Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), also known as basic FGF (bFGF), is one of the earliest recognized members of the FGF family. As a ligand for FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4, it plays an important role in regulating cell survival, division, differentiation, and migration. FGF2 can induce angiogenesis and is a key mitogen in tissue homeostasis and cancer. It regulates the self-renewal of multiple stem cell types and has been used to culture cancer stem cells in vitro.
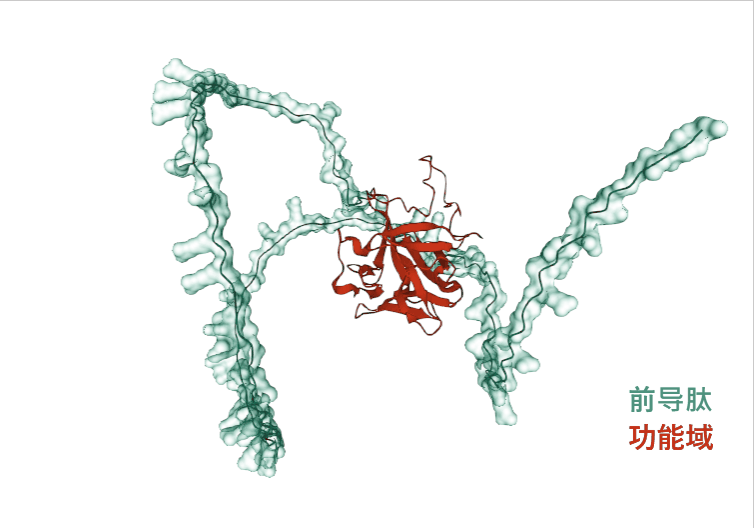
(Data source: AlphaFold)
FGF-2 is composed of 288 amino acids, with the main functional domain being segments 143-288 and the leader peptide segment 1-142, which guides protein secretion and localization. Structurally, the leader peptide encapsulates the protein, inhibiting the activity of the functional domain.
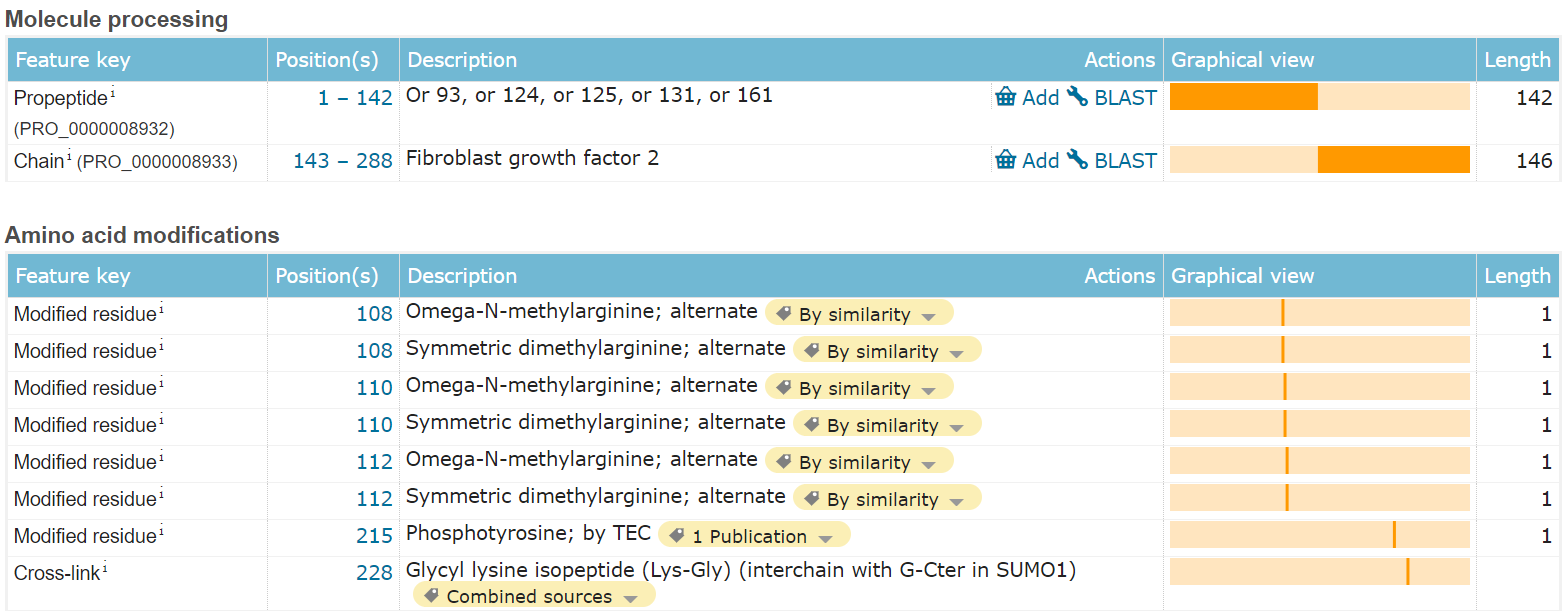
(Data source: Uniprot)
FGF2 and FGF1 are both members of the FGF1 subfamily , and the biggest difference between them lies in the length of the N-terminal leader peptide.

(Comparison of amino acid sequences of FGF2 and FGF1)
This also means that although FGF2 lacks a signal peptide to be transported along the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi-dependent secretory pathway, it can use its own leader peptide characteristics to adopt an unconventional secretion method of direct translocation of the plasma membrane to enter the extracellular space to exert its function.

(Data source: Pallotta MT, et al. J Cell Sci. 2020)
FGF2 is a regulatory factor for fibroblasts. The latest studies have shown that FGF2 & FGFRs cell signaling is positively and negatively regulated by two different types of sphingolipids (Gb4 and GM1), thereby prompting fibroblasts to reshape into different cell morphologies.

(Data source: Capolupo L, et al. Science. 2022)
In addition, in the acute kidney injury (AKI) model, proximal tubular cells secrete FGF2 through autophagy to regulate fibroblasts, mediate fibroblast activation and renal fibrosis; inhibiting FGF2 can inhibit the expression of fibrosis genes, providing a new therapeutic theoretical basis for the treatment of renal fibrosis after AKI.

(Data source: Livingston MJ, et al. Autophagy. 2022)
FGF2 is also a new type of thermogenic regulator and plays different roles in the formation and differentiation of white fat. Knocking out the FGF2 gene will lead to increased thermogenic capacity of brown and beige fat, increased expression of mitochondrial brown fat uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), increased respiratory exchange rate, and increased thermogenic potential to cold exposure, protecting mice from high-fat-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis; while exogenous FGF2 can inhibit the expression of PGC-1α and PPARγ, thereby inhibiting UCP1 expression in brown and beige fat cells.
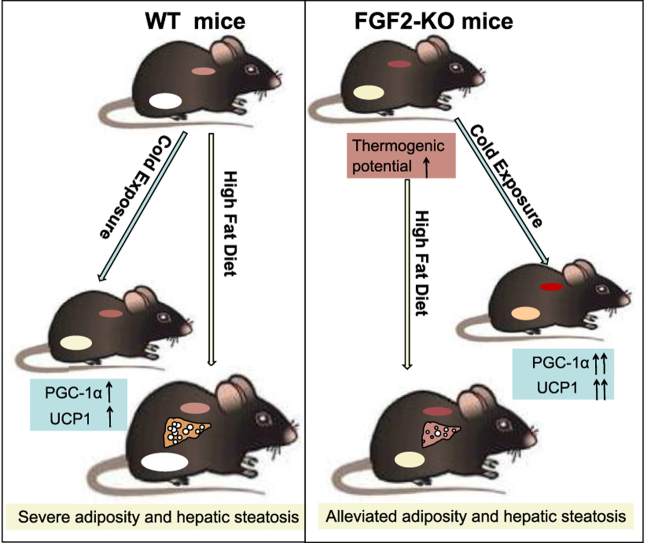
(Data source: Li H, et al. Mol Metab. 2021)
FGF2 affects macrophages in the tumor microenvironment, controls tumor growth and anti-tumor immunity, and is a key regulator of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Reducing FGF2 expression or using FGF2 blocking antibodies can significantly improve survival rates after radiotherapy.

(Data source: Im JH, et al. Nat Commun. 2020)
FGF2 plays a positive pathophysiological role in tissue remodeling, bone health, and regeneration, such as repairing neuronal damage, healing skin wounds, protecting joints, and controlling hypertension. Currently, clinical trials for recombinant FGF2 protein therapy focus on restorative treatments for conditions such as oral health, periodontitis, tympanic membrane perforation, and age-related macular degeneration.

(Data source: Clinical trials)
As an important cell signaling protein closely related to cell growth and tissue repair, FGF2 is also a known oncogenic factor in glioblastoma (GBM). It contributes to glioma growth, vascularization, and GBM self-renewal. Therefore, the FGF2/FGFRs signaling axis may be a potential target for therapeutic approaches to inhibit the progression and spread of this disease. In addition, RNA aptamers developed by the Institute of Medical Science, University of Tokyo, that inhibit FGF2 expression are currently undergoing clinical trials to evaluate their therapeutic effects on age-related macular degeneration (wet AMD) and achondroplasia (ACH).
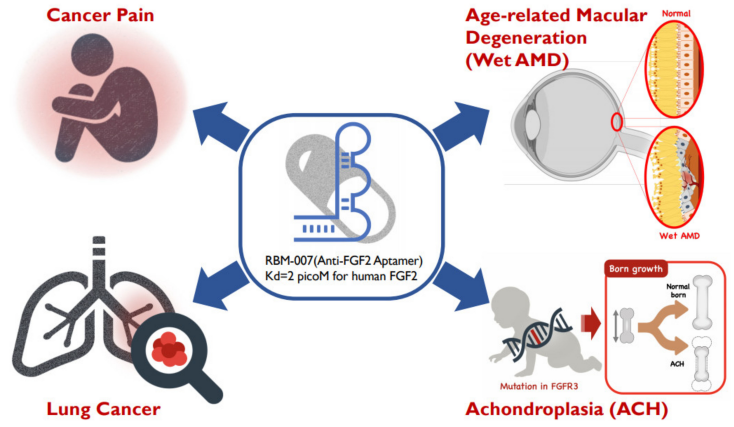
(Data source: Nakamura Y. Cells. 2021)
Overall, research on the differential effects of FGF2 in different tissues and diseases is relatively scattered, with the fastest overall progress mainly in tissue repair and wet AMD treatment, which also mainly relies on its clear mechanism of promoting the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells in the process of promoting new blood vessel growth.
