Guanylate cyclase (GUCY2C), also known as GUC2C or STAR, is a guanylate cyclase that catalyzes the synthesis of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) from GTP. It is a receptor that plays a central role in regulating intestinal homeostasis and in the development of colorectal cancer, and is a highly promising therapeutic target.
GUCY2C expression distribution
GUCY2C is mainly expressed in the gastrointestinal tract, and is expressed in intestinal endocrine cells, Paneth cells, proximal intestinal epithelial cells, goblet cells, undifferentiated cells, and distal intestinal epithelial cells.
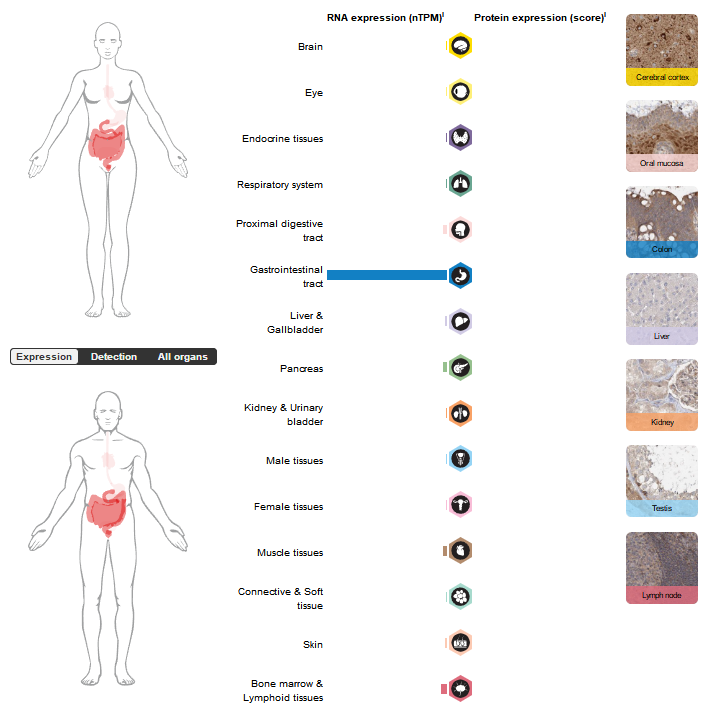

(Data source: uniprot)
The structure of GUCY2C and its receptor
The GUCY2C gene is located in the q12 region of chromosome 12 and encodes a type I transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 120 kDa, composed of an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain. The extracellular domain is responsible for recognizing and binding specific ligands. The transmembrane domain anchors the receptor to the cell membrane. The intracellular domain possesses guanylate cyclase activity and is central to its signal transduction function.

(Data source: Rampuria P, et al. Sci Rep. 2023)
GUCY2C signaling pathways and regulation
Ligand binding to GC-C catalyzes the formation of cGMP from GTP. Increased intracellular cGMP levels lead to cGMP-dependent activation of PKGII. PKGII-mediated inhibition of NHE3 phosphorylation results in reduced intestinal sodium absorption. PKGII phosphorylation and activation of the CFTR anion channel increase in intestinal chloride and water secretion. Increased cGMP activates the CNG ion channel, promoting Ca2+ influx and thereby recruiting CaR to the plasma membrane. cGMP production activates PKGII and p38 MAPK, leading to phosphorylation of the Sp1 transcription factor. Sp1 upregulates p21 expression and mediates cell repression. PKGII-mediated signaling can counteract pro-survival and pro-proliferative phenotypes mediated by the β-catenin/TCF and Akt pathways.
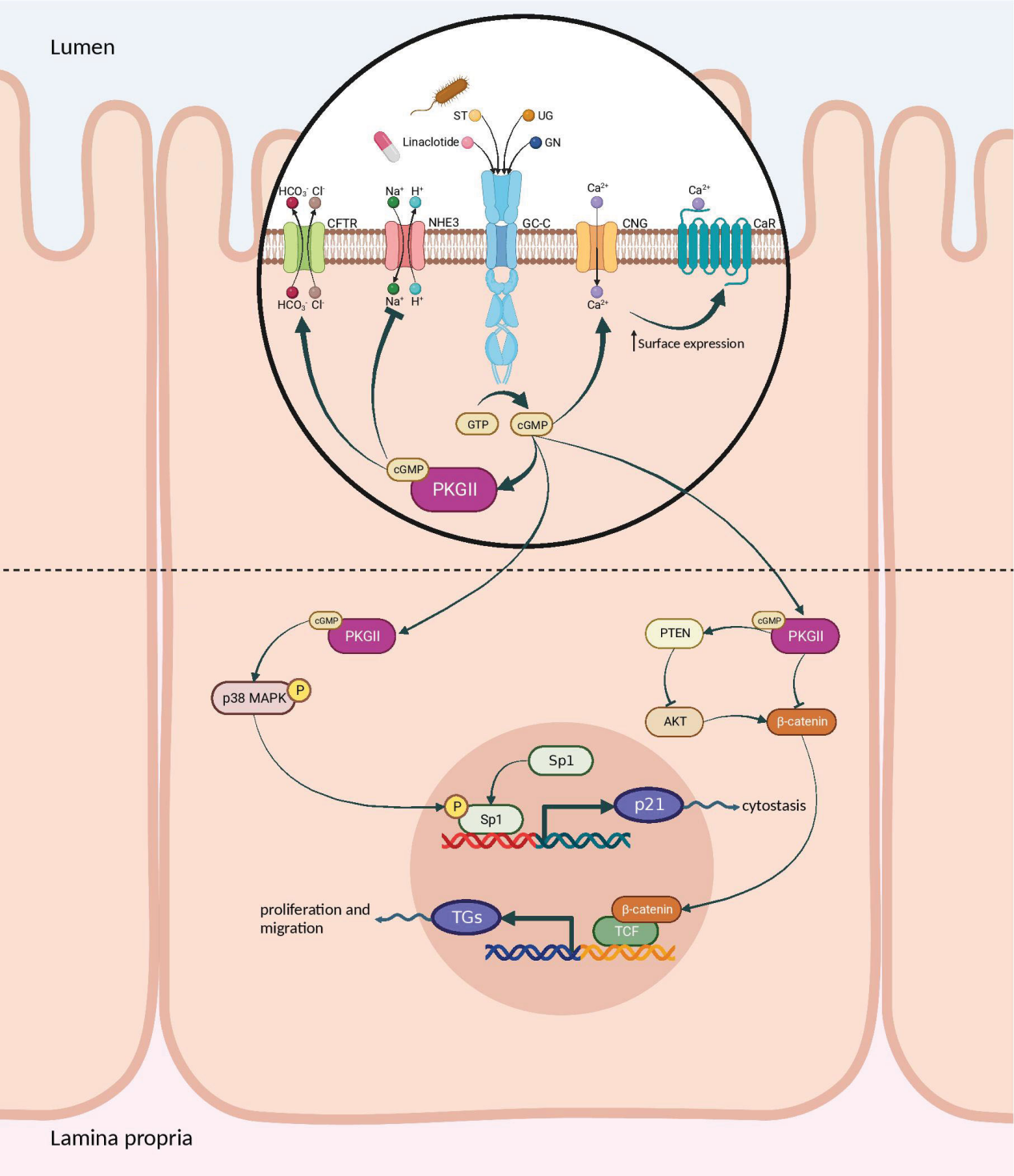
(Data source: Piroozkhah M, et al. Front Oncol. 2023)
Targeted therapy with GUCY2C
Indusatumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting GUCY2C for the treatment of tumors, but its current clinical trial status is unclear.
DXC022 is an antibody-drug conjugate targeting GUCY2C, developed by Hangzhou Duoxi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., for the treatment of solid tumors, and is currently in the preclinical research stage.
HDP-201 is a novel Exatecan-based multimeric connector ADC from Heidelberg Pharma AG, targeting guanylate cyclase C (GCC) for the treatment of gastrointestinal malignancies. It has demonstrated potent antitumor effects in preclinical models, including complete tumor remission in a GCC-expressing CDX model and significant inhibition of tumor growth in a gastrointestinal PDX model. The single intravenous dose is 60 mg/kg. HDP-201 is well-tolerated in Cynomolgus-Affe n, with no signs of serious toxicity.
