (BV) is a CD30 -targeting antibody-drug conjugate developed by Pfizer and has been approved in the United States for the treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, germ cell tumor, mesothelioma, lymphatic diseases, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
BV binds to CD30 on the surface of tumor cells. The resulting complex is internalized and transported to lysosomes. The linker is degraded by proteases, and MMAE is released into the cytoplasm. It binds to tubulin, arrests mitosis in the G2/M cell cycle, and triggers apoptosis. Simultaneously, MMAE diffuses into the tumor microenvironment (TME), exerting its anti-tumor effects through a " bystander effect. "
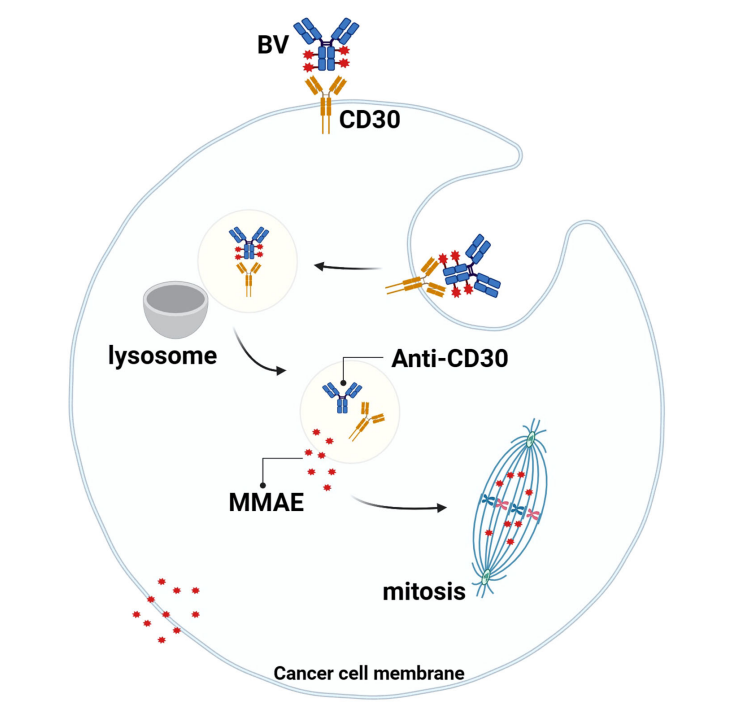
Brentuximab vedotin (BV) can be used in combination with other antibody drugs to treat HL, PTCL, and B lymphocytic leukemia.
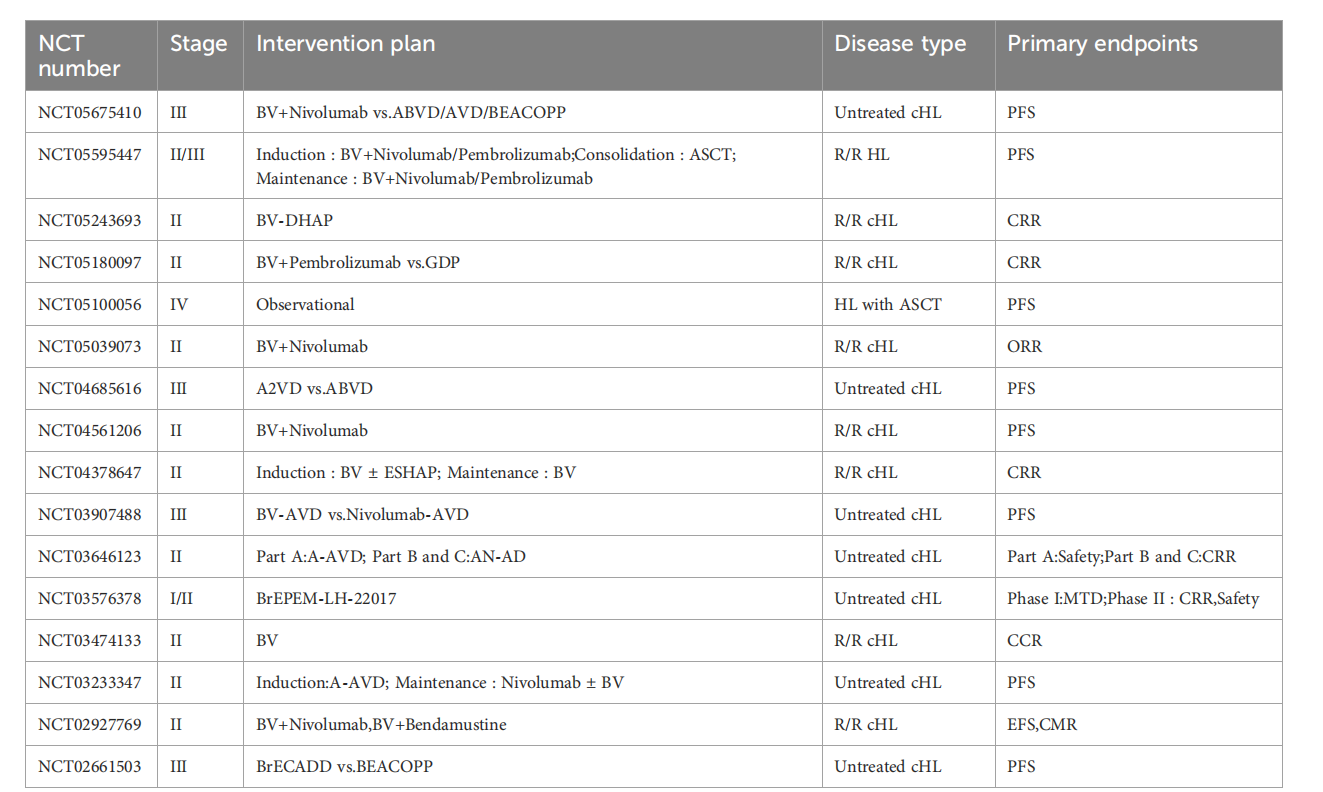
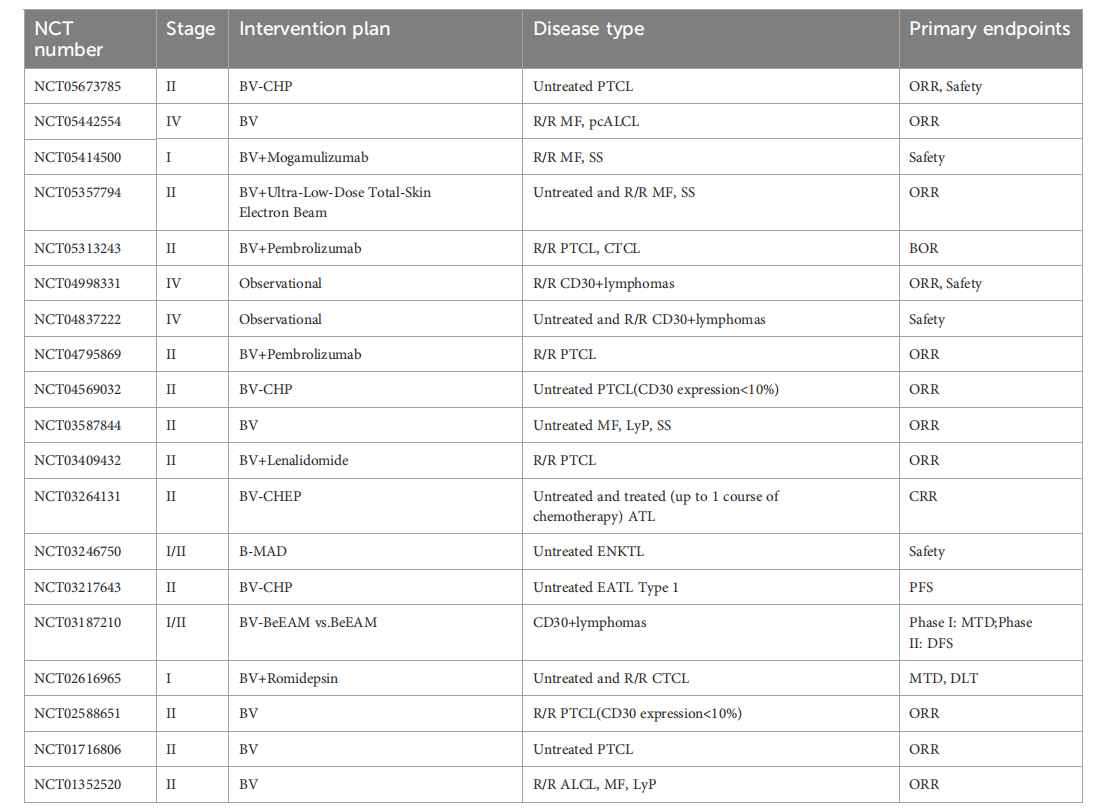
In the Phase III ECHELON-1 clinical trial, the BV combined with AVD regimen significantly improved the 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rate in treatment-naive HL patients compared to the ABVD regimen. The A+AVD group demonstrated higher 6-year overall survival (OS) and PFS compared to the ABVD group, with lower rates of subsequent treatment (including transplantation) and second cancers. In patients with relapsed/refractory HL (R/R HL), BV monotherapy demonstrated promising anti-tumor effects. Furthermore, BV combined with immunotherapies such as nivolumab has also demonstrated high objective response rates (ORR), 3-year PFS, and OS in the treatment of R/R HL.
In the Phase III ECHELON-2 clinical trial, the median PFS of patients with CD30-positive PTCL treated with BV combined with CHP was significantly longer than that of the CHOP regimen, with advantages across all subgroups. For patients with relapsed/refractory sALCL, the ORR of BV monotherapy reached 86%.
The ORR of the first-line treatment of CD30-positive B-cell lymphoma with BV combined with rituximab-R-CHP was 100%. In patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, BV combined with lenalidomide and other regimens have also shown some efficacy.

(Data source: Li Z, et al. Front Oncol. 2023)
Other CD30-targeting drugs are in clinical development, including bispecific antibodies such as AFM13, which targets CD16a and CD30 on natural killer (NK) cells. This interaction leads to NK cell activation, followed by the release of cytotoxic substances such as granzyme B and perforin, which lyse CD30-positive cells. The NCT01221571 study aims to determine the safety and tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and activity of a single cycle of AFM13 in patients with CD30-positive refractory and/or relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma.
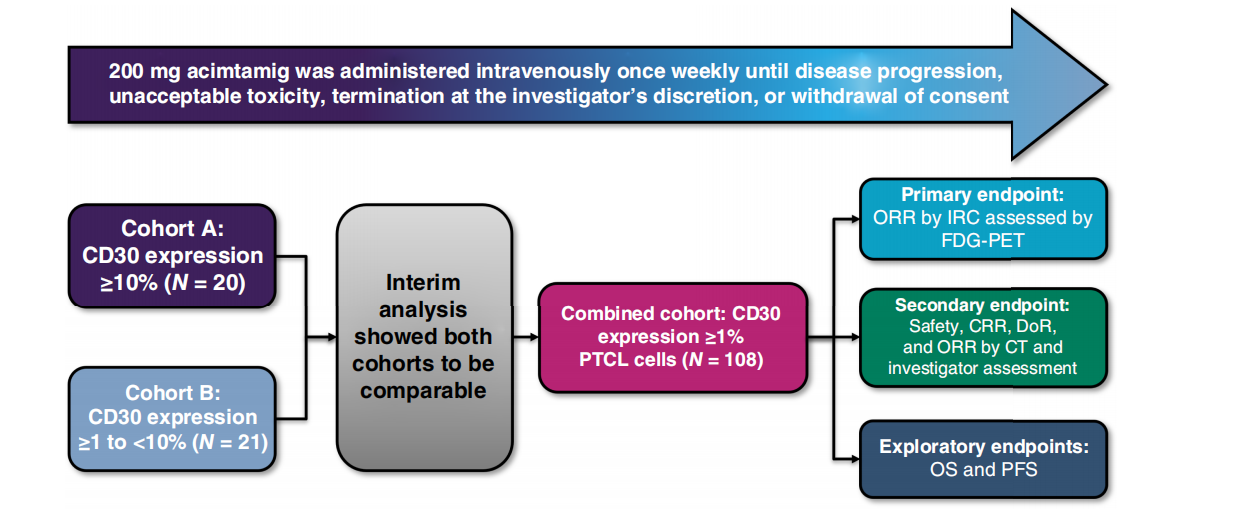
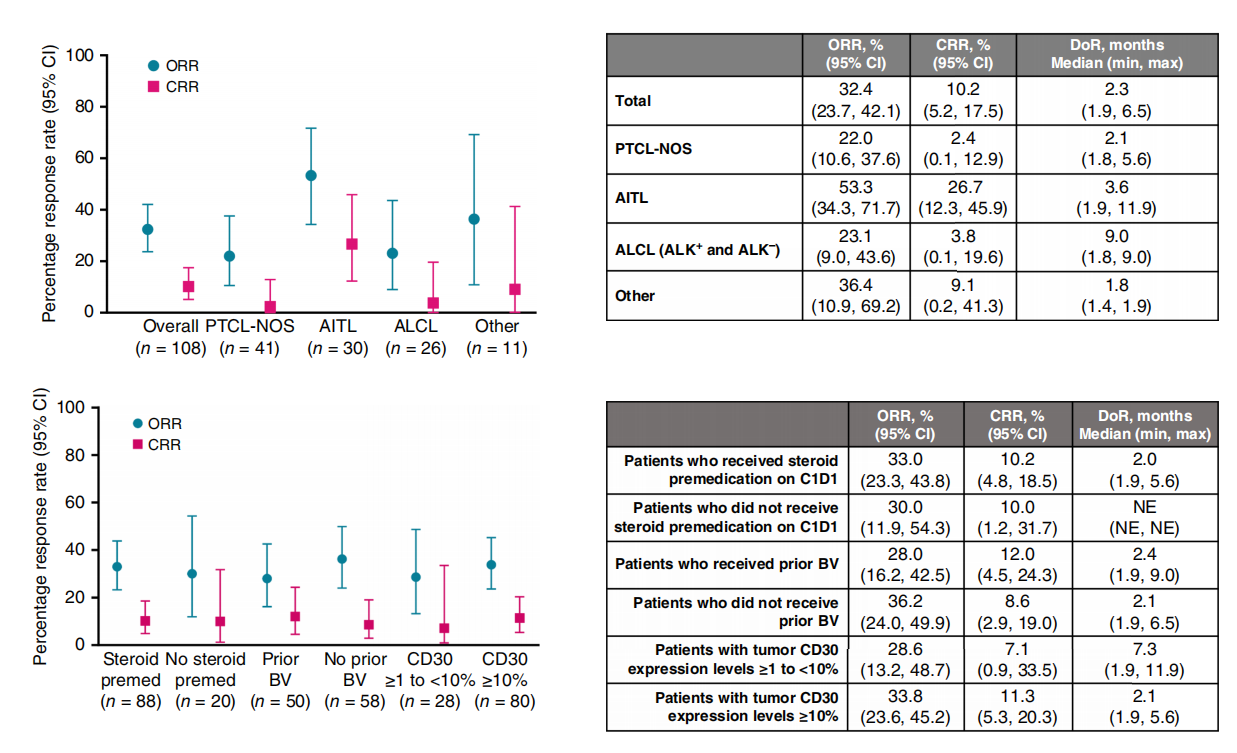
Acimtamig has demonstrated clinical activity as a monotherapy . The NCT04101331 (REDIRECT) study is a Phase II clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of AFM13 in patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) . The overall response rate (ORR) and complete response rate (CRR) assessed by an independent review committee (FDG-PET) were 32.4%, and 10.2%, respectively. Acimtamig demonstrated significant efficacy in the angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) subtype (ORR 53.3%, CRR 26.7%). The median duration of response was 2.3 months, progression-free survival was 3.5 months, and overall survival was 13.8 months. Treatment-related adverse events were grade 1 or 2, with the most common being infusion-related reactions (25.0%) and neutropenia (10.2%). No cases of cytokine release syndrome or treatment-related deaths were reported. Acimtamig's pharmacokinetic profile was similar to that of previous studies. Although the study did not reach the primary endpoint, A- cimtamig showed promising anti-tumor activity and tolerable safety in PTCL patients who had previously received multiple lines of treatment, and is expected to be further developed in the future, including combination therapy with allogeneic NK cells.
(Data source: Kim WS, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2025)
