
(Data source: AlphaFold)
Fibroblast growth factor 3 (FGF3) is composed of 239 amino acids and is a secreted extracellular protein. The main functional domain is the 18-239 segment, which includes an N-type glycosylation modification and a disordered structure at the C-terminus.
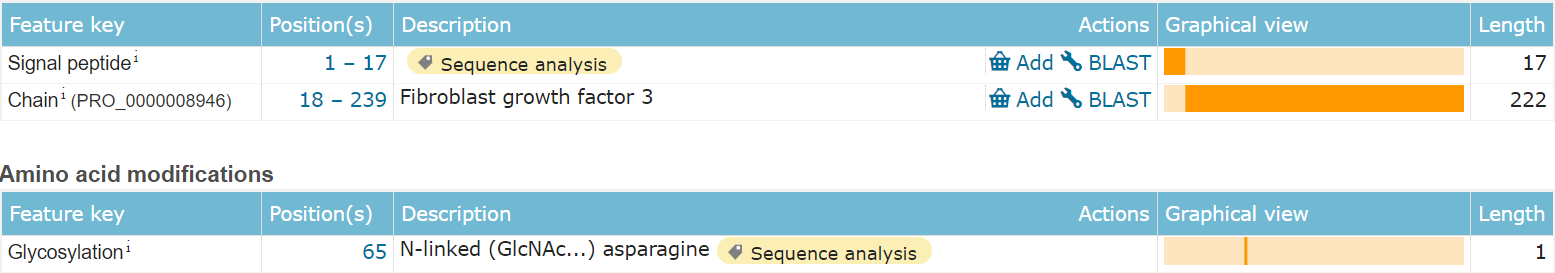
(Data source: Uniprot)
FGF3 exhibits a restricted expression profile and is primarily expressed in the cerebellum. It plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, and cell differentiation, and is required for normal ear development.

(Data source: Protein Atlas)
FGF3 is essential for regulating telencephalon development: within the diencephalon, FGF3 and FGF8 work together to form the ventral thalamus and are involved in the regulation of optic stalk formation, while the absence of FGF3 alone leads to developmental defects of the zona limitina (ZLI) within the thalamus; in the absence of FGF3 or FGF8, forebrain commissure formation is abnormal; however, the most severe forebrain developmental defects are observed in the absence of both.
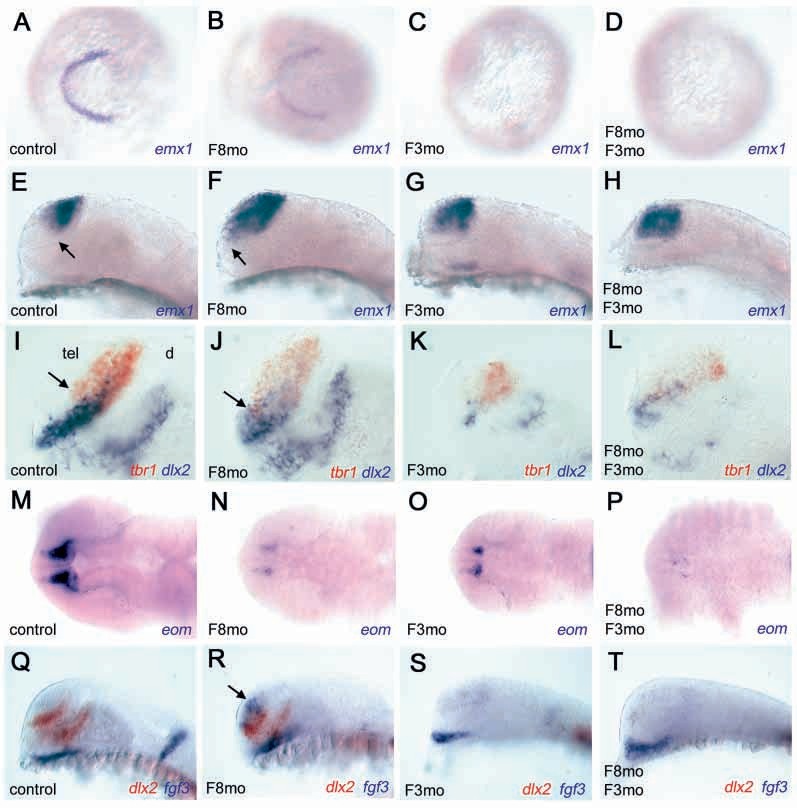
(Data source: Walshe J, et al. Development. 2003)
FGF3 is required for dorsal patterning and morphogenesis of the inner ear epithelium: it is expressed in the hindbrain via endolymphatic duct outgrowth and in the prospective neurosensory domain of the otic epithelium at the onset of morphogenesis. FGF3 prevents the ventral expansion of Wnt3a in the r5-6 neuroectoderm, serving to concentrate inductive WNT signaling on the dorsal otic vesicle, highlighting a novel example of crosstalk between two signaling systems.

(Data source: Hatch EP, et al. Development. 2007)
The above functional characteristics of FGF3 correspond to the clinical results: homozygous mutations in the FGF3 gene can lead to congenital deafness accompanied by inner ear hypoplasia, microtia and microdontia.

(Data source: Tekin M, et al. Clin Genet. 2008)
In addition, the FGF3 & BMP signaling axis can regulate the closure of the caudal neural tube, neural crest specification, and anterior-posterior axis extension: FGF3 is secreted by the mesoderm and negatively regulates the expression of another type of secreted signaling molecule, BMP, in the neuroepithelial cells. In the absence of FGF3, excessive BMP signaling leads to delayed neural tube closure, premature specialization of neural crest cells, and negative effects on the mesoderm, resulting in premature termination of the embryonic axis.
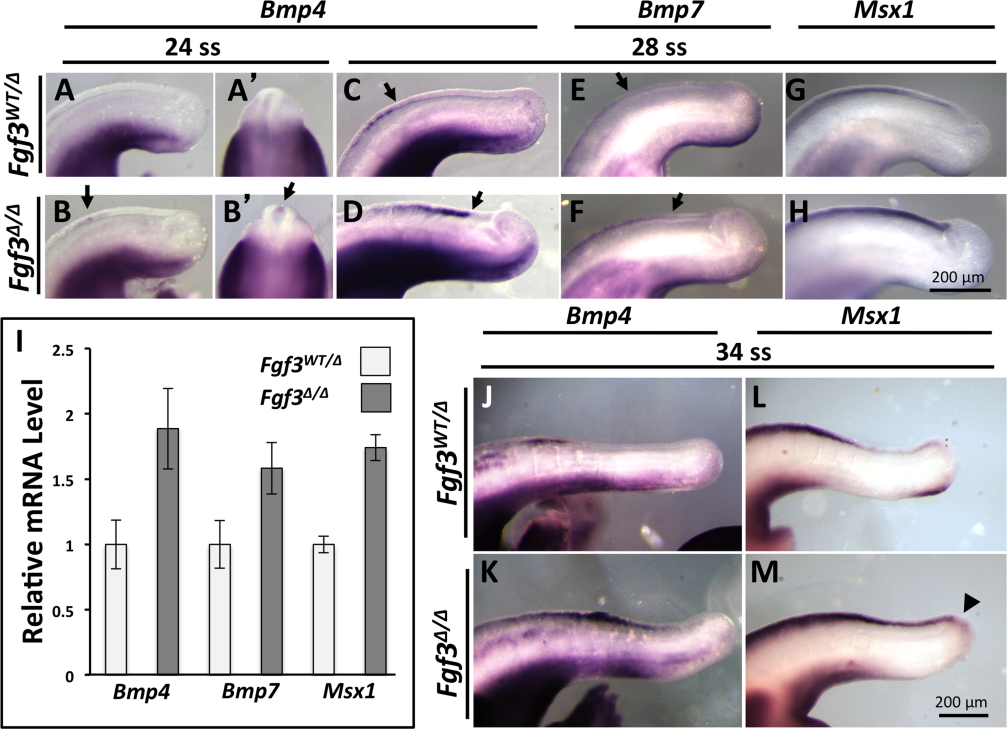
(Data source: Anderson MJ, et al. PLoS Genet. 2016)
Much of the research on FGF3 was completed in the early stages, and the subsequent mechanisms have not been studied in depth. This may also be because it involves the early developmental regulation of the embryo, which makes the research more difficult.
