Fibroblast growth factor 1 ( FGF1 ) was discovered in 1979, and its molecular identity and properties were determined over the next decade. A series of studies beginning in 1989 linked FGF1 to central regulation of feeding, and in 2012, a role for FGF1 in fat energy homeostasis was discovered. Shortly thereafter, the therapeutic benefits of both peripheral and central administration of FGF1 were described. In recent years, the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the antidiabetic effects of FGF1 have also begun to be deciphered.

(Data source: Gasser E, et al. Nat Metab. 2022)
FGF 1 is composed of 155 amino acids, the main functional domain is the 16-155 segment, and the 2-15 segment is the leader peptide part that guides protein secretion and localization.
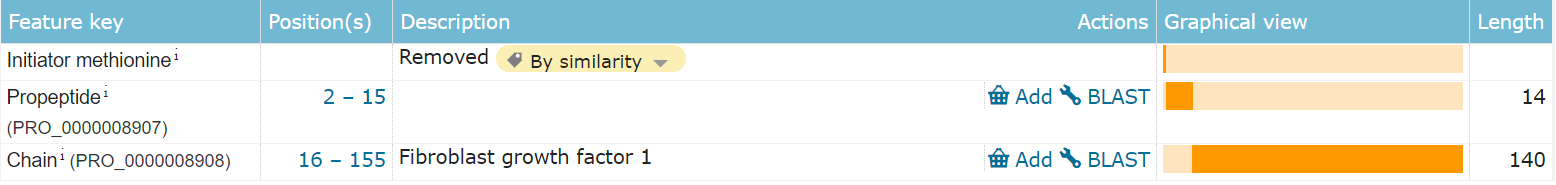
(Data source: Uniprot)
FGF1 is ubiquitously expressed, with the highest levels detected in the brain and pituitary gland, and is abundantly expressed in peripheral tissues such as adipose, liver, skeletal muscle, heart, lung, and kidney.
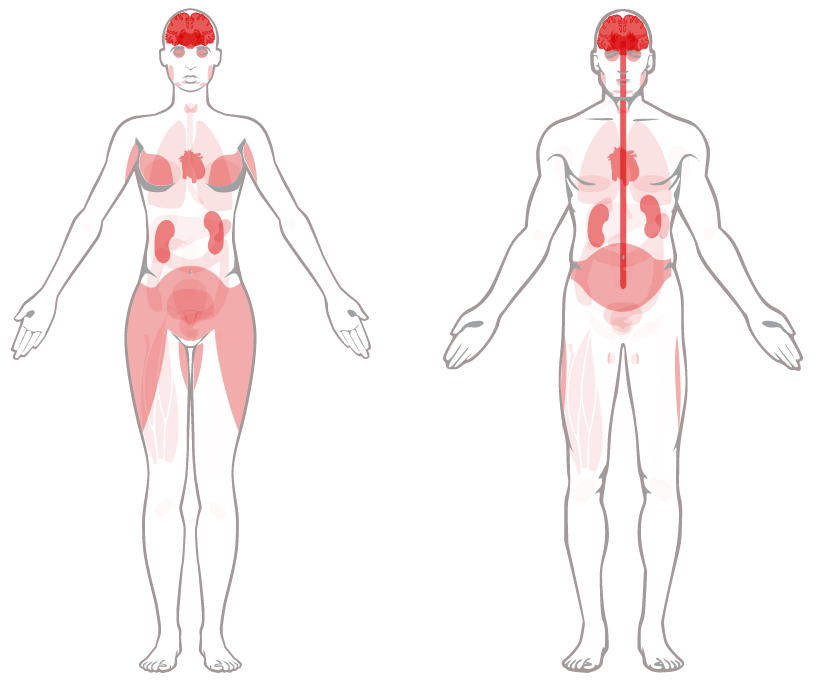
(Data source: Protein Atlas)
As an autocrine/paracrine regulator, FGF1 effectively blocks its own circulation upon binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs). Crystallographic studies have shown that HSPGs promote the formation of a 2:2:2 dimer between FGF1, FGFR, and HSPGs.
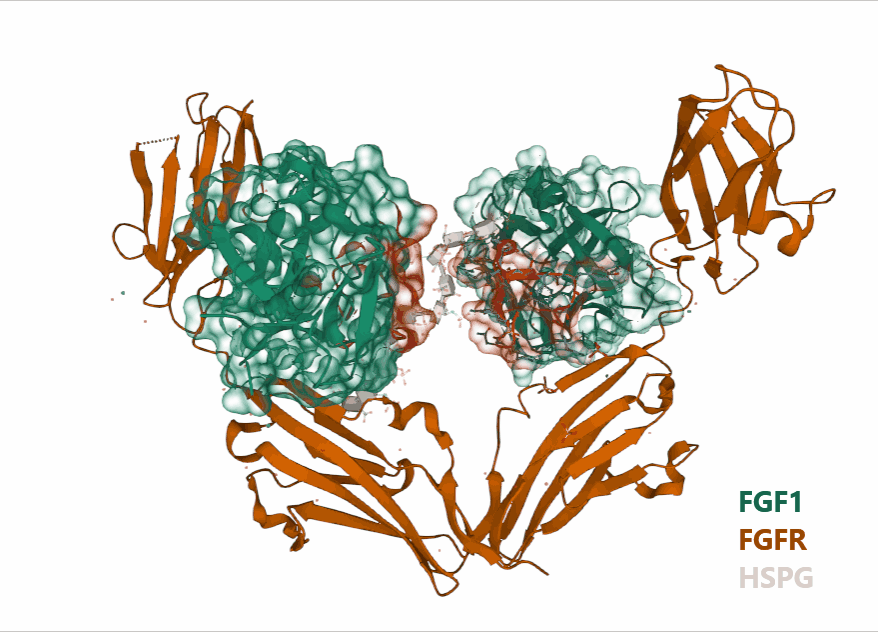
(Data source: RCSB PDB)
Delayed wound healing is a serious health problem for diabetic patients. FGF-1 has a positive effect on enhancing cell proliferation, promoting extracellular matrix synthesis, and promoting angiogenesis, proliferation, and differentiation. As early as 2005, recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 1 (rh-FGF1), developed by Chinese scientists, received approval from the China Food and Drug Administration, becoming the world's first marketed FGF-1 drug. In 2006, rh-FGF1 was launched for the treatment of diabetic ulcers.
Recent research on the mechanisms of FGF1 in metabolic processes and white adipose tissue remodeling has refocused attention on its key role. This is primarily demonstrated by the following: (a) FGF1 regulates high-fat diet (HFD)-induced adipose remodeling. HFD acts as a stressor triggering FGF1 release through nutrient sensing and mechanosensing pathways, respectively. FGF1 promotes the formation (proliferation) of new adipocytes through paracrine effects on preadipocytes via FGFR1. Hyperplasia is associated with more metabolically beneficial outcomes than hypertrophy. In hypertrophy, pre-existing mature adipocytes respond to nutrient overload by expanding in size. Knockout of FGF1 or Piezo1 leads to impaired adipose remodeling and increased insulin resistance under HFD. (b) FGF1 lowers blood glucose by inhibiting lipolysis. In models of obesity, FGF1 can act autocrine/paracrine on adipocytes to activate PDE4E (phosphodiesterase 4E) and inhibit the cAMP/PKA pathway, thereby inhibiting white fat mobilization and reducing the allosteric activation of PC, a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, by acetyl CoA in the liver, thereby inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis. (c) FGF1 (or its cognate ligand for FGFR1c) mediates increased glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. FGF1 promotes GLUT4 expression and increases GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane. These FGF1 regulations are relayed through FGFR1 and AMPK.

(Data source: Gasser E, et al. Nat Metab. 2022)
Based on the food intake suppression and blood sugar lowering effects of FGF1 in blood sugar control, some clinical trials have been carried out.
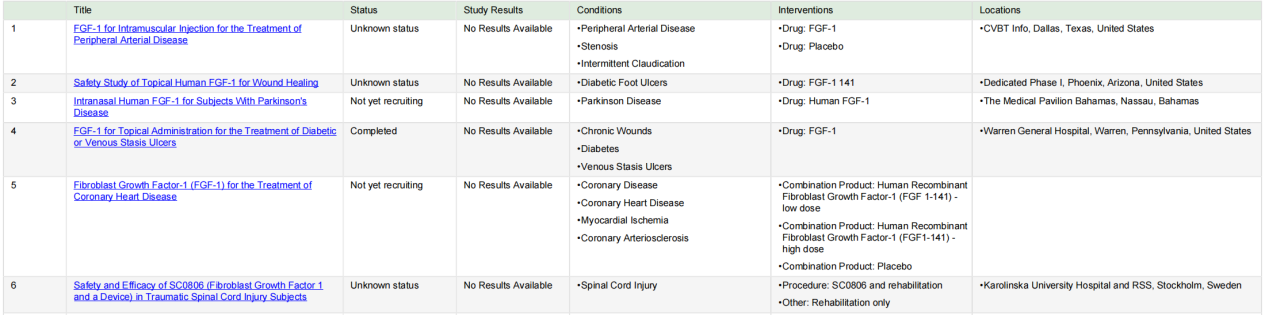
(Data source: Clinical trials)
Furthermore, FGF1 and its receptor, FGFR, regulate key biological processes such as cell proliferation and differentiation. Abnormal activation of FGFR can promote tumor growth and angiogenesis in many tumor types, including lung and breast cancer. Based on the role of the FGF1 & FGFR signaling axis in cancer, many new drugs targeting this pathway are under development. For example, after FGF1 neutralizing antibodies blocked binding to FGFR1, significant anti-proliferative activity was observed in in vitro cell models.

(Data source: Chudzian J, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018)
At present, FGF1 has attracted great attention mainly for its peripheral anti-lipolysis properties, because this pathway can enter through the periphery, can lead to safe acute and chronic hypoglycemic effects, and has made great progress in its mechanistic basis, paving the way for other intervention strategies . We look forward to the early development of therapeutic FGF1 recombinant protein and its derivatives for the benefit of mankind.
