OLR1 is a receptor that mediates the recognition, internalization, and degradation of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) by vascular endothelial cells. Besides binding to oxLDL, it also acts as a receptor for HSP70 protein, participating in the process of antigen cross-presentation from dendritic cells to naive T cells, thus participating in cell-mediated antigen cross-presentation. It also participates in inflammatory processes, acting as a leukocyte adhesion molecule at the vascular interface in endotoxin-induced inflammation. OLR1 is associated with atherosclerotic events such as myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke, particularly the incidence of ischemic stroke.

(Data source: Akhmedov A, et al. Eur Heart J. 2021)
OLR1 expression distribution
OLR1 is highly expressed in endothelial cells and vascularized organs such as the placenta, lungs, liver, brain, aortic intima, bone marrow, spinal cord, and substantia nigra. It is also expressed in monocytes, trophoblasts, glial cells, neutrophils, and dendritic cells.

(Data source: uniprot)
Structure of OLR1 and its receptor
OLR1 is a 50 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein (52 kDa after glycosylation). LOX-1 belongs to the C-type lectin superfamily and is composed of 273 amino acids . OLR1 contains an extracellular coiled-coil domain (NECK), a transmembrane domain (TM), and an intracellular cytoplasmic region or C-terminal lectin-like domain (CTDL).
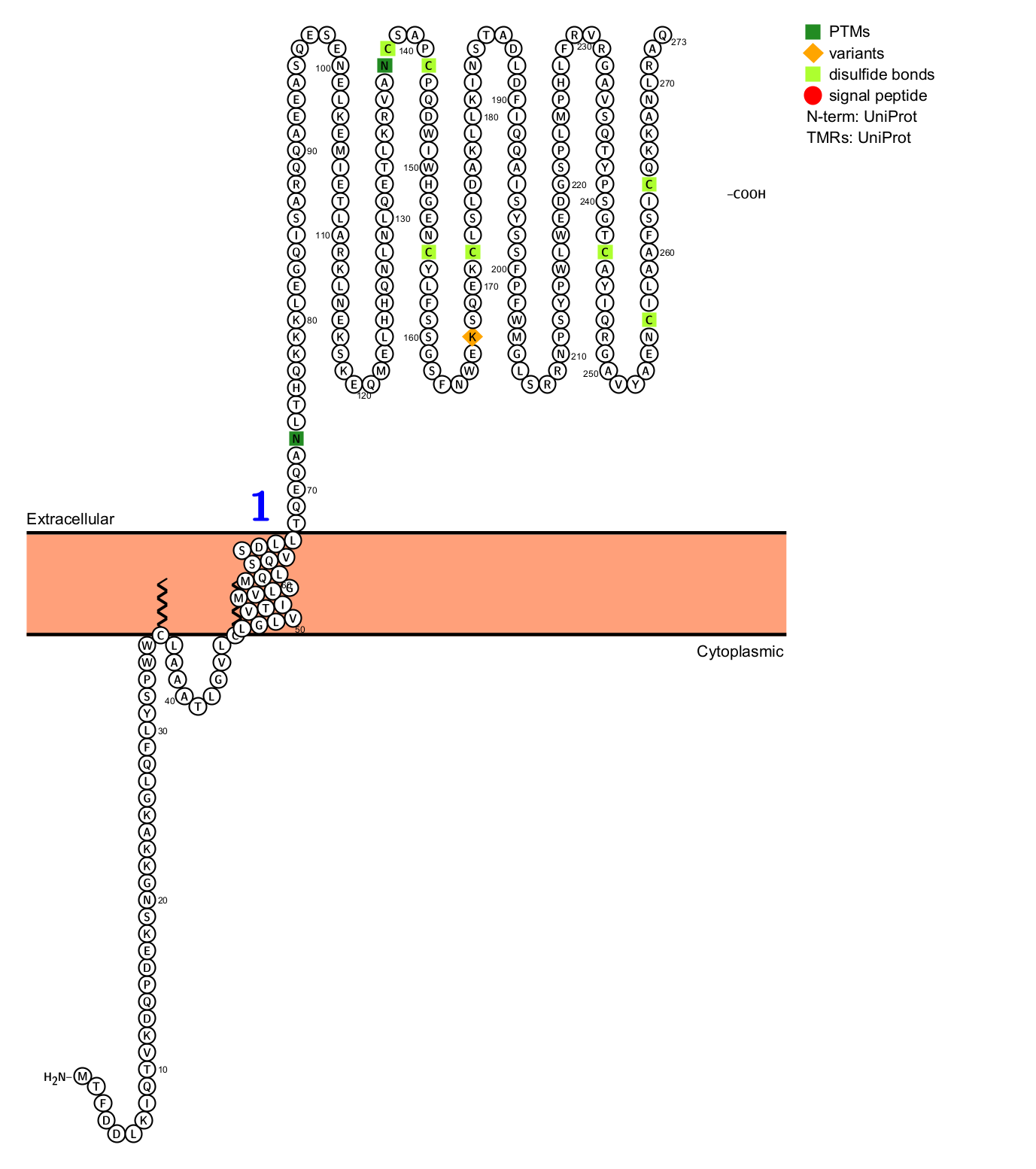
(Data source: uniprot)
OLR1 signaling pathway and regulation
Ox-LDL binding to LOX-1 can increase ROS production and decrease NO release, and can also activate the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β cascade. Activation of these two pathways leads to the triggering of transcription factors associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT-TFs) and NF-κB. Reduced NO release can also activate inflammatory signaling (IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β). The end result is activation of hypoxia pathways (VEGF , HIF-1α) and enhanced expression of mesenchymal markers (MMP-2 and MMP-9). The outcomes of these processes determine cell transformation, angiogenesis, and EMT.
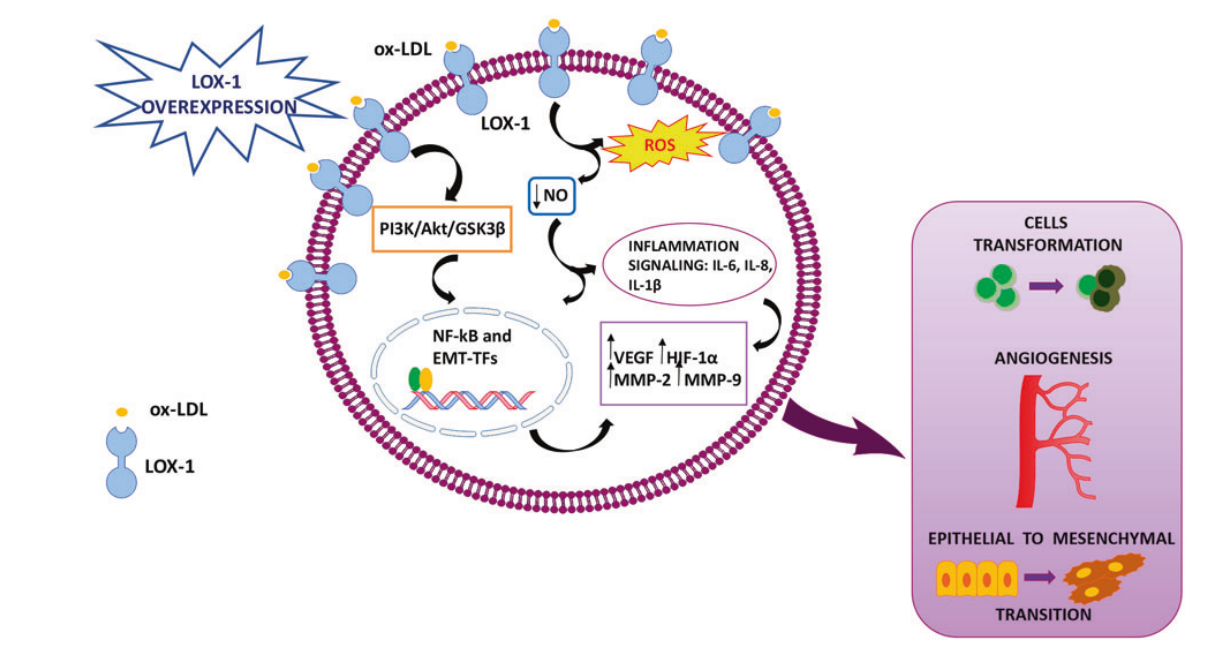
(Data source: Murdocca M, Cancer Gene Ther. 2021)
OLR1 targeted therapy
Golocdacimab (MEDI-6570) is a monoclonal antibody targeting OLR1, developed by MedImmune LLC, for the treatment of coronary artery disease, inflammation, and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. It is currently in Phase II clinical trials. NCT04610892 is a Phase IIB parallel-group study evaluating the efficacy and safety of MEDI6570 in patients with prior myocardial infarction.
