Since the first report of monoclonal antibody (mAb) development using hybridoma cell lines in 1975, the development of therapeutic antibodies, detection antibodies, and diagnostic antibodies has flourished rapidly. Antibodies are indispensable tools for a wide range of applications in basic and translational bioscience research. However, the use of traditional hybridoma antibodies or polyclonal antibodies produced in animals has numerous drawbacks.
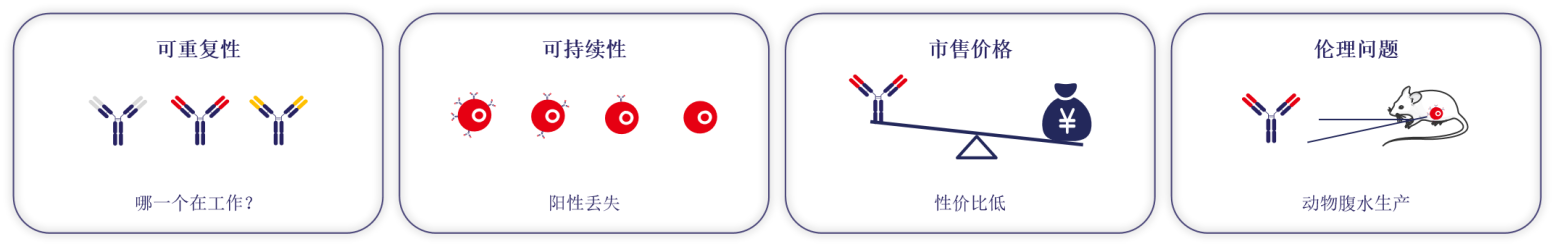
Reproducibility: Due to the lack of standardized and well-defined antibodies, in many cases antibodies are incompletely characterized, not confirmed at the molecular level, and exhibit variability in performance across batches;
Sustainability: The continued availability of traditionally produced antibodies cannot be guaranteed, as the quality of such antibodies depends on stability in maintenance and storage, or on continued production in animals;
Commercial price: For many researchers, the cost of traditional commercially available antibodies is too high, which severely limits research innovation;
Ethical issues: Large numbers of vertebrates are used to generate traditional antibodies for biomedical research.
To address these issues, researchers are constantly developing practical methods and tools. With the development of antibody mass spectrometry sequencing and hybridoma sequencing, combined with advances in host cell production and purification process technologies, the expression and manufacturing of recombinant antibodies is also moving forward. Improvements in expression hosts, expression vectors, cell culture media, and production and purification processes have increased antibody expression levels to hundreds of milligrams per liter or even grams per liter. Recombinant antibodies avoid many of the problems listed above with traditional antibodies: first, recombinant antibodies produced using an unchanging amino acid sequence improve reproducibility; second, recombinant antibodies can be used permanently after the sequence is determined; and third, recombinant antibodies can be mass-produced using low-cost expression and purification systems.

(Recombinant monoclonal antibody preparation process)
Antibody sequence analysis:
By obtaining antibody sequence information and combining it with software and data-based analysis of the antibody library, the specific amino acid sequence information of the antibody variable region can be clarified (to facilitate subsequent antibody backbone design).
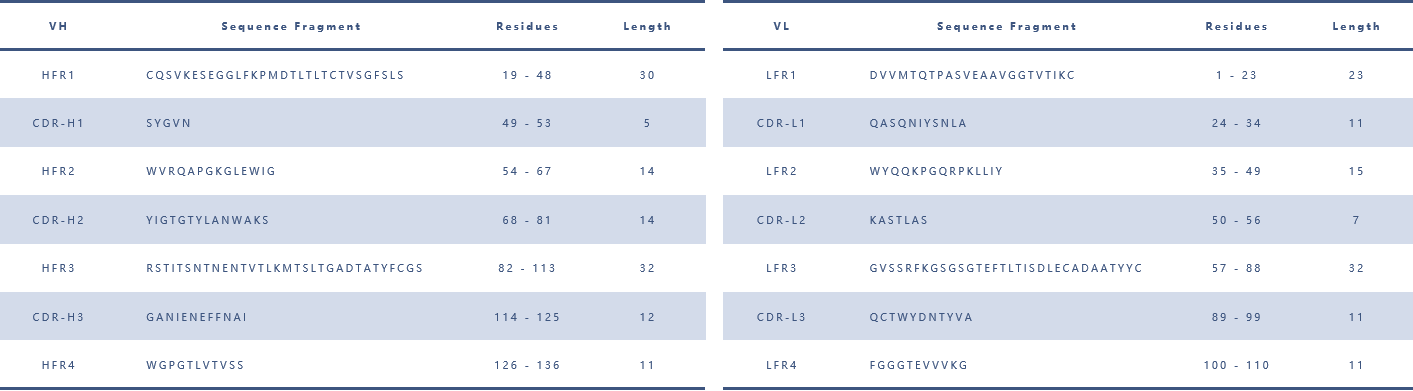
(Antibody heavy and light chain variable region framework examples)
Antibody expression vector construction:
Based on the variable region sequence information and combined with the customer's specific antibody type and framework subtype requirements, expression vectors with different antibody structures are constructed.
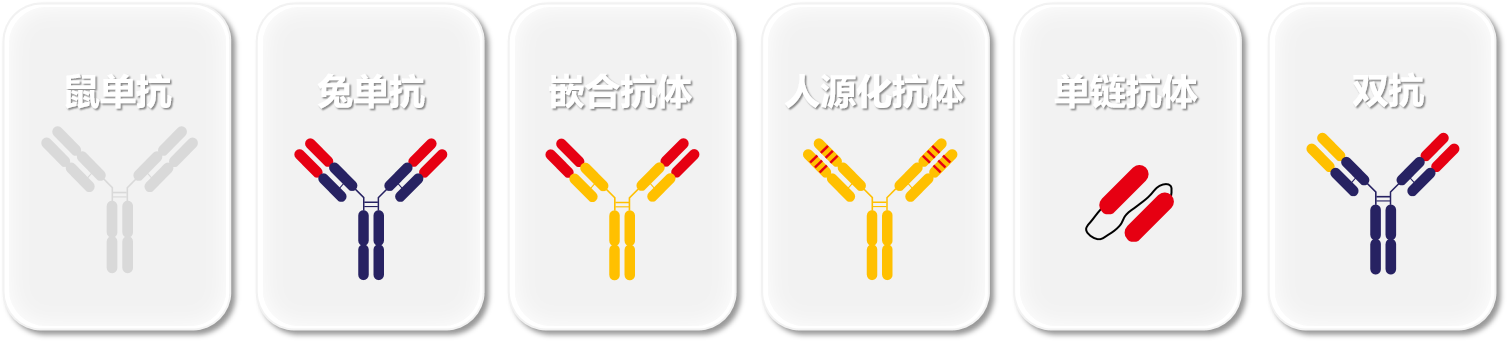
(Examples of different types of antibody backbones)
Antibody recombinant expression verification:
Relying on the mammalian cell recombinant expression platform, we produce and prepare expression systems such as 80ml, 1L, 5L, and 10L according to different demand volumes, and simultaneously perform corresponding purification and verification to obtain high-purity specific recombinant antibodies.

(Example of expression process)
Wuhan Mabnus Biotechnology Co., Ltd. has developed practical methods and tools based on the mammalian cell recombinant expression platform, which can develop and prepare a variety of recombinant monoclonal antibodies based on the original antibody sequence, achieving low-cost and high-yield delivery.
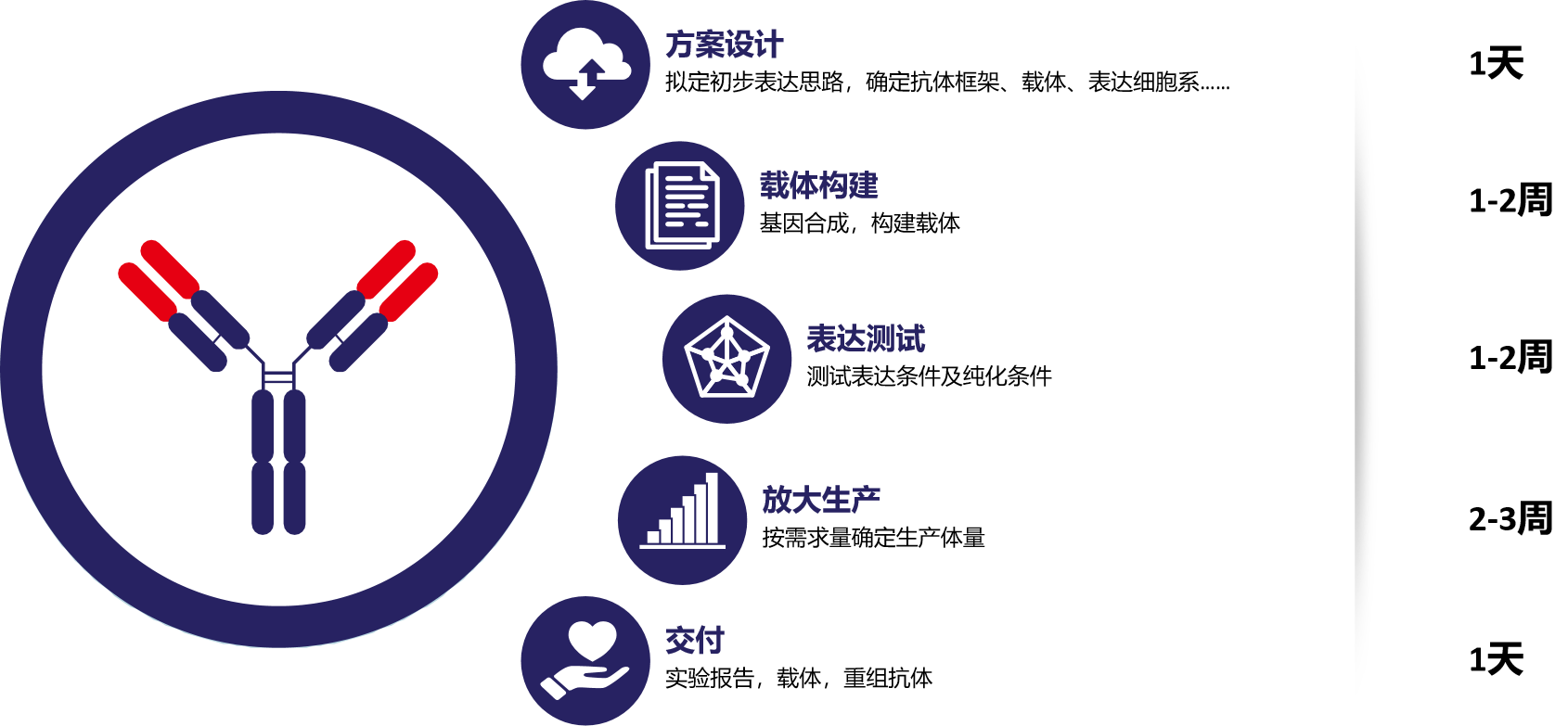
(Service Content)
