Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a homodimeric vasoactive glycoprotein and a key mediator of angiogenesis. The VEGF family consists of five separate gene products: VEGF-A, VEGF-B, and placental growth factor (PIGF), which are key regulators of vascular growth; and VEGF-C and VEGF-D, which regulate lymphangiogenesis. VEGF-A binds with high affinity to two VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases (VEGFR1 and VEGFR2) . VEGFRs are involved in regulating vascular permeability, a key property of blood vessels in health and disease.

(Data source: Shaik F, et al. Biomolecules. 2020)
VEGFA expression and function
VEGFA is widely expressed in many cells, mainly in granulocytes, Langerhans cells, alveolar cell type 1, glandular epithelial cells, and specialized epithelial cells.

(Data source: Uniprot)
Cardiac myocytes are the primary source and target of VEGFA and express its receptors, VEGFR1 and VEGFR2, on their cell surface. Various stimuli, including inflammation, mechanical stress, endothelin-1, and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), induce CMs to produce and release VEGF-A, which functions to promote angiogenesis in myocardial tissue. CMs are also targets of VEGF-A, which is produced by various cell types and activates during cardiac injury by binding to surface-expressed VEGFR1 and VEGFR2. VEGF-A-induced cardiomyocyte activation enhances cardiomyocyte survival, contractility, cardiac stem cell recruitment, myocardial angiogenesis, and reduces potassium currents (IKs).

(Data source: Braile M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020)
The structure of VEGFA
The VEGF-A gene locus is located on chromosome 6p21.1 and contains eight exons and seven introns. Alternative splicing of VEGFA produces multiple protein isoforms, such as VEGF-A 121, VEGF-A 165
VEGF-A 189.

(Data source: Pérez-Gutiérrez L, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023)
VEGFA is a secreted glycoprotein composed of multiple α-helices and β-sheets. VEGF-A is typically a homodimer formed by two antiparallel VEGF-A monomers, each with a receptor binding site at one pole or carboxyl terminus. Specific sites on the VEGFA molecule bind to the IgD2 and IgD3 domains of VEGFR, and these binding sites are crucial for the specific interaction between VEGFA and VEGFR.
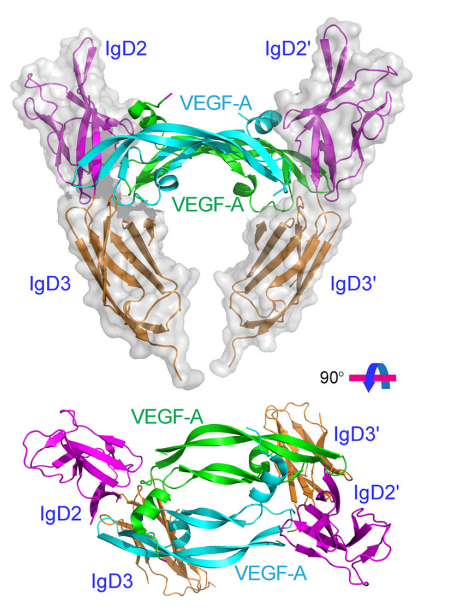
(Data source: Wang X, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020)
VEGF signaling pathway and regulation:
VEGFB, PLGF, and VEGFA bind to VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1) and its soluble form (sVEGFR1). Upon VEGF binding, VEGFR1 is weakly phosphorylated at Tyr1169, resulting in only modest activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phospholipase C isoform-γ ( PLCγ ) -protein kinase C (PKC) pathway. VEGFR1 is expressed in vascular endothelial cells (ECs), hematopoietic stem cells, immune cells, and even some tumor cells. VEGFA also binds to neuropilin 1 (NRP1) and VEGFR2, which is activated by binding to VEGFE and the processed forms VEGFC and VEGFD. Upon VEGFR2 stimulation, multiple pathways are activated. The PLCγ-PKC pathway activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and ERK2 to control cell proliferation, migration, and homeostasis, and regulates extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion and vascular permeability through FAK.
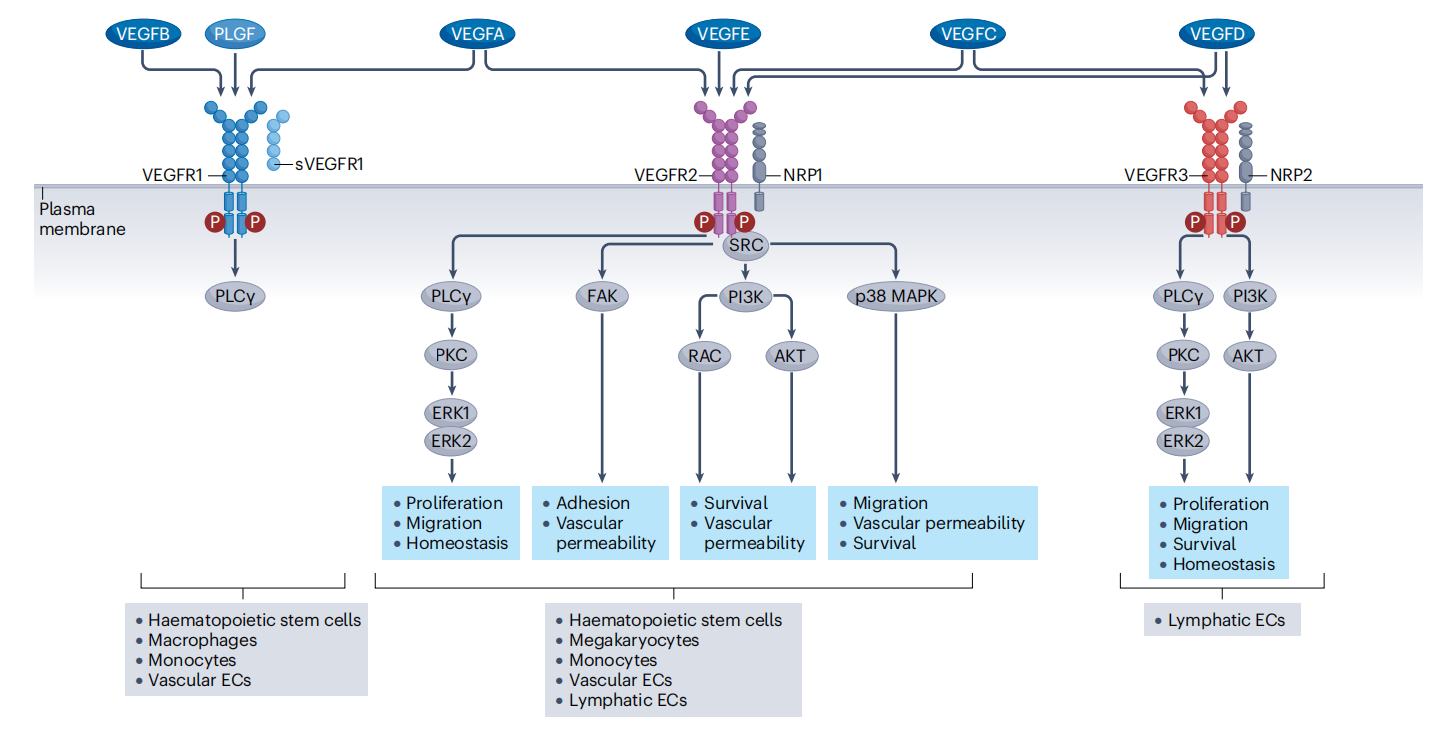
(Data source: Pérez-Gutiérrez L, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023)
VEGFA-targeted therapy
Current therapeutic strategies targeting VEGF primarily include targeting the VEGF/VEGFR interaction and inhibiting VEGFR tyrosine kinase (TK) activity. Inhibitors inhibit VEGFR downstream signaling pathways. Numerous drugs are currently marketed and in clinical development for the treatment of various diseases, particularly cancer and retinal diseases such as diabetic macular edema (DME) and neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD). The VEGF/VEGFR axis is a key system for regulating both physiological and pathological angiogenesis.

(Data source: Wang L, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2024)
So far, seven VEGF/VEGFR interaction inhibitors have been approved by the FDA, one of which (Conbercept) has been approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China. Two of these biomolecules are approved as anti-angiogenic drugs for the treatment of cancer, and six are used to treat ocular vascular diseases.


(Data source: Wang L, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2024)
