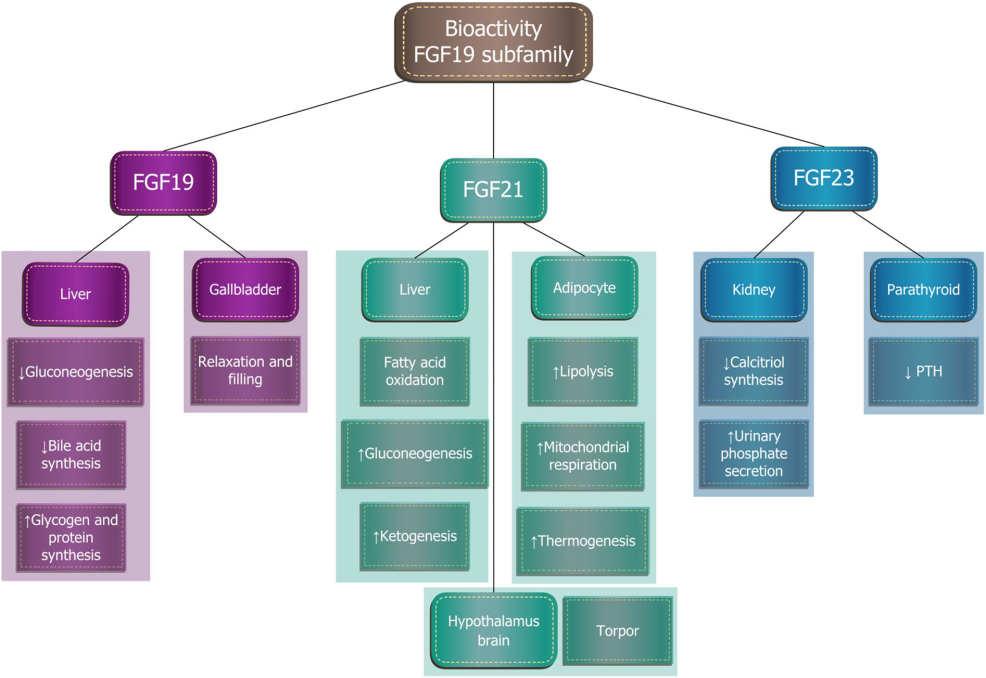
The fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) subfamily includes three proteins: FGF19, FGF21, and FGF23, which show activity on FGFR1c, 2c, 3c, and 4 receptors, but cannot bind to FGFR1b, 2b, and 3b receptors.
(Data source: Dolegowska K, et al. J Physiol Biochem. 2019)
Unlike the classical FGF subfamily members, FGF19 subfamily proteins have only weak or no heparin-binding affinity, which enables them to enter the systemic circulation and act in an endocrine manner to regulate various aspects of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Let’s take a look at the relevant research information of FGF19:
(Data source: AlphaFold)
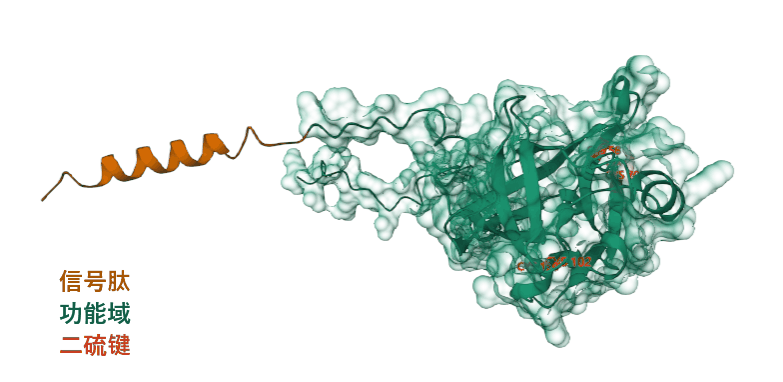
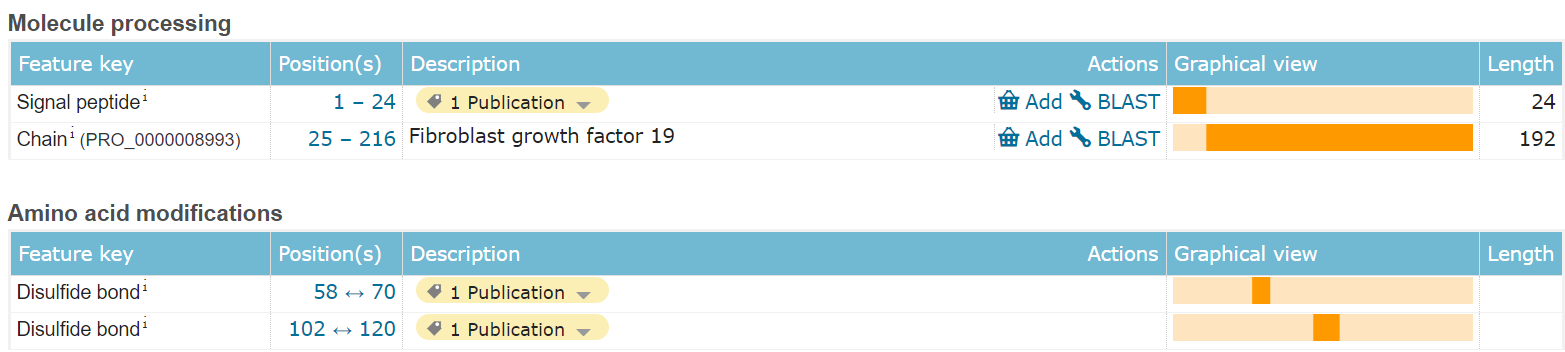
FGF19 is composed of 216 amino acids and is an endocrine extracellular protein. Segments 1-24 are signal peptides that guide secretion, while the main functional domain is segments 25-216, which include two pairs of disulfide bonds: the first disulfide bond helps maintain the extended loop formed by the β-sheet , while the second disulfide bond stabilizes the protein backbone , enhancing its stability.
(Data source: Uniprot)
FGF19 was originally discovered in the fetal brain and is believed to play a key role in early neuronal development. Subsequent studies in transgenic mice expressing FGF19 revealed an increase in metabolic rate and a decrease in obesity, revealing for the first time that FGF19 is involved in metabolic regulation. Further studies have revealed that FGF19 participates in feedback inhibition of the bile acid biosynthesis pathway, inhibiting cholecystokinin (CCK), a gut hormone known to empty the gallbladder, by binding to FGFR, thus playing a key role in regulating bile acid circulation.

(Data source: Phuc P , et al. Cells. 2021)
To determine the serum FGF19 levels in 304 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by ELISA and to identify FGF19 as a potential new biomarker for HCC, which may help improve the prognosis of HCC patients.

(Data source: Maeda T, et al. BMC Cancer. 2019)
The main reason is that the abnormal expression of FGF19 and FGFR4 leads to the recruitment of FRS2 and growth factor receptor binding protein 2 (GRB2), ultimately leading to the activation of the Ras-Raf-ERK1/2MAPK and PI3K-Akt pathways, stimulating tumor proliferation and leading to HCC.
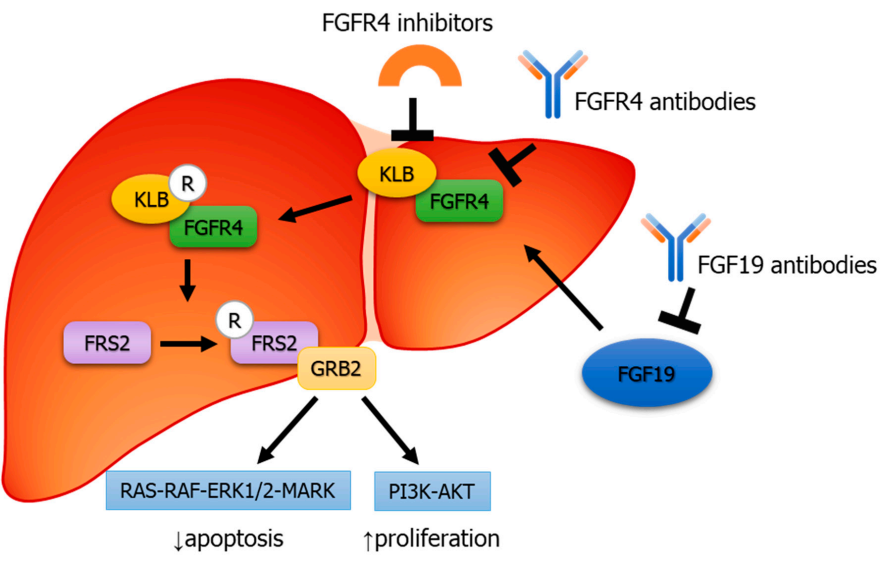
(Data source: Bo Xu , et al. JCI Insight. 2021)
In addition, FGF19 and FGFR4 can also promote the progression of gallbladder cancer (GBC) through an autocrine pathway that depends on the GPBAR1-cAMP-EGR1 axis.

(Data source: Chen T, et al. Oncogene. 2021)
FGF19 may also be a new diagnostic indicator for screening lung cancer, as it combines with FGFR4 to drive the progression of lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSQ). This provides new ideas for using the FGF19/FGFR4 signaling axis to block therapies in FGF19-driven LSQ.

(Data source: Li F, et al. Oncogene. 2020)
As a metabolic regulator implicated in numerous diseases, particularly the FGF19-associated FGFR4 signaling pathway, FGF19 has sparked interest in targeting this pathway with new or existing drugs. Currently, there are 105 ongoing and ongoing clinical trials for FGF19, and NGM282 ( aldafermin ), an engineered FGF19 analog, appears to be one of the most promising therapeutic agents currently undergoing clinical trials. Aldafermin treatment in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) has shown significant reductions in liver fat content and a trend toward improved fibrosis. Administration to patients with metabolic/cholestatic liver diseases has demonstrated that the drug inhibits glycine-conjugated hydrophobic bile acids, which have high cytotoxic and detergent activity, allowing for the use of aldafermin in the treatment of gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
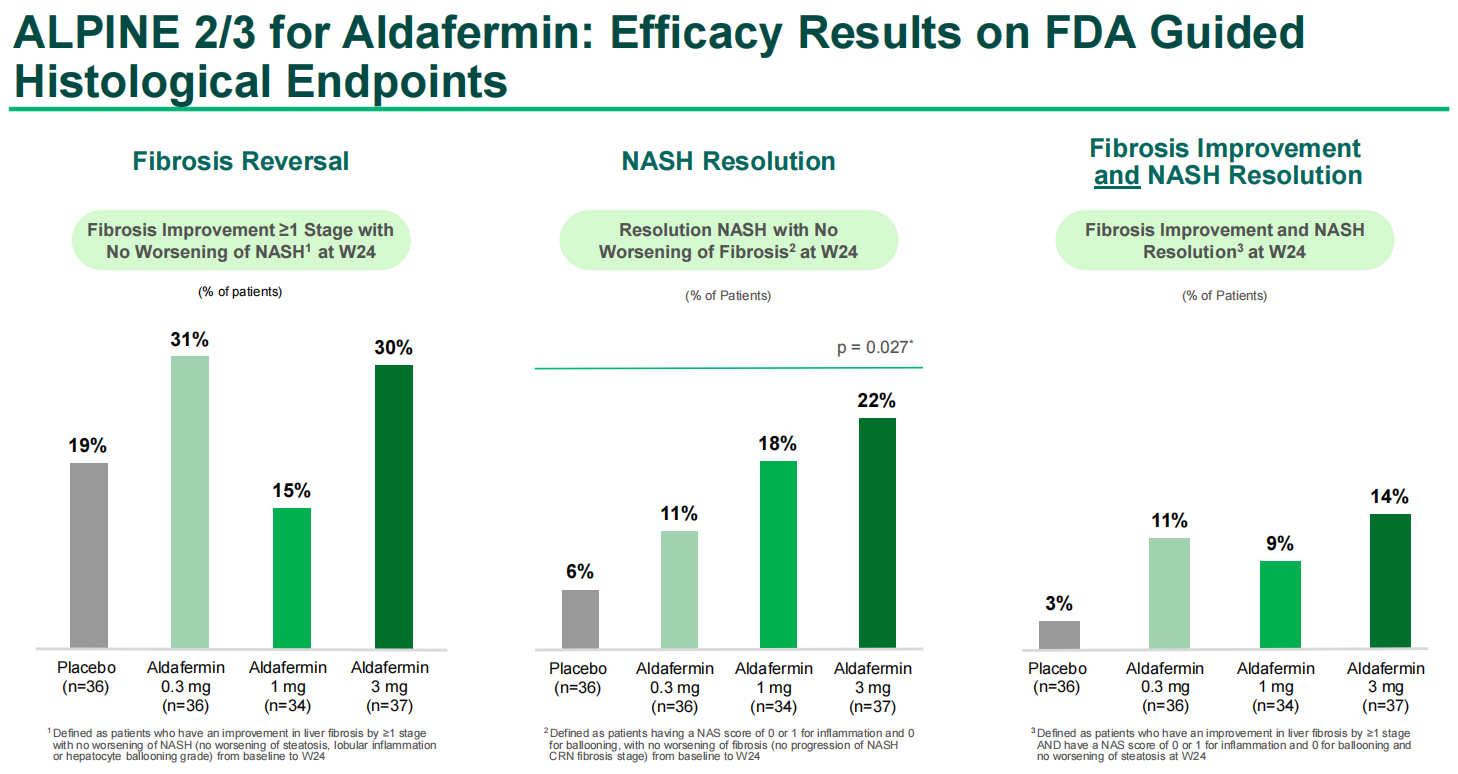
(Data source: NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Inc.)
Continuing research on FGF19 as a therapeutic agent will hopefully lead to some new and exciting clinical applications in the near future.
