IGF1R, also known as the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (CD221), is a type II tyrosine kinase receptor that regulates cell growth and proliferation and is activated by IGF1, IGF2, and insulin. Activated IGF1R is involved in controlling cell growth and survival. IGF1R is crucial for neoplastic transformation and the survival of malignant cells. Dysregulation of IGF1R is associated with human diseases, including growth retardation and cancer.
IGF1R expression distribution
IGF1R is primarily expressed in glandular epithelial cells, oligodendrocytes, microglia, excitatory neurons, oligodendrocyte precursor cells, and inhibitory neurons. IGF1R is also expressed to a lesser extent in immune cells such as T cells and B cells.
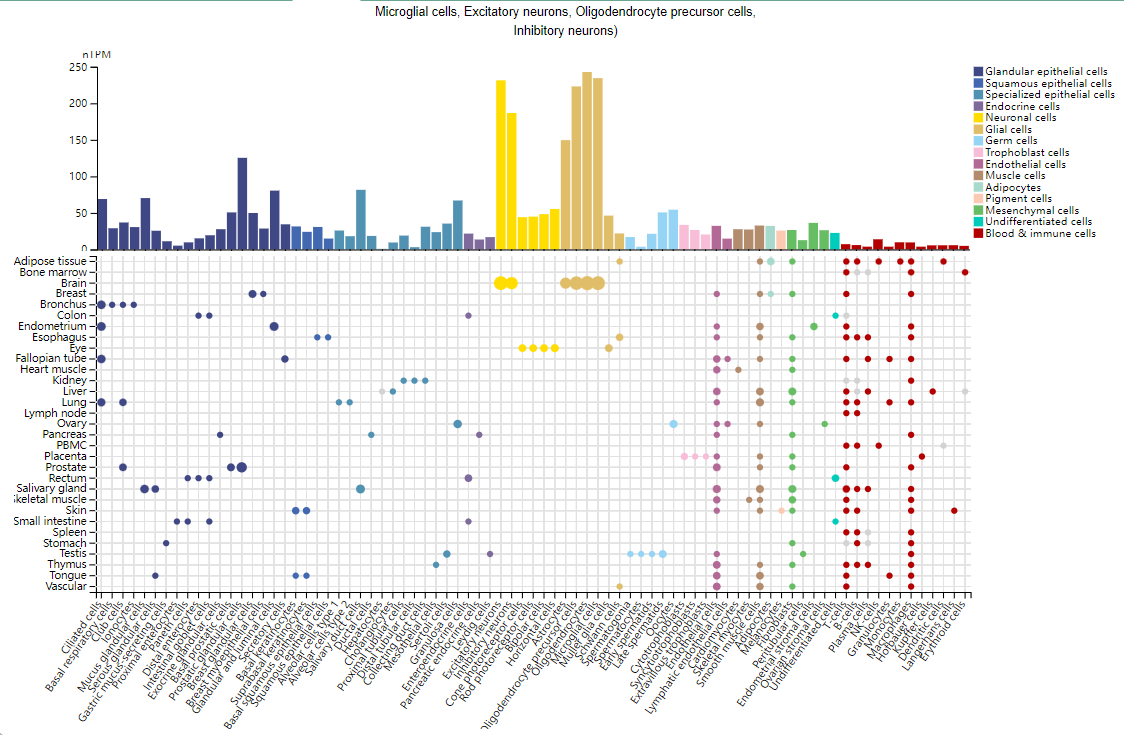
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of IGF1R and its receptor
IGF1R is a type I membrane protein composed of 1,367 amino acids. It is closely related to the insulin receptor (IR), sharing 57% sequence identity and high structural similarity. The active state of IGF1R exists as a dimer. Each IGF1R and IR protomer consists of L1, CR, L2, FnIII-1, -2, -3, a transmembrane (TM), and a kinase domain. The IGF1 binding site is formed by the L1 and CR domain (CRD) of one IGF1R subunit and the α-CT' and FnIII-1' domains of the other subunit. The overall structure of the IGF1R-IGF1 complex is an asymmetric Γ shape, with only one IGF1 molecule bound to the IGF1R dimer; it is located at the top of the Γ . Binding of one IGF1 molecule to the IGF1R dimer hinders the binding of the second IGF1 molecule (i.e., negative cooperativity).

(Data source: Li J, et al. Nat Commun. 2019)
IGF1R signaling pathway and regulation:
IGF1R is activated upon interaction with IGF1, which recruits multiple docking or adaptor proteins to activate downstream signal transduction pathways, including the PI3K, MAPK, and JAK/STT signaling pathways, which are involved in cancer cell proliferation and survival as well as immune regulation.
The recruitment and phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrates (IRS) are mediated by IGF1R, leading to the activation of different PI3K isoforms, including α, β, γ, and δ isoforms, as well as their downstream signaling pathways. All of these PI3K isoforms promote tumor cell survival, proliferation, and metastasis by regulating different processes, including tumor cell metabolism, angiogenesis, and regulation of the TME and immunity through activation of the AKT/mTOR and GSK3β/β-catenin pathways.
SHC domain proteins are mainly involved in the activation of BRAF/MAPK and JAK/STATs signaling pathways, both of which are important regulators of tumor progression and immune regulation.
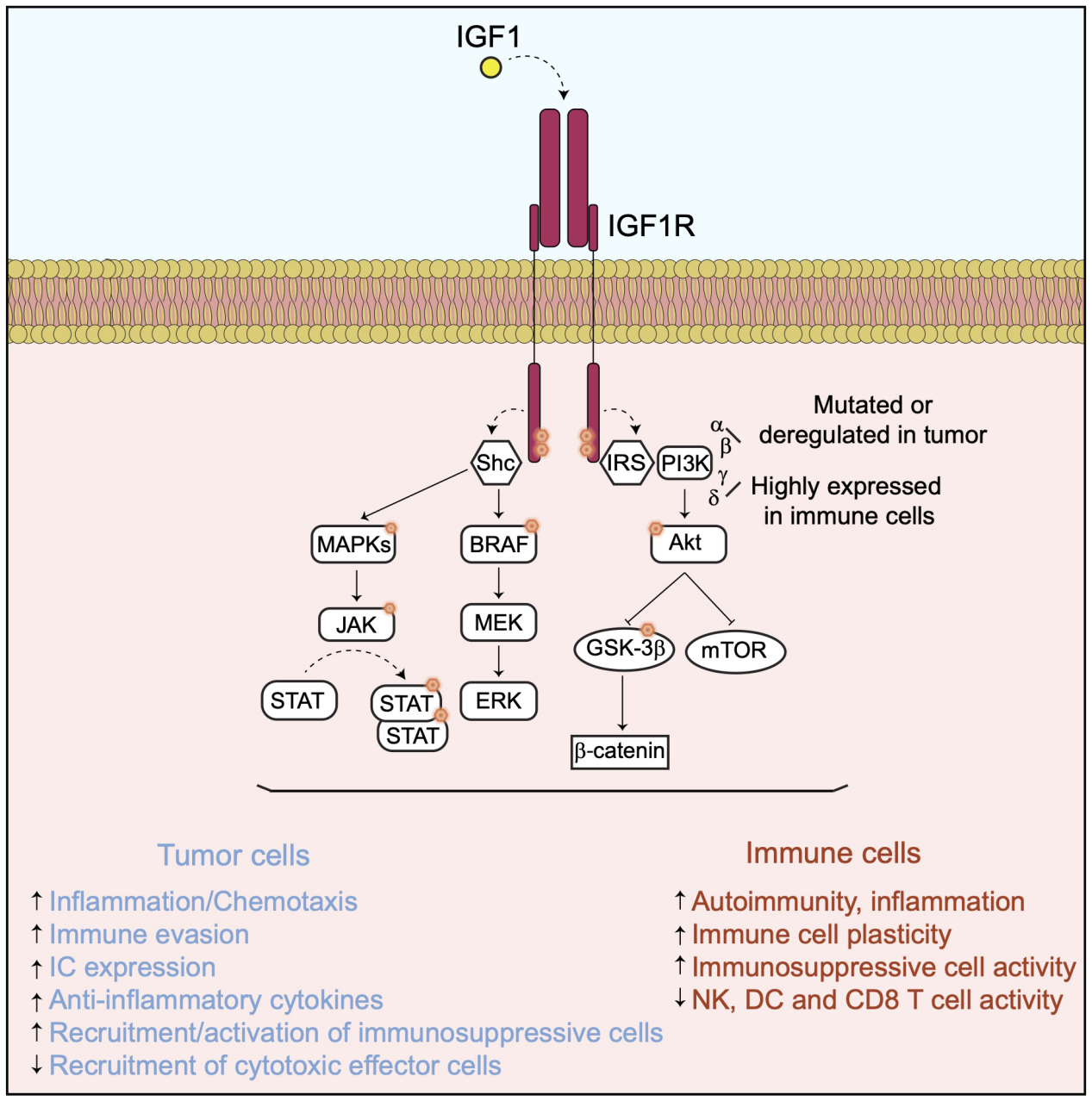
(Data source: Pellegrino M, et al. Front Immunol. 2024)
IGF1R -targeted therapy
In cancer, several strategies targeting IGF1R have been developed, such as small molecule drugs, monoclonal antibodies targeting IGF1R, and bispecific antibodies.
Teprotumumab-TRBW is a monoclonal antibody targeting IGF1R that was approved for marketing in 2020 for the treatment of Graves' ophthalmopathy and Ewing sarcoma .
Veligrotug (VRDN 001) is an antibody targeting IGF1R. On December 16, 2024, Viridian Therapeutics announced that Veligrotug achieved positive primary results in the THRIVE-2 Phase III clinical trial in patients with chronic thyroid eye disease (TED). Veligrotug significantly reduced symptoms such as diplopia and proptosis in TED patients.
Another IGF1R-targeting drug from Viridian Therapeutics is VRDN-003, which is currently in Phase 3 clinical trials. VRDN-003 is an iterative, long-acting IGF-1R antibody with an extended dosing cycle of once every four or eight weeks. It also features a lower dose and uses an automatic injector, taking less than half a minute to administer.
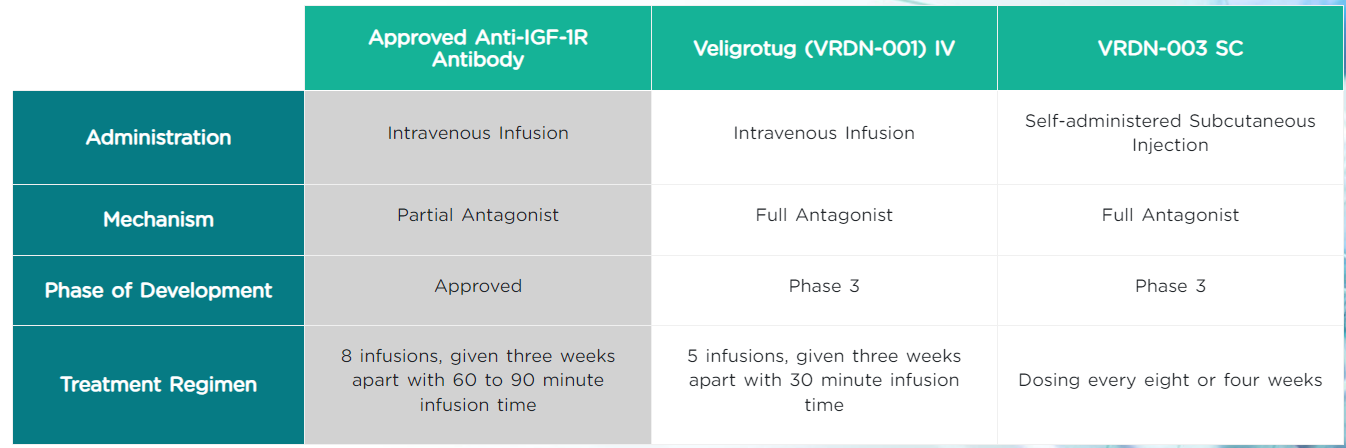
(Data source: Viridian Therapeutics official website)
Lonegutamab, with its unique mechanism of action, has become the first subcutaneous anti-IGF-1R drug to demonstrate robust efficacy comparable to standard intravenous therapy in patients with TED. Recently released Phase II TED clinical trial data showed clinically meaningful and competitive improvements across all manifestations of thyroid eye disease (TED), with significant response rates for proptosis demonstrated using a 50 mg loading dose and a 25 mg weekly (QW) subcutaneous dose of lonigutamab. This efficacy was achieved at lower exposure levels compared to intravenous anti-IGF-1R drugs.
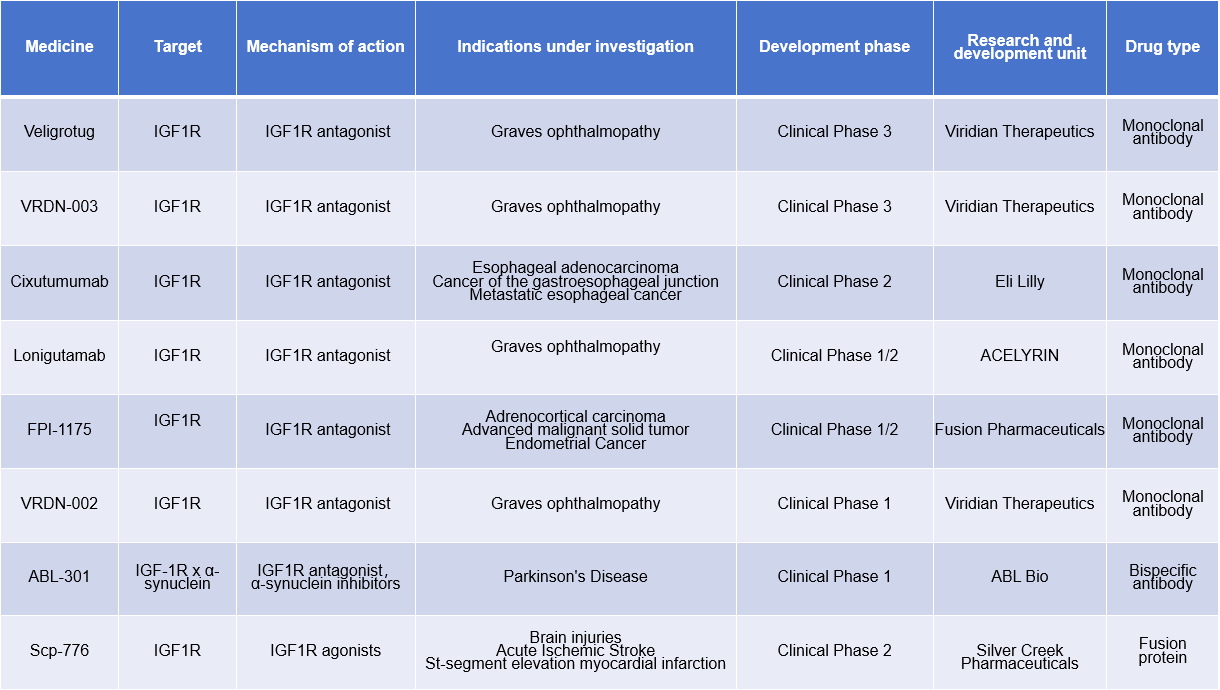
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
