The ATP-adenosine pathway plays a key role in establishing an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) by converting proinflammatory extracellular ATP into immunosuppressive adenosine. CD39 is a member of the NTPDase family, cytidine triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 (ENTP1), also known as guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 (ENTPD1), ATP diphosphohydrolase, or lymphocyte activation antigen. CD39 suppresses the immune system by degrading extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine monophosphate (AMP), which is then further degraded to adenosine by CD73. Targeting CD39 in cancer not only reduces adenosine levels in the tumor microenvironment but also increases ATP levels. Targeting CD39 can also limit the function of Treg cells that express high levels of CD39.

(Data source: Liu Y, et al. Biomark Res. 2023)
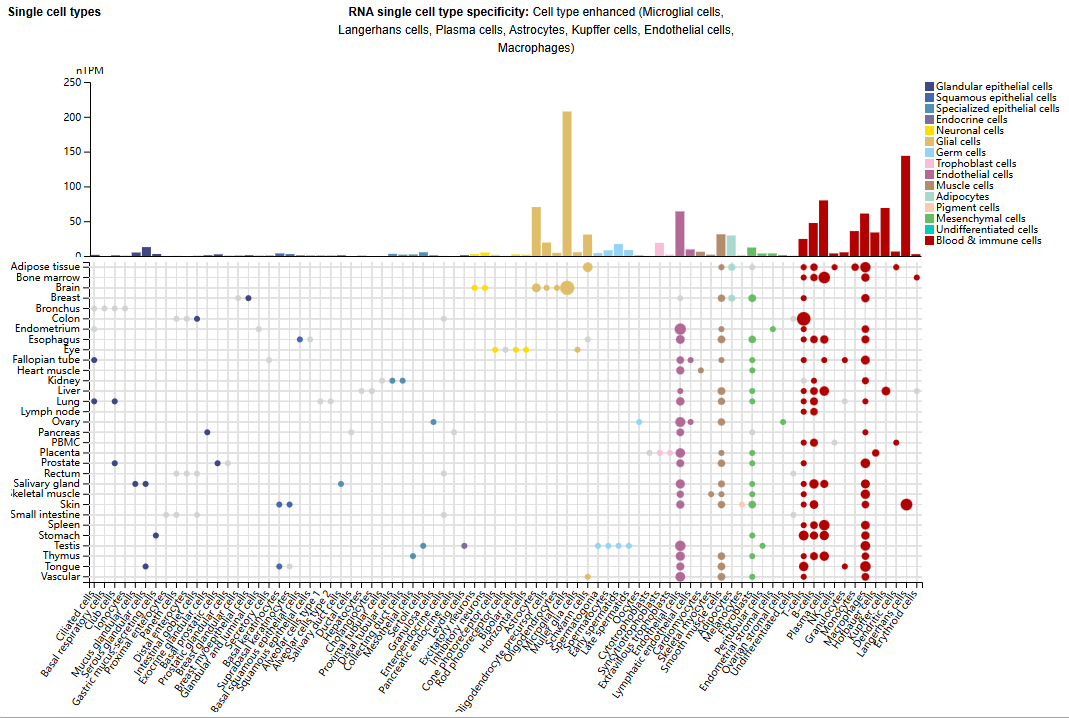
Expression distribution of CD39
CD39 is mainly expressed in microglia, Langerhans cells, T cells, B cells, plasma cells, astrocytes, Kupffer cells, endothelial cells, monocytes, and macrophages.
(Data source: Uniprot)
Within the TME, CD39 expression is enriched in vascular endothelial cells, fibroblasts, myeloid cells, T regulatory cells (Tregs), tumor-specific T effector cells, and NK cells. CD39 expression is increased in a variety of human tumors, including melanoma, colon cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, renal cancer, lung cancer, thyroid cancer, testicular cancer, sarcoma, lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Increased CD39 expression leads to an immunosuppressive microenvironment with high adenosine levels, which can inhibit immune cell function and promote tumor growth.

(Data source: Liu Y, et al. Biomark Res. 2023)
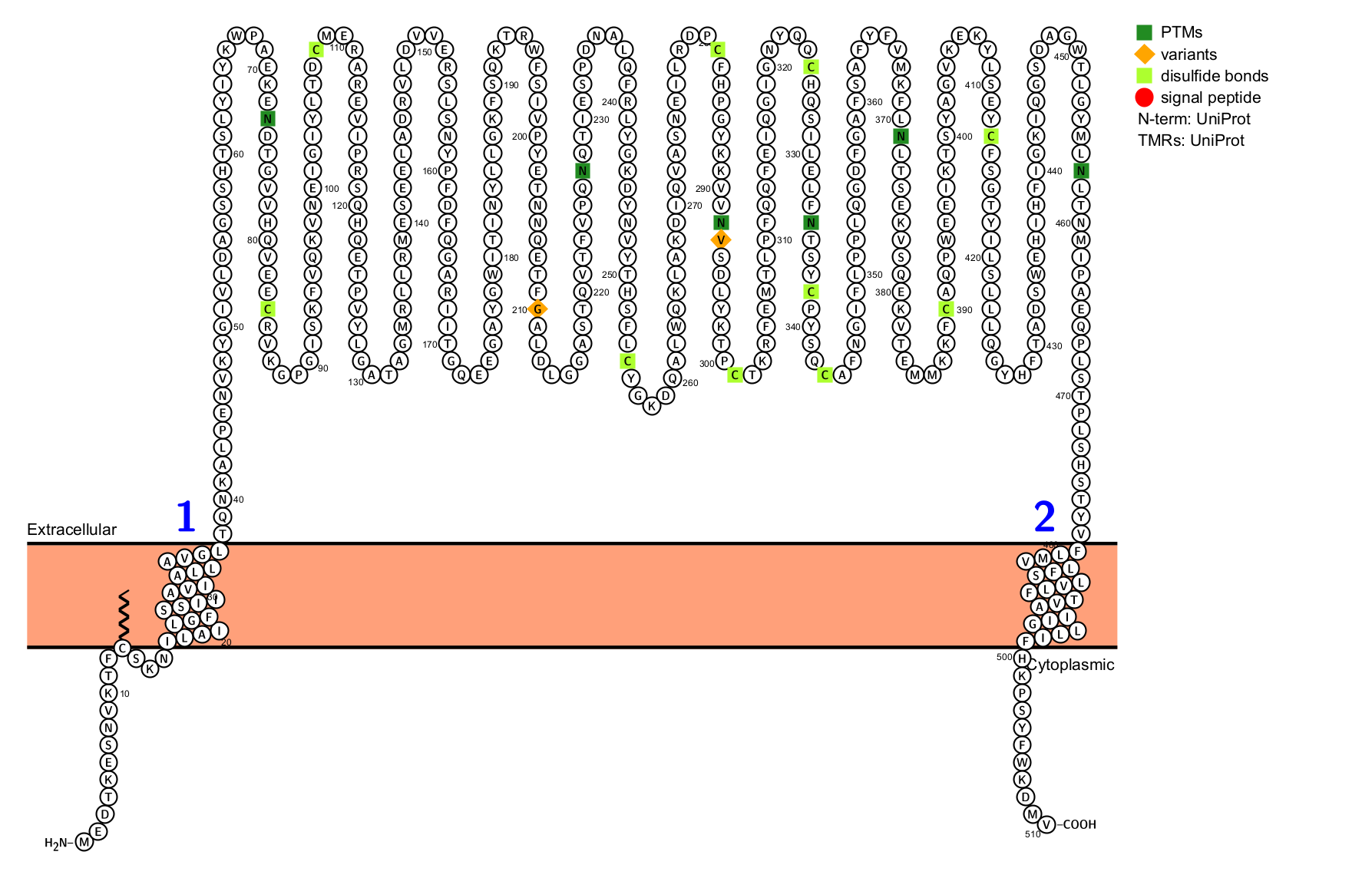
Structure of CD39
CD39 is a transmembrane protein consisting of 510 amino acids with seven N-glycosylation sites and 11 cysteine residues. Structurally, CD39 consists of two transmembrane domains, a small cytoplasmic domain, and a large extracellular region rich in hydrophobic residues. The cytoplasmic domain comprises the N-terminus and the C-terminus, while the extracellular region contains five conserved ATPase domains.
(Data source: uniprot)
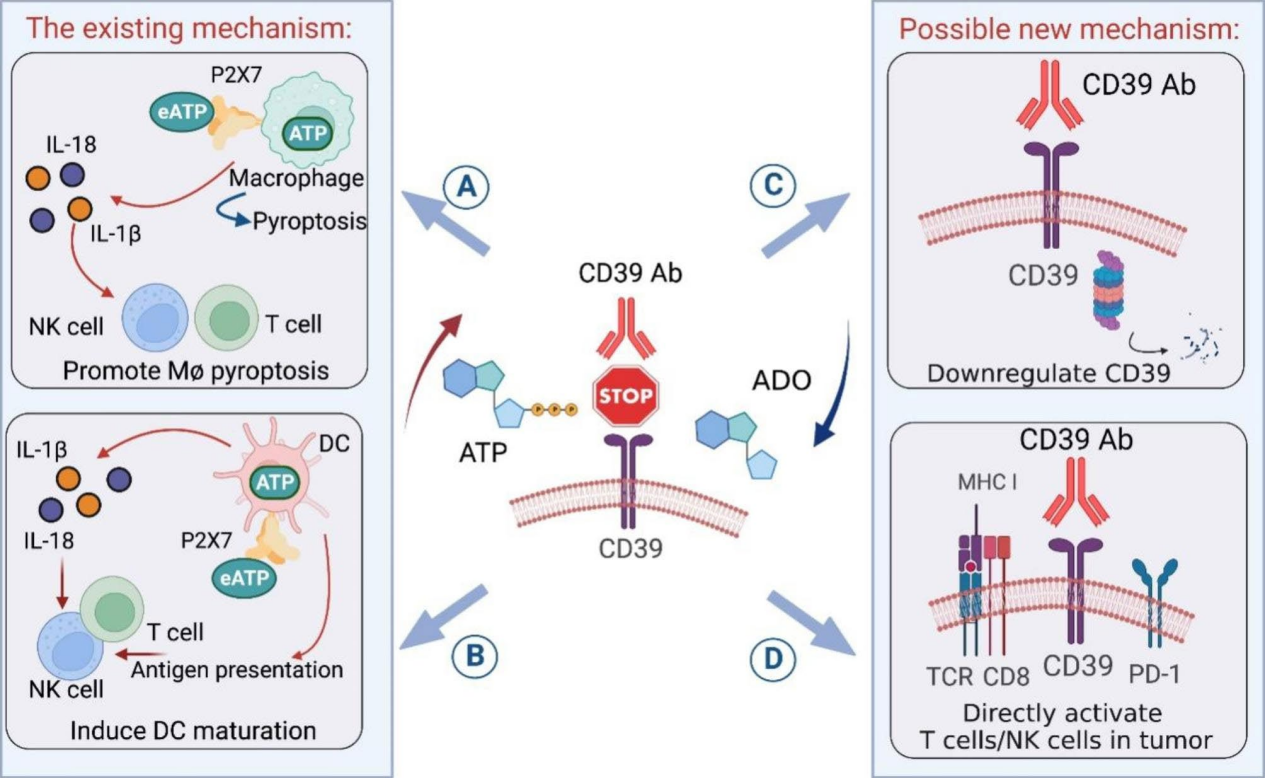
Mechanisms of action of targeting CD39 in cancer
CD39 -blocking antibodies can increase extracellular ATP (eATP) levels in the tumor microenvironment (TME) by inhibiting ATP degradation by CD39. Increased eATP levels activate P2×7 receptors on macrophages and dendritic cells ( DCs ), leading to inflammasome-mediated release of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-18 and IL-1β, which support cytotoxicity mediated by effector T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Increased eATP levels not only induce pyroptosis in P2×7+ macrophages but also bind to P2×7 on DCs, promoting antigen presentation and maturation, further supporting cytotoxicity mediated by effector T cells and NK cells . Targeting CD39 may downregulate CD39 expression by binding to the CD39 receptor and directly activate CD39+ tumor-specific T cells or CD39+ NK cells.
(Data source Liu Y, et al. Biomark Res. 2023)
CD39-targeted therapy combined with other therapies
Many monoclonal antibodies targeting CD39 have been developed and are in the clinical development stage. In addition, CD39 can also be combined with other treatment methods.
Synergistic inhibition of CD39 with other adenosine pathway members (CD73, A2A receptor, A2B receptor, and CD38) may provide therapeutic benefits by simultaneously increasing immunostimulatory extracellular adenosine (eATP) levels and completely blocking the immunosuppressive effects of adenosine (ADO). Combination therapy with other immune checkpoints (PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA4) has shown combined anti-tumor efficacy; combined with chemotherapy and radiotherapy, induced tumor cell death increases eATP and tumor antigen release.


(Data source: Moesta AK, Li XY, Smyth MJ. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020)
IPH5201 is a blocking antibody targeting the CD39 immunosuppressive pathway , developed by innate-pharma for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer ( NSCLC ). Blocking CD39 enhances anti-tumor activity by promoting the accumulation of immunostimulatory ATP and preventing the production of immunosuppressive adenosine. IPH5201 is currently in Phase 2 clinical development in combination with a PD-1 antibody ( durvalumab ) and chemotherapy for the treatment of patients with early-stage, operable NSCLC.

(Data source: innate-pharma official website)
TTX - 030 is a first-in-class antibody that inhibits CD39 activity. By inhibiting adenosine production in the tumor microenvironment (TME), TTX-030 prevents adenosine-mediated suppression of immune effector cells, including T cells, B cells, NK cells, and myeloid cells. By maintaining high levels of extracellular ATP, TTX-030 stimulates dendritic and myeloid cells that support innate and adaptive immunity. This dual mechanism of action is designed to reverse the immunosuppressive state in the tumor microenvironment and restore the immune system's ability to suppress tumors.

TTX-030 is in Phase 1/1b clinical trials as a monotherapy and in combination with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy and standard chemotherapy for the treatment of adults with advanced cancer (NCT03884556 and NCT04306900).
Results from a Phase 1 clinical trial of TTX-030 as a first-line treatment for patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer were presented at the 2024 EMSO Congress . TTX-030, with or without budigallimab, was well tolerated in combination with gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel. The TTX-030 combination regimen demonstrated promising progression-free and overall survival in first-line treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. A retrospective analysis found an association between high HLA-DQ tumor expression at baseline and clinical benefit with the TTX-030 combination regimen. The ongoing randomized, three-arm Phase 2 ELTIVATE study (NCT06119217) is designed to further evaluate the activity of these TTX-030 combinations.

(Data source: trishulat company official website)
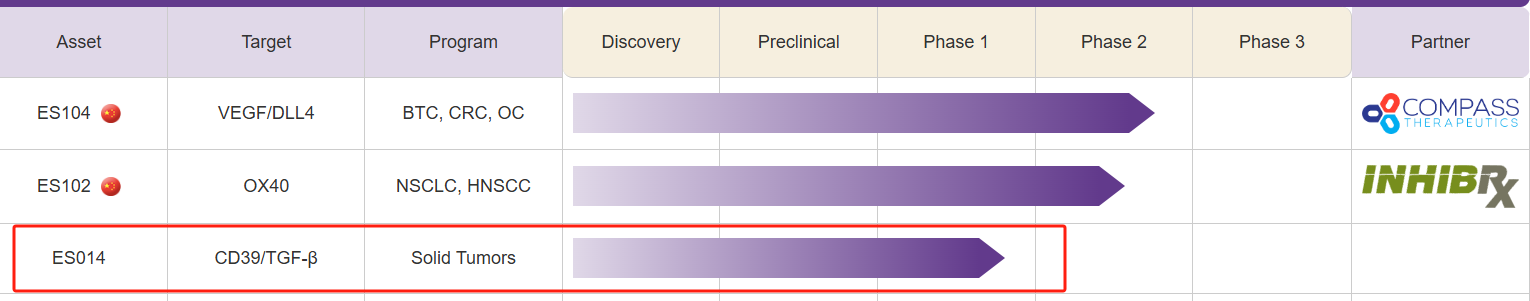
ES-014 is a first-in-class anti-CD39xTGF-β bispecific antibody developed by Covance Biopharmaceuticals for the treatment of malignant solid tumors. It simultaneously targets the adenosine and TGF-β pathways, two major immunosuppressive mechanisms within the tumor microenvironment. By simultaneously targeting CD39 and TGF-β, ES014 inhibits the production of immunosuppressive adenosine, promotes the formation of immunostimulatory ATP, and neutralizes the immunosuppressive cytokine TGF-β. It selectively delivers TGFβ " traps " to CD39-expressing immune cells , blocking CD39-mediated adenosine production and eliminating TGFβ-induced immunosuppression to restore anti-tumor immunity.
(Data source: elpiscience official website)
