Fibroblast growth factor 5 (FGF5) was first isolated as a human oncogene in 1988. It belongs to the FGF4 subfamily and has a cleavable N-terminal signal peptide. It mediates the biological response of extracellular proteins by binding and activating fibroblast growth factor receptors 1-4 (FGFR1-4).
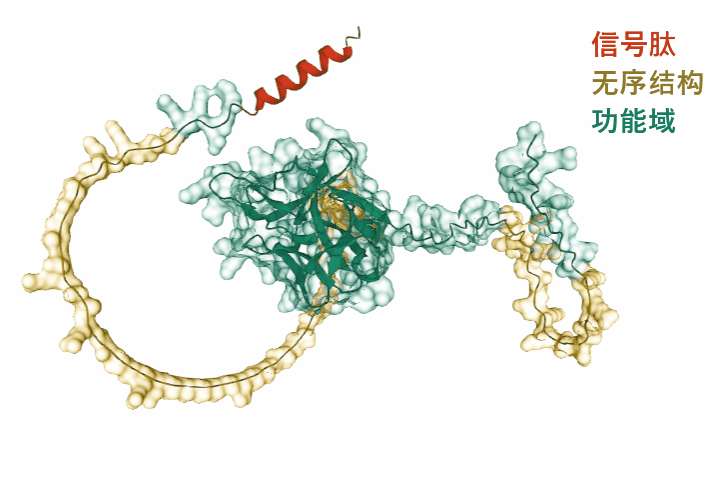
(Data source: AlphaFold)
FGF 5 is composed of 268 amino acids and is a secretory extracellular protein. Its main functional domain is the 21-268 segment, which includes two disordered structures.

(Data source: Uniprot)
FGF5 became well-known in a 1994 Cell study: mice with an FGF5 null allele, generated by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells, exhibited abnormally long hair phenotypes, and demonstrated that FGF5 is localized to the outer root sheath during the growth phase of the hair growth cycle, acting as an inhibitor of hair elongation. Similar results were reported in a 2009 Science study : researchers conducted a genome-wide association study of over 1,000 dogs from 80 domestic breeds and identified different mutations in three genes, RSPO2, FGF5, and KRT71, that were associated with canine coat phenotypes (plus and minus signs indicate the presence or absence of a variant).

(Data source: Cadieu E, et al. Science. 2009)
Subsequently, FGF5 was also shown to be a key regulator in human hair growth regulation: different pathogenic mutations in FGF5 can easily lead to extreme growth phenotypes of human eyelashes, and in hair follicle organ cultures, FGF5 induces the degeneration of human hair follicles.
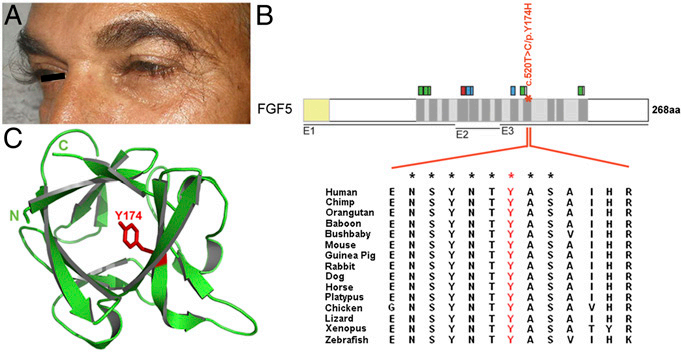
(Data source: Higgins CA, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014)
Genetic variation in FGF5 has been shown to underlie hair length regulation in mice, cats, dogs, and even other species, including donkeys and cashmere goats. Deletion mutations within the FGF5 gene can serve as molecular markers for hair growth in animal breeding. FGF5 also exhibits a high degree of conservation across species.

Recent studies have revealed that the FGF5 and FGFR2 signaling axis plays a role in HER2-targeted therapy resistance and tumor progression: breast cancer cells recruit and activate healthy stromal fibroblasts. Activated fibroblasts produce FGF5, which binds to FGFR2 in cancer cells and transactivates HER2, promoting tumor cell resistance to HER2-targeted therapy. This study has identified FGFR2 and FGF5 as potential therapeutic targets for drug-resistant HER2-positive breast cancer and has identified stromal FGF5 expression as a new prognostic biomarker for HER2-positive patients.
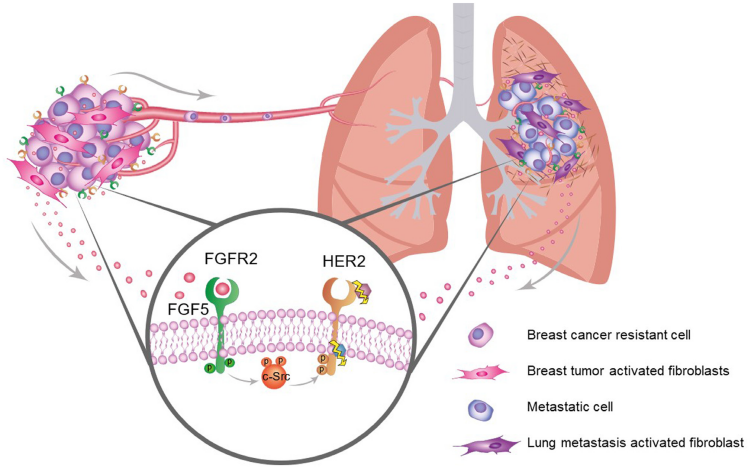
(Data source: Bragado P, et al. Oncotarget. 2020)
Most research on FGF5 has focused on the regulation of mammalian hair phenotype, with limited involvement in tumor-related studies. There are reports that FGF5 is a carcinogen in human glioblastoma multiforme (and its main high-affinity receptor (FGFR1 IIIc) is overexpressed in astrocyte brain tumor specimens and cell cultures). FGF5 methylation can be used as a sensitivity marker for radical chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. However, these studies are largely at the basic level and require further in-depth mechanistic research to achieve breakthroughs.
