Cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6), also known as CD66c or NCA-90, is a cell surface glycoprotein that plays a role in cell adhesion and tumor progression. CEACAM6 is commonly upregulated in pancreatic, breast, non-small cell lung, gastric, colon, and other cancers and promotes tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis. CEACAM6 may be a valuable diagnostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for human cancers in which CEACAM6 is overexpressed.
(Data source: Johnson B, et al. Clin Cancer Drugs. 2015)
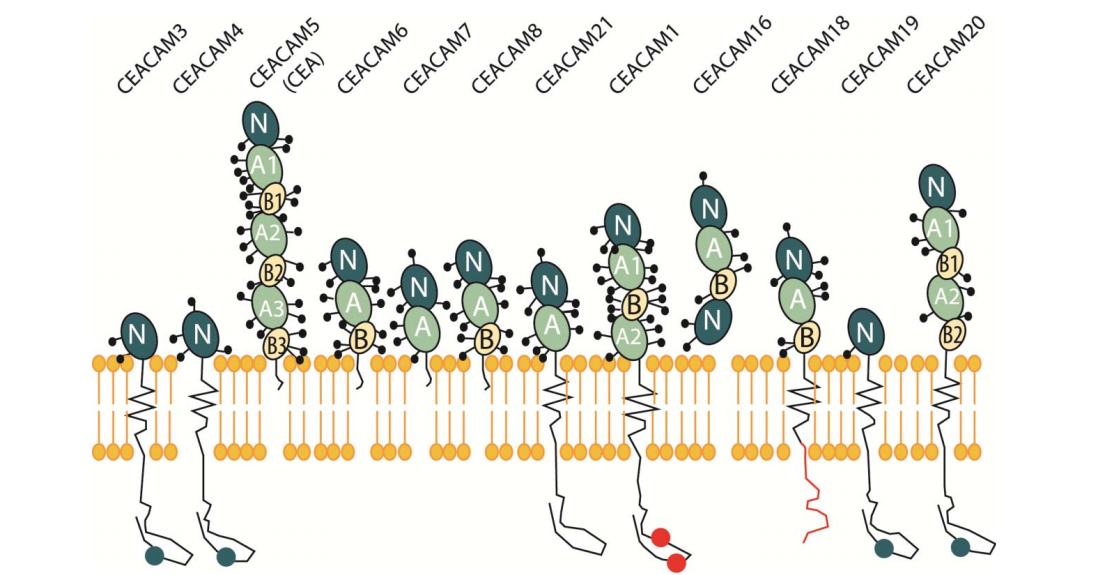
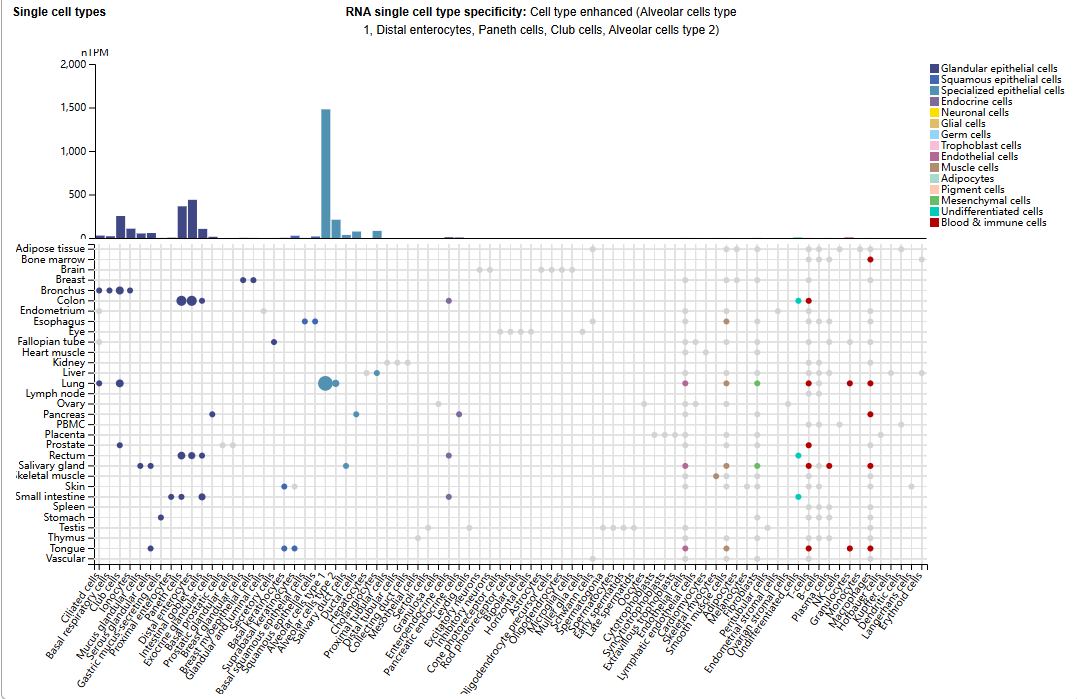
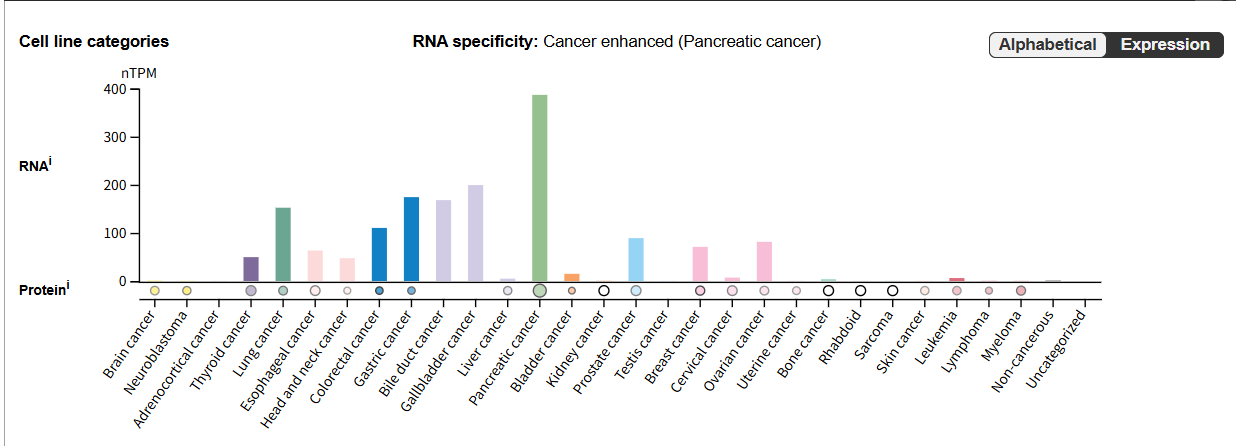
Expression distribution of CEACAM6
CEACAM6 is expressed in neutrophils, type 1 alveolar cells, Paneth cells, goblet epithelium and goblet cells of the colon, and in many tumor cell lines, such as pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, gastric cancer, colon cancer, extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma, intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma, etc.
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of CEACAM6 and its receptor
CEACAM6 is located at locus 19q13.2 in the human genome. The coding region consists of six exons and 344 amino acids. CEACAM6 includes an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain, two N-terminal IgC-like domains, and a membrane-bound glycoprotein. The extracellular N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain is required for homophilic and heterophilic cell adhesion. CEACAM6 is anchored to the cell surface via the transmembrane domain of the membrane-bound glycoprotein. α-1,6 - mannosyl glycosylopeptide 6-β-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase promotes N-glycosylation at Asn256 of CEACAM6 . CEACAM6 can form homodimers or heterodimers with CEACAM8 through homodimerization of its Ig-like V-type domain.

(Data source: uniprot)
Signaling pathway and regulation of CEACAM6
Upstream of the CEACAM6 signaling pathway, CD151 promotes SMAD3 phosphorylation through TGF-β1. This leads to SMAD3 phosphorylation, which in turn promotes CEACAM6 transcription. On the other hand, miR-146, miR-26a, miR-29a/b/c, miR-128, and miR-1256 inhibit CEACAM6 transcription. CEACAM6 transcriptional expression is also regulated by promoter DNA methylation. Furthermore, MGAT5 promotes N-glycosylation of CEACAM6 at Asn256. Downstream of the CEACAM6 signaling pathway, CEACAM6 promotes tumor proliferation by increasing cyclin D1 and CDK4 protein levels. CEACAM6 stimulates tumor proliferation, invasion, migration, resistance to anaesthetics and chemotherapy, and angiogenesis by directly or indirectly activating the EGFR, ERK1/2/MAPK, or SRC/FAK/PI3K/AKT pathways.

(Data source: Wu G, et al. Int J Oncol. 2024)
CEACAM6-targeted therapy
CEACAM6 has been identified as a highly specific marker for aggressive cancers and shows great potential as an effective cancer therapy target. Antibodies targeting CEACAM6 have demonstrated significant therapeutic effects in numerous tumors, including directly blocking intracellular signaling, reducing drug resistance, and promoting drug accumulation in tumor cells. Numerous antibodies are currently in clinical development.
BAY1834942 is a monoclonal antibody targeting CEACAM6. NCT03596372 is an open-label, Phase 1, first-in-human study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tumor response characteristics of BAY1834942 in patients with advanced solid tumors.
NEO-201, an antibody targeting CEACAM5 and CEACAM6, is being developed by Precision Biologics and is in Phase 1/2 clinical development. A patent granted by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) on July 16, 2024, describes NEO-201's ability to bind to regulatory T cells (Tregs) and its use for targeting Tregs. NEO-201 can be used to isolate and detect Tregs and can mediate Treg cell killing in vitro through complement-mediated cytotoxicity (CDC). NEO-201 can be used in combination with another anticancer agent. In a Phase 1 clinical trial, NEO-201 was used as a monotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors that had progressed or not responded to standard therapy. NEO-201 was shown to bind to and reduce the number of circulating Tregs in patients with stable disease after treatment . NCT03476681 is an expansion cohort Phase 1/2 study of NEO-201 in adults with chemotherapy-resistant solid tumors.
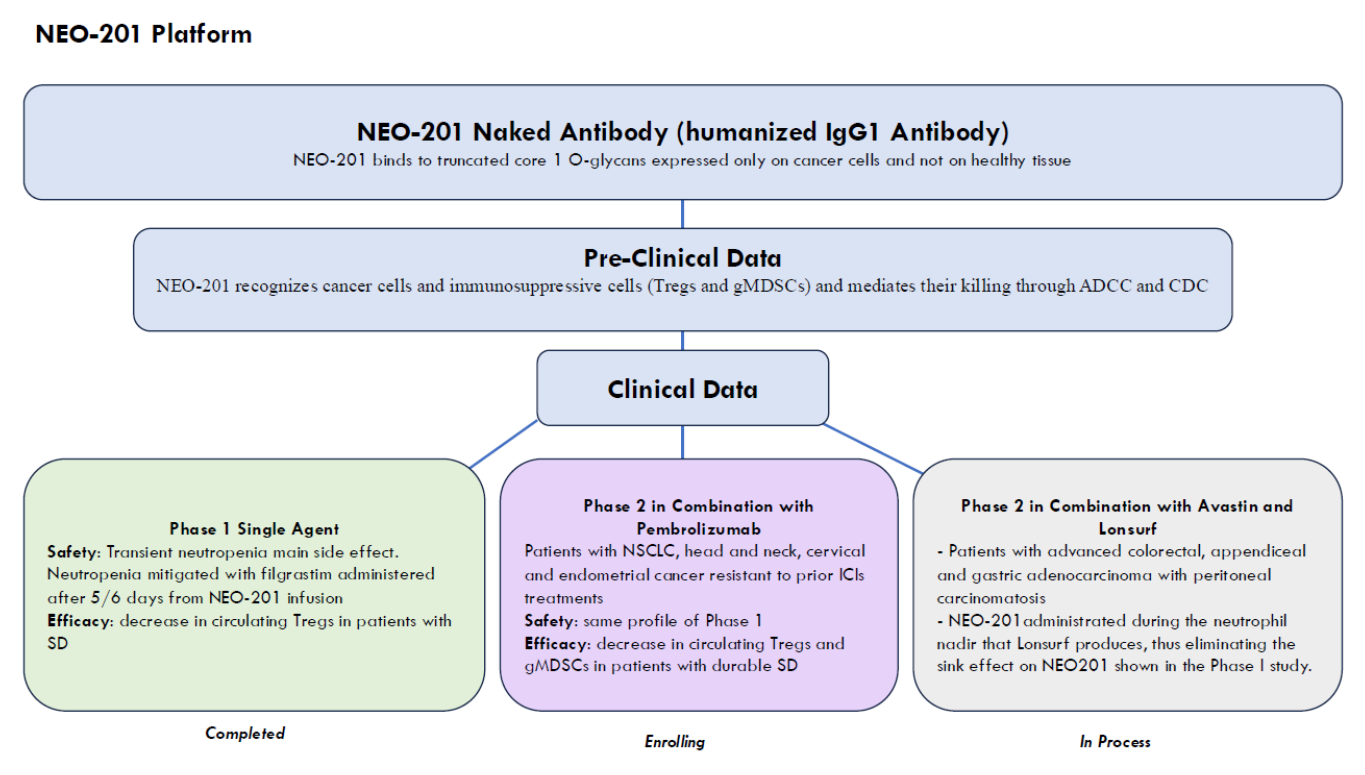
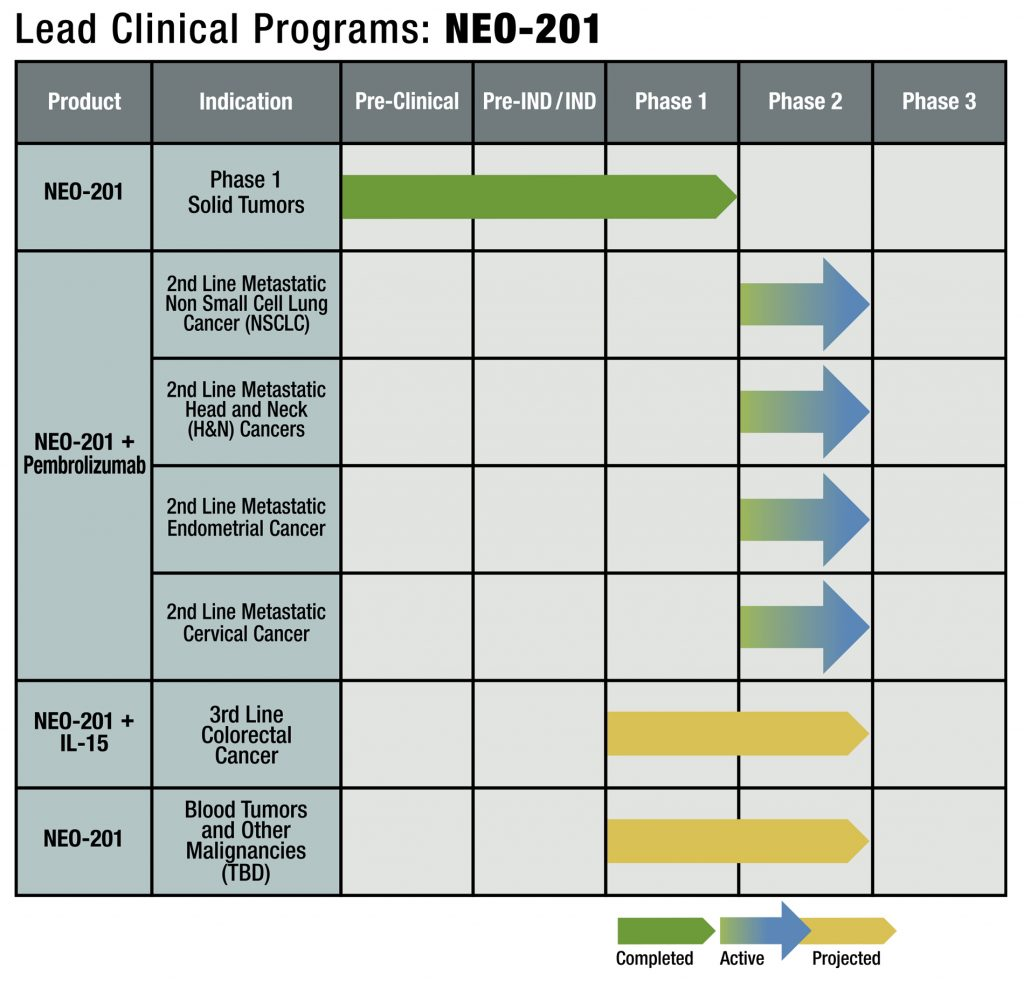
(Data source: precision-biologics official website)
EBC-129 is the first Singapore-made antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) to enter clinical development. It selectively targets tumor-specific N-glycosylated epitopes on CEACAM5 and CEACAM6. The FDA has granted EBC-129 Fast Track designation for the treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). An ongoing Phase 1 trial of EBC -129 is evaluating its safety and tolerability as a single agent and in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors. Enrollment in the PDAC cohort of the Phase 1 dose-expansion study is now complete, while enrollment in the gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma (GEA) and IHC-positive cohorts is ongoing.
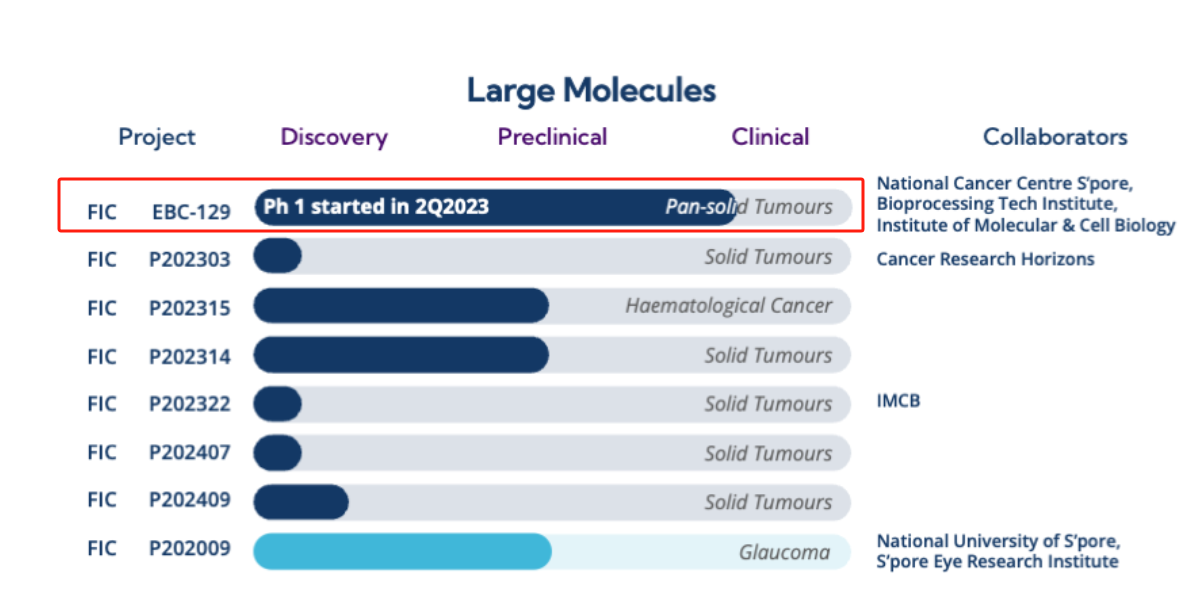
(Data source: EDDC official website)
