CD40 is a co-stimulatory receptor molecule, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 (TNFRSF5), whose ligand is CD40L. The CD40-CD40L interaction plays a key role in activating anti-tumor immune responses, making CD40 agonists a promising target for cancer immunotherapy.
Distribution of CD40
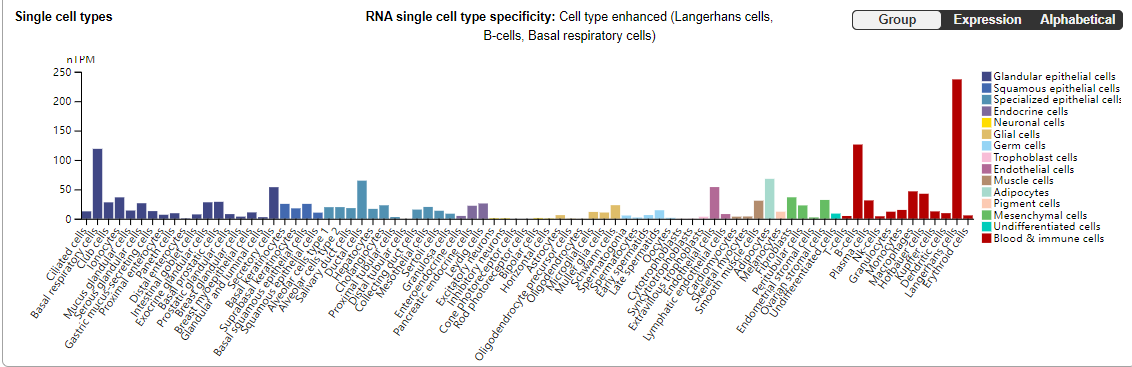
CD40 is mainly expressed in B lymphocytes, dendritic cells (DC), monocytes, and Langerhans cells, and plays an important role in connecting innate immunity and adaptive immunity.
(Data source: uniprot)
Molecular structure of the CD40/CD40L checkpoint
CD40 is a 48 kDa type I transmembrane protein composed of 193 amino acids. Its structure is divided into extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular domains. Its ligand, CD40L, is a type II transmembrane protein whose extracellular structure facilitates the characteristic trimerization of TNF superfamily members. CD40 exists in two forms: membrane CD40 (mCD40) and soluble CD40 (sCD40). A portion of mCD40 and sCD40 self-assemble into non-covalent homodimers via CRD1 in the extracellular domain.

(Data source: Tang T, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 2021)
CD40/CD40L signaling pathway and regulation:
CD40 signaling primarily utilizes an adaptor protein called TNF receptor-associated factor, thereby activating multiple downstream signaling pathways, including the canonical and non-canonical NFκB pathways, the MAPK pathway, the PI3K pathway, and the JAK3/STAT5 pathway. These signaling pathways trigger diverse biological responses in different cell types, such as promoting the activation, proliferation, and differentiation of B cells and dendritic cells, or inducing apoptosis in certain cells.

(Data source: Zhou Y, et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024.)
CD40/CD40L activation in immune cells
Dendritic cells (DCs): CD40 activation promotes the production of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in immature DCs. CD40 activation also upregulates the expression of costimulatory molecules (such as CD80 and CD86) and adhesion molecules (such as CD54 and CD58). Costimulatory signals can "authorize" DCs to present exogenous antigens in the context of MHC-I molecules, thereby cross-presenting them to CD8+ T cells.
Promotes B cell activation and differentiation: The binding of CD40L to CD40 is essential for B cell proliferation, differentiation, high-affinity antibody production, isotype switching, memory responses, and co-stimulatory activity. The CD40/CD40L interaction between T cells and B cells also promotes the co-stimulatory activity of B cells, which then act as competent antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to prime T cells.
Activation of myeloid cells (such as monocytes and macrophages): CD40/CD40L interactions regulate the differentiation, co-stimulatory activity, cytokine production, and antimicrobial activity of monocytes and macrophages.
Enhanced T cell activation: CD40/CD40L interaction regulates Th1 differentiation. CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activation and memory CTL maintenance provide an amplification loop in the immune response through a two-way dialogue between T cells and APCs.
Platelet activation: CD40/CD40L interaction regulates platelet activation and platelet-leukocyte aggregation, and this interaction plays an important role in thrombosis and tissue inflammation.
Regulating tumor cell growth and apoptosis: CD40/CD40L interaction can promote cell proliferation in certain malignant tumor cells, but can also induce cell apoptosis.

(Data source: Zhou Y, et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024.)
CD40 targeted therapy strategies and mechanisms
CD40 agonist therapy:
1. Agonist CD40 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), such as CP-870 and 893, bind to CD40 to enhance CD40/CD40L signaling, thereby activating immune cells. Currently, there are many agonist CD40 mAbs in clinical trials, along with other treatments (such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immune checkpoint blockade, and other immunomodulatory approaches).


(Data source: Zhou Y, et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024.)
2. Gene therapy: Use adenovirus carrying the CD40L gene (Ad-CD40L) or plasmid/messenger RNA electroporation technology to increase CD40L expression and thereby enhance CD40 signaling.
3. Trimeric soluble CD40L: Using trimeric soluble CD40L (such as Avrend) to mimic the natural structure of CD40L and enhance binding to CD40.
CD40 antagonist therapy:
1. Antagonist monoclonal antibodies: Antagonist CD40 monoclonal antibodies, such as Ch5D12 and Bleselumab, are used to block the CD40/CD40L interaction.
2. CD40L antagonists: Use specific CD40L antagonists to block the binding of CD40L to CD40.

(Data source: Tang T, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 2021)
