DKK1 is a canonical Wnt signaling inhibitor that is overexpressed in many cancers and is often associated with poor clinical outcomes. DKK1 antagonizes canonical Wnt signaling by inhibiting the interaction of LRP5/6 with Wnt and forming a ternary complex with the transmembrane protein KREMEN, promoting the internalization of LRP5/6 . Dkks play an important role in vertebrate development, where they locally inhibit Wnt-regulated processes such as anterior-posterior axis patterning, limb bud development, somite generation, and eye formation. In adults, Dkks have been implicated in bone formation and bone disease, cancer, and Alzheimer's disease.
Expression distribution of DKK1
DKK1 is primarily expressed in mesenchymal cells, such as endometrial stromal cells, with smaller amounts also found in smooth muscle cells and alveolar cells. DKK1 is secreted by osteoblasts and mature bone cells and is also expressed in other tissues, such as the placenta, skin, prostate, vascular endothelium, and kidney.
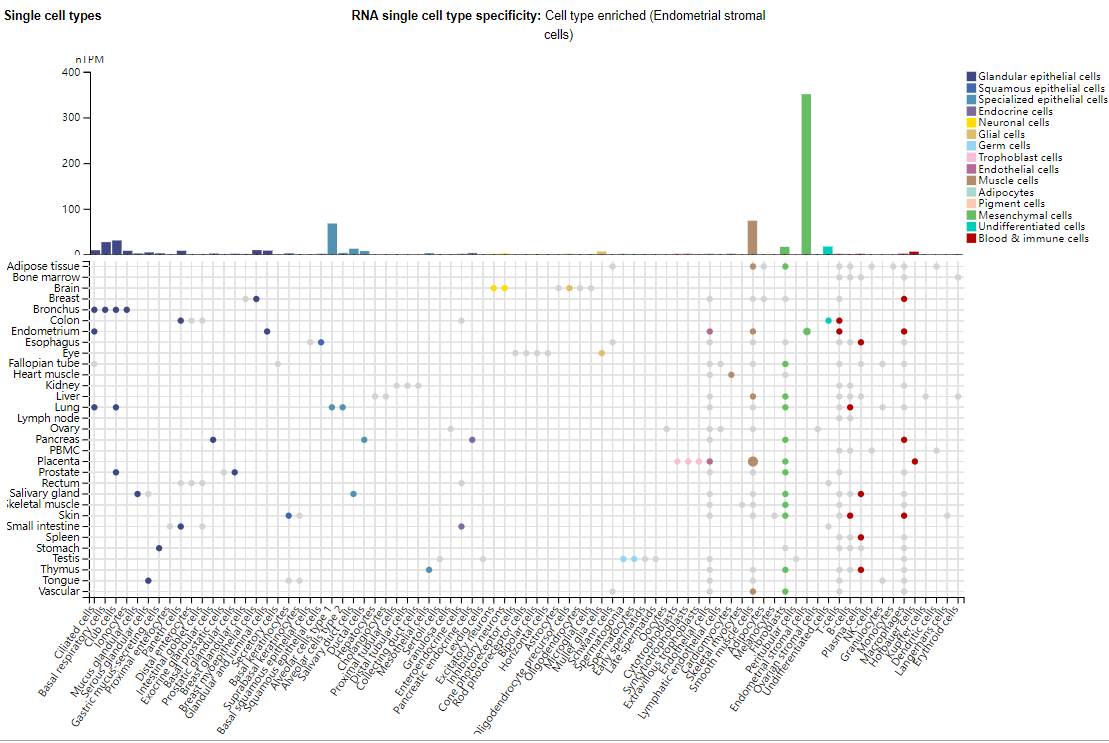

(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of DKK1 and its receptor
DKK1 is a secreted protein consisting of 266 amino acids and contains two conserved cysteine-rich domains, CRD-1 and CRD-2 (also known as CYS-1 and CYS-2), located at its amino and carboxyl termini, respectively. CRD-1 is specific to each DKK family member, while CRD-2 is highly conserved among all members.

(Data source: Chu HY, et al. Front Immunol. 2021)
Signaling pathways and regulation of DKK1
DKK1-mediated inhibition of canonical Wnt signaling: DKK1 inhibits β-catenin-dependent Wnt signaling by binding to LRP5/6 co-receptors and blocking Wnt binding, leading to β-catenin degradation.
DKK1-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling activation: DKK1 binds to the CKAP4 receptor, activating PI3K/Akt signaling and stimulating cell proliferation. When DKK1 binds to both LRP6 and CKAP4 simultaneously, cell proliferation is further promoted compared to when DKK1 binds to CKAP4 alone.
DKK1 activates the JNK pathway: Competitive binding of DKK1 to LRP5/6 diverts the Fz receptor to the JNK pathway.
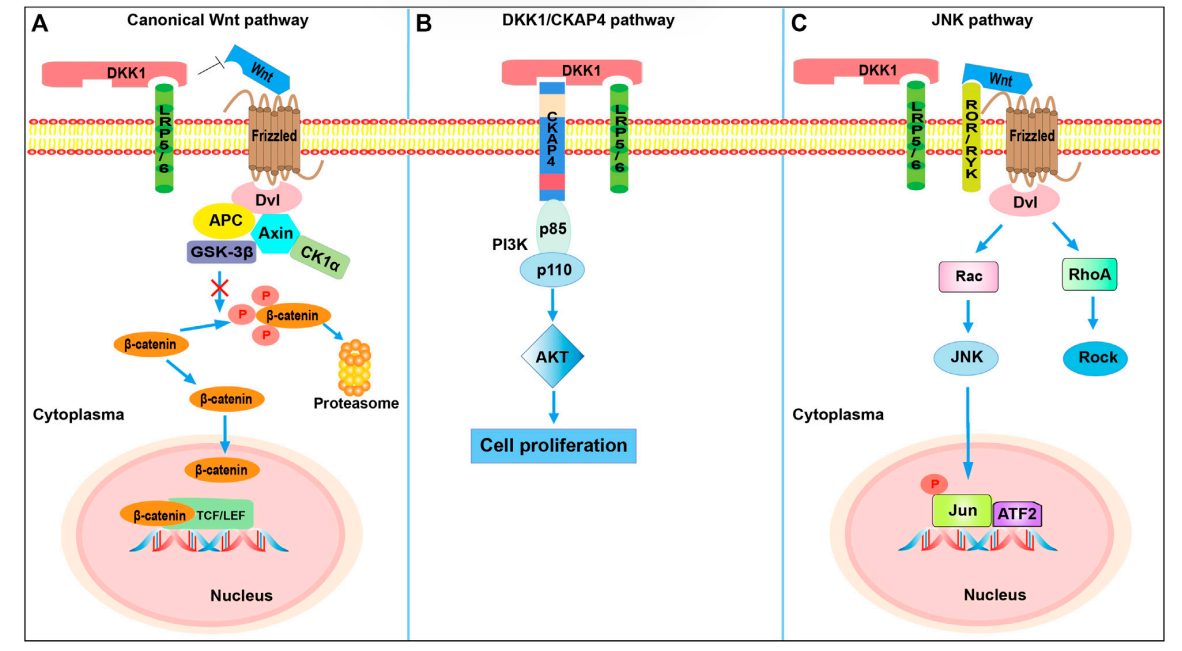
(Data source: Jiang H, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022)
The role of DKK1 in tumor immunity
DKK1 inhibits CD45+ T cell proliferation by regulating the β-catenin-independent Wnt signaling pathway, promoting an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment that favors the expansion of MDSCs and thereby facilitates tumor immune escape. Regardless of β-catenin dependence, DKK1 helps cancer cells acquire stem-like properties by preventing Wnt activation. DKK may promote tumor cell proliferation by interacting with the CKAP4 receptor and activating the Akt signaling pathway. In an allergen challenge model, platelet-derived DKK1 enhances Th2 responses and increases the secretion of IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-13, while suppressing Th1 responses by reducing IFN-γ expression.
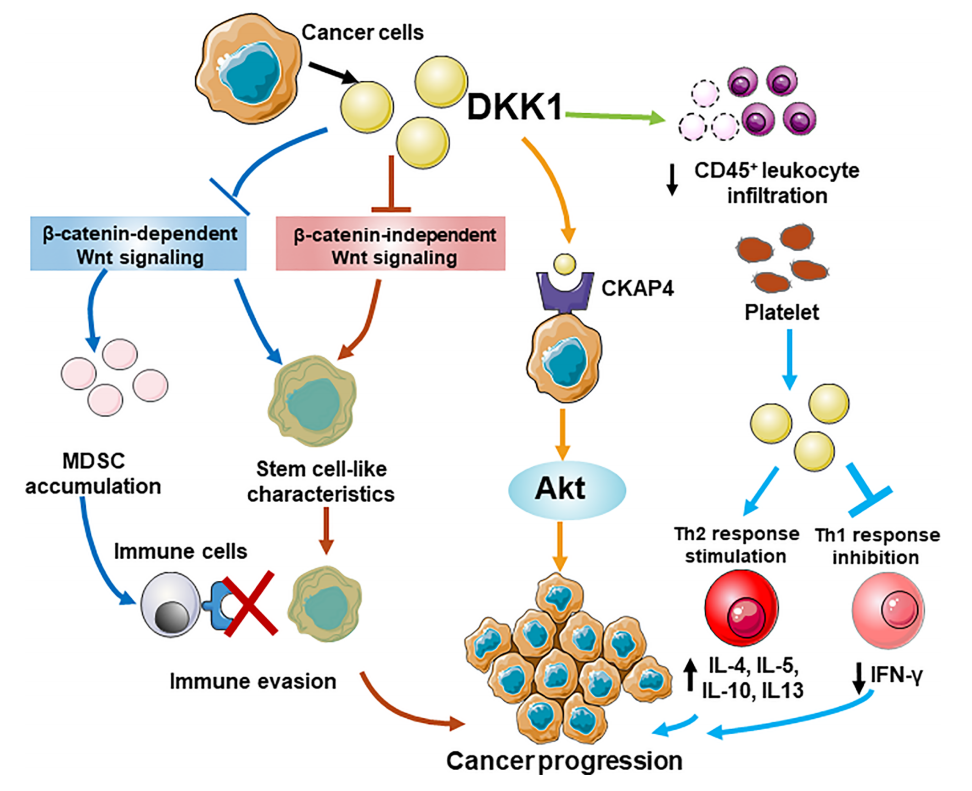
(Data source: Chu HY, et al. Front Immunol. 2021)
DKK1 targeted therapy
Sirexatamab ( DKN-01 ) is a DKK1-targeting monoclonal antibody developed by Leaptx. It binds to and eliminates free DKK1 in the TME. DKN-01 inhibits Akt through CKAP4 and PI3K signaling, reducing cell proliferation and inhibiting MDSCs. It also reduces angiogenesis and upregulates key cytokines, including IFNγ, IL-15, and IL-33. It also upregulates NK cell ligands on tumors, leading to granzyme B production by activated NK cells. DKN-01 has demonstrated activity both as a single agent and in combination with other therapies in three different tumor types (gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, and endometrial cancer). It is well tolerated as a monotherapy and in combination with chemotherapy or checkpoint inhibitors.
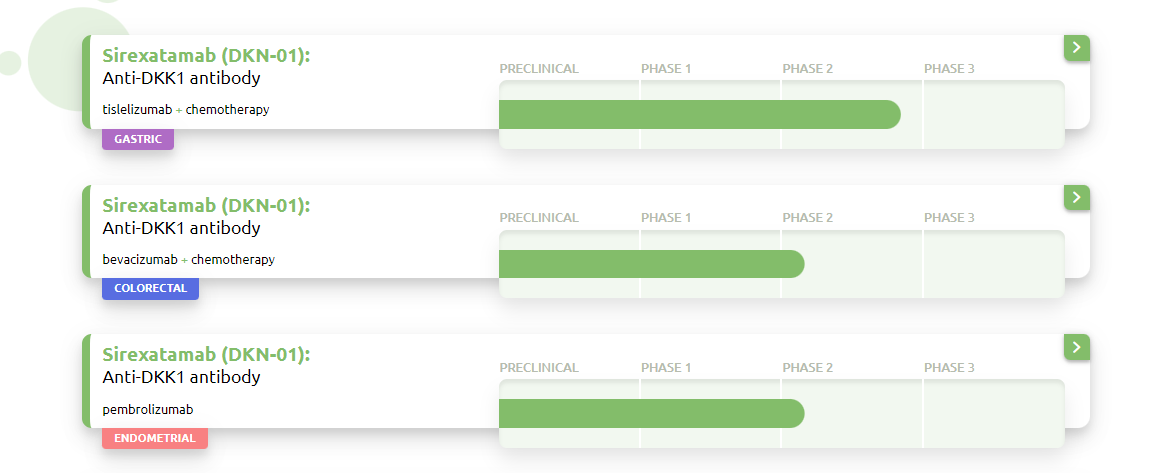
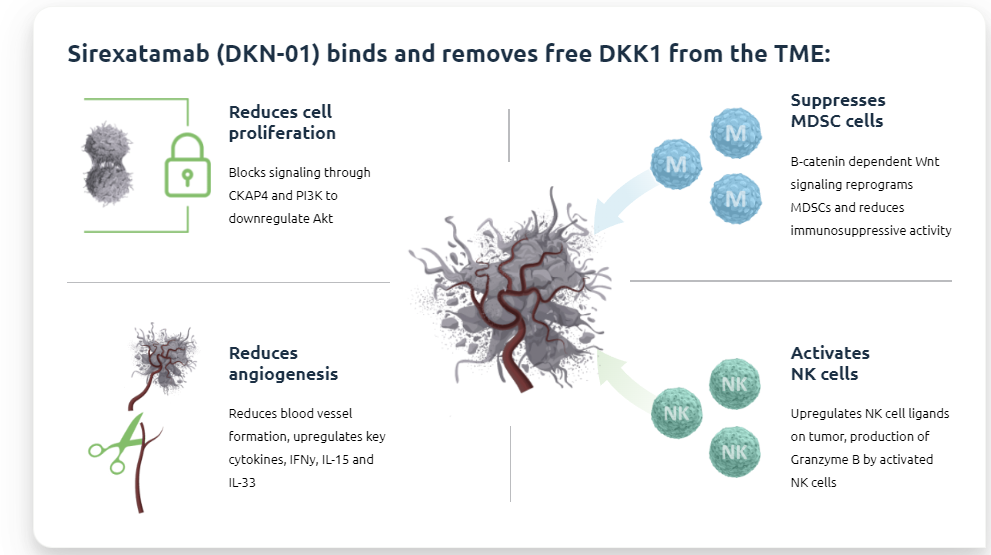
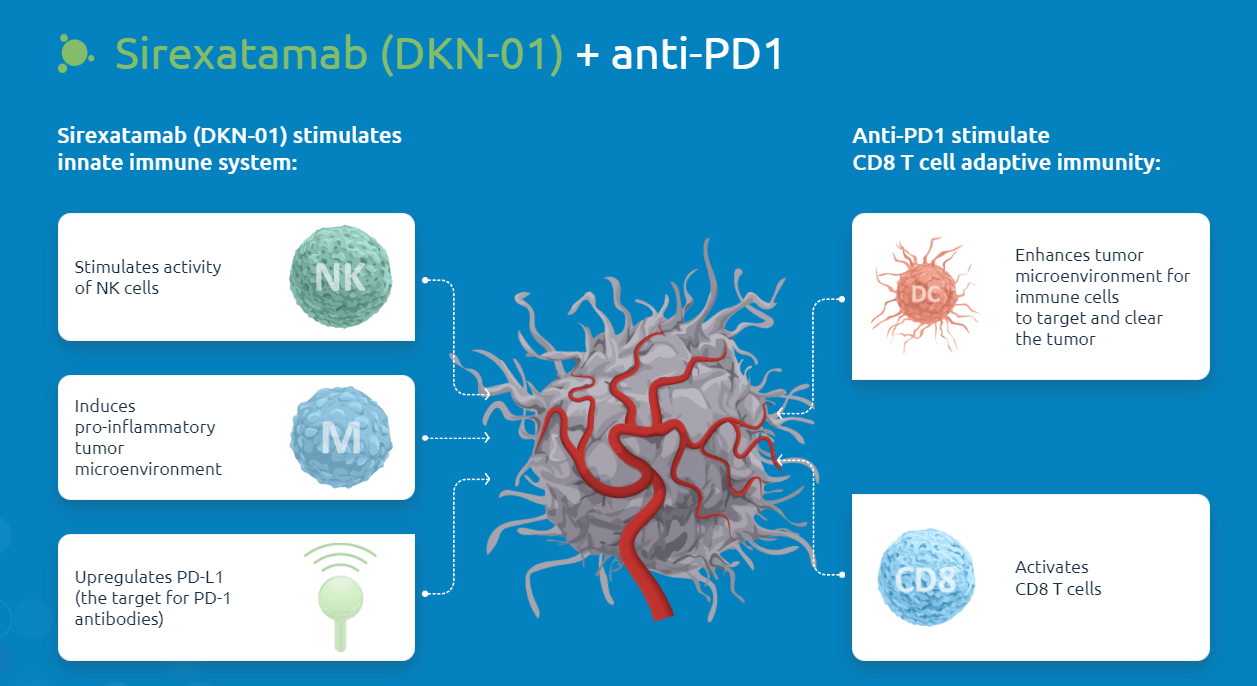
(Data source: leaptx official website)
JS015 is a recombinant humanized anti-DKK1 monoclonal antibody independently developed by Junshi Biosciences, primarily intended for the treatment of advanced malignant solid tumors. JS015 binds with high affinity to DKK1 secreted in the tumor microenvironment, blocking its interaction with its ligands LRP5/6 and activating the Wnt signaling pathway. Furthermore, by binding to DKK1, JS015 promotes NK cell activation, inhibits the activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), and suppresses the transmission of immunosuppressive signals, exerting its anti-tumor effects. JS015 is currently in Phase II clinical trials.
At the 2025 ACCR meeting, clinical study results for the DKK1 monoclonal antibody JS015 were presented for the first time as a Late-Breaking Research Poster. This was the first such presentation of clinical study results for an anti-DKK1 monoclonal antibody in China. JS015 combination therapy demonstrated encouraging preliminary efficacy in patients with advanced gastrointestinal cancers. In second-line treatment of patients with advanced colorectal cancer (CRC), JS015 combined with bevacizumab and chemotherapy achieved an objective response rate (ORR) of 31.6%. In second-line CRC patients who had not received prior bevacizumab, an ORR as high as 80% was observed; in first-line CRC patients who had not received prior systemic anti-cancer therapy, the ORR was 100%. In first-line treatment of patients with advanced gastric cancer (GC), JS015 combined with toripalimab and chemotherapy achieved an ORR of 66.7%. These data suggest that JS015 combination therapy warrants further investigation in gastrointestinal cancer.
