Interleukin 19 (IL19), a member of the IL-2RγC chain family, is a pleiotropic cytokine that regulates the functions of various cells. Originally identified as a growth factor for T cells and mast cells, IL19 is primarily involved in the development of allergic diseases, autoimmune disorders, and parasitic infections. IL19 , derived from Th9 cells , plays a crucial role in tumors and allergic diseases.
Origin and function of IL9
IL9 is expressed in multiple helper T (TH) cell subsets, including TH2, TH9, TH17, and regulatory T (TReg) cells. This cytokine has diverse functions in physiological immune responses and diseases.
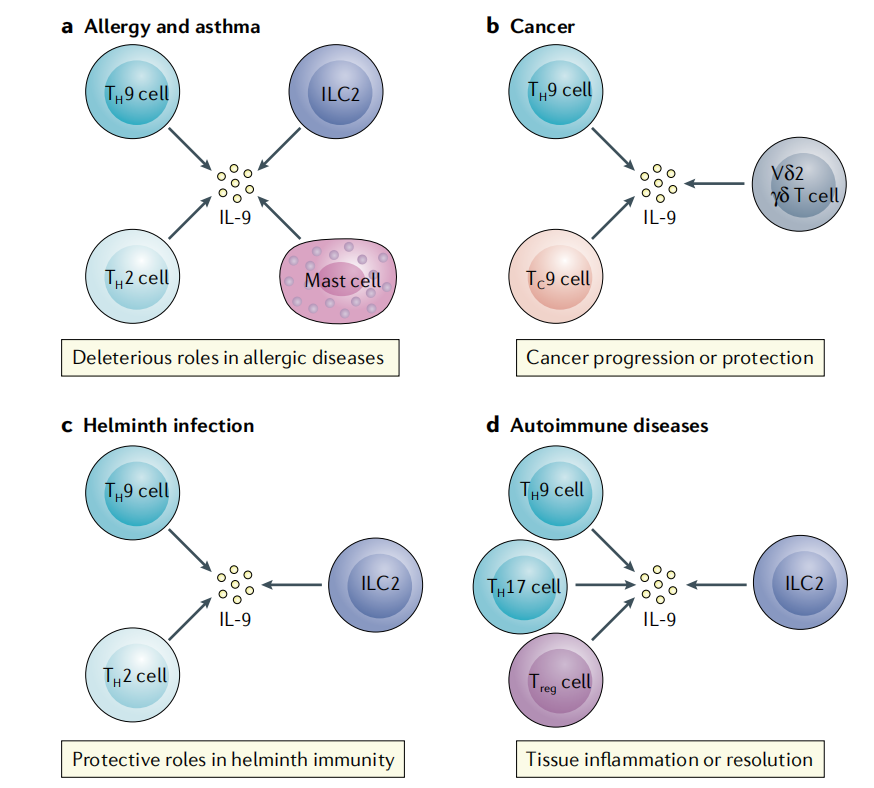
(Data source: Angkasekwinai P, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021)
IL9 signaling pathway and regulation:
The IL9 receptor is composed of the cytokine-specific IL9 receptor α chain (IL9Rα) and the γ chain, which form a heterodimeric receptor complex to activate downstream signaling. Receptor stimulation leads to rapid activation of JAK1 and JAK3 kinase activity, resulting in a transcriptional program mediated by STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5. Induction of differentiation genes appears to be mediated exclusively by STAT1, whereas protection from apoptosis is dependent on STAT3 and STAT5.
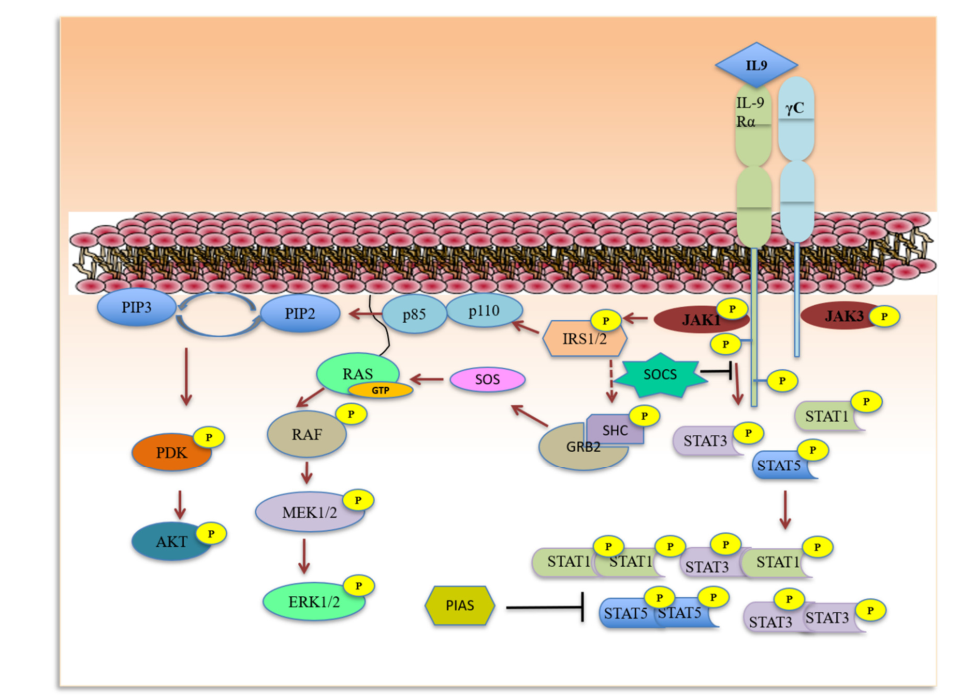
(Data source: Chakraborty S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019)
The role of IL9 in allergic diseases
In allergic reactions, helper T cells (TH9 cells), TH2 cells, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), and mucosal mast cells are the primary IL9- producing cells. IL9 derived from these cells has multiple effects on other cell types: it promotes the survival and expansion of mast cell populations and the production of immune mediators such as mast cell proteases and cytokines; it promotes B cell memory responses and IgE production; it can act on non-hematopoietic cells (such as epithelial cells and smooth muscle cells), inducing mucus production and chemokine expression; and it can act on eosinophils, promoting their tissue infiltration, survival, and mediator secretion. In chronic allergic airway diseases such as asthma, IgE-mediated food allergies, and skin inflammation, IL9 -producing cells induce effector actions that occur through both IL9- dependent and IL9- independent pathways, leading to amplified allergic reactions and exacerbated allergic symptoms.
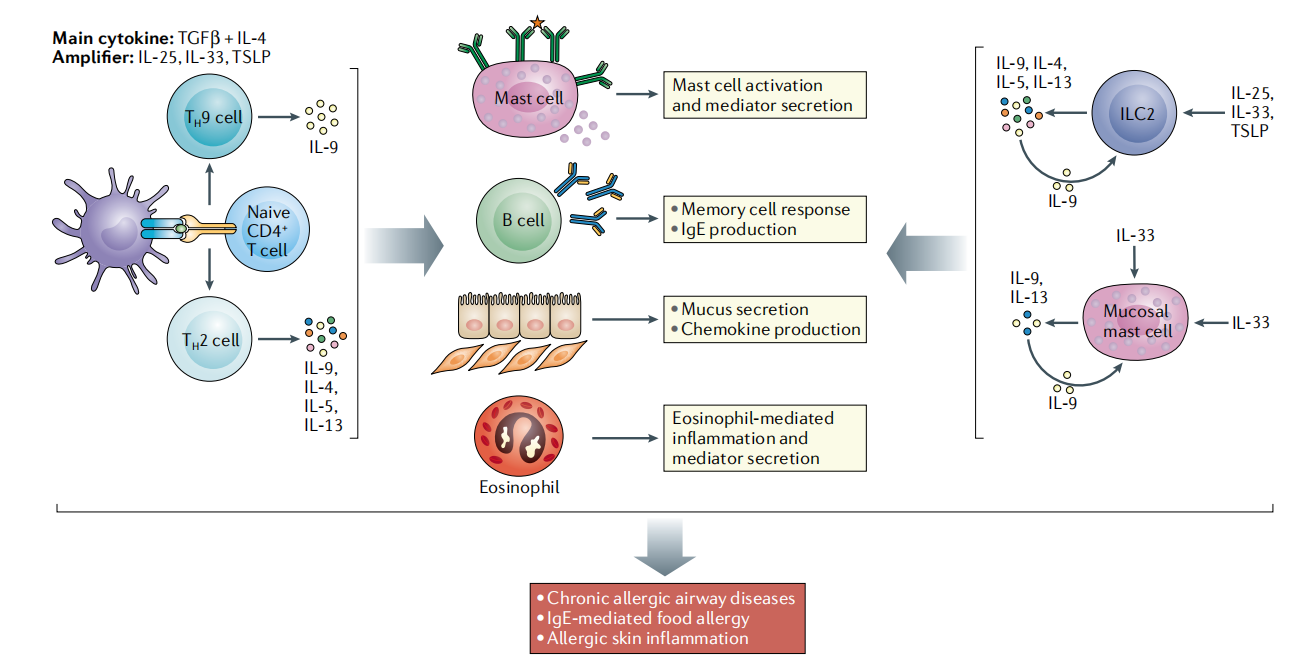
(Data source: Angkasekwinai P, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021)
The role of IL9 in tumors
TH9 cells play a dual role in promoting or inhibiting cancer development. IL9 , derived from TH9 cells , acts as a growth factor, promoting the survival and proliferation of hematopoietic tumor cells (such as Hodgkin's lymphoma) or non-hematopoietic tumor cells (such as breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma) characterized by overexpression of the IL9 receptor. Furthermore, IL9 derived from TH9 cells promotes cancer development by inhibiting adaptive anti-tumor immunity through the recruitment and suppressive properties of regulatory T cells (Treg cells) and mast cells. In various cancer types, particularly melanoma, TH9 cells contribute to anti-tumor immunity through the production of IL9 , IL-21, and granzymes.
The mechanisms by which TH9 cells enhance anti-tumor immunity include supporting mast cell activation and cytotoxic function, promoting the activation and recruitment of CC chemokine receptor 6-positive (CCR6+) dendritic cells, promoting anti-tumor cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses, enhancing natural killer (NK) cell function and directly killing tumor cells.
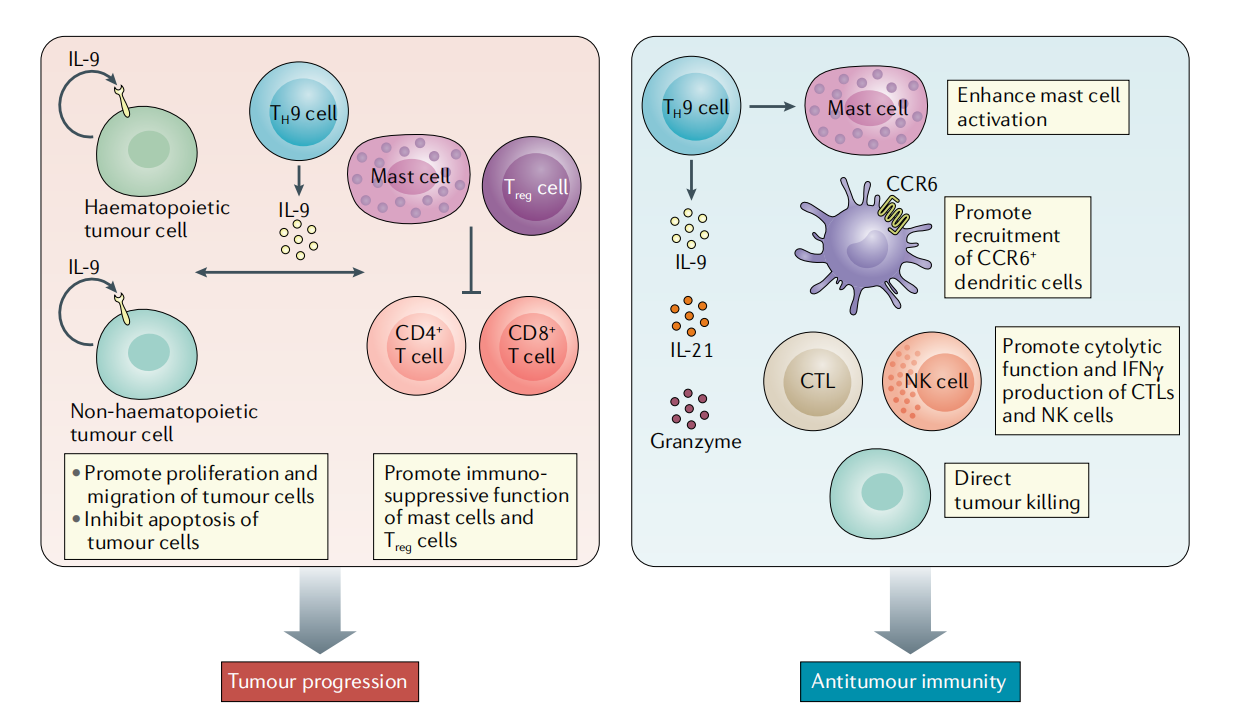
(Data source: Angkasekwinai P, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021)
Targeted therapy for IL9
Because T helper 9 cells (TH9) have multiple biological activities, potential therapeutic strategies for allergic diseases and cancer include targeting the pathways for TH9 cell generation, promoting epigenetic modifications of IL9 sites, and neutralizing IL9 receptors and IL9 production. Currently, there are few antibody drugs targeting IL9.
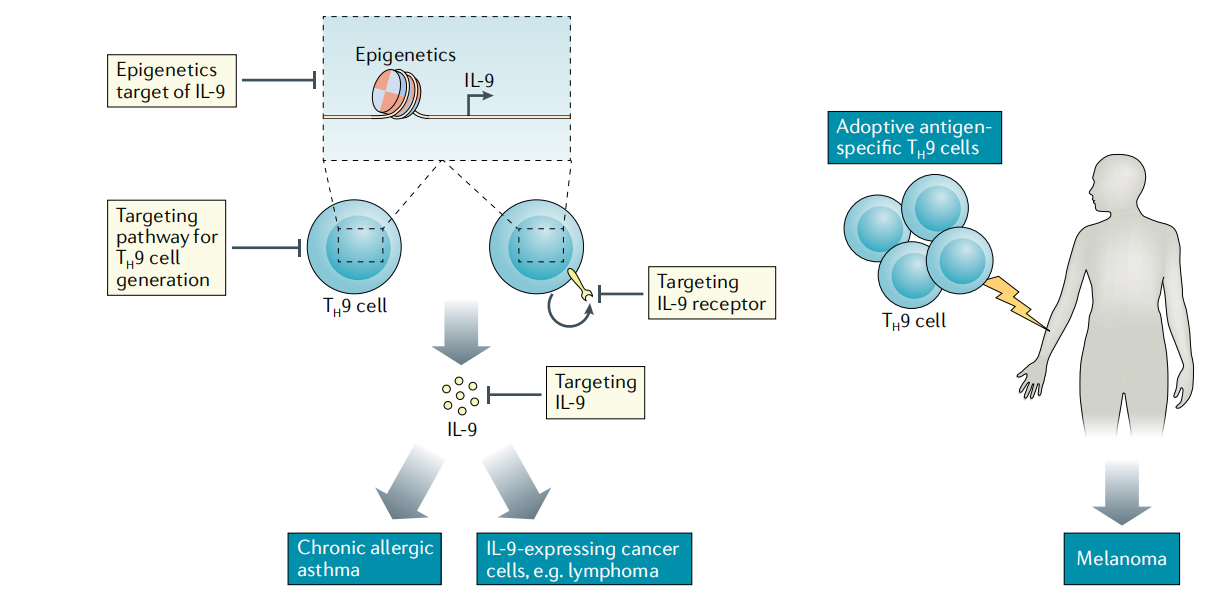
(Data source: Angkasekwinai P, et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021)
Enokizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-9, demonstrated an acceptable safety profile in a phase I study. The drug entered phase II clinical trials in 2011. However, during this phase, the drug (30, 100, and 300 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks for 24 weeks, in addition to concomitant asthma medications) did not result in any improvements in ACQ-6 scores, asthma exacerbation rates, or FEV1 values. The study was subsequently terminated.
Argenx is developing a monoclonal antibody targeting IL9, which is currently in the preclinical research stage for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammation, and tumors.
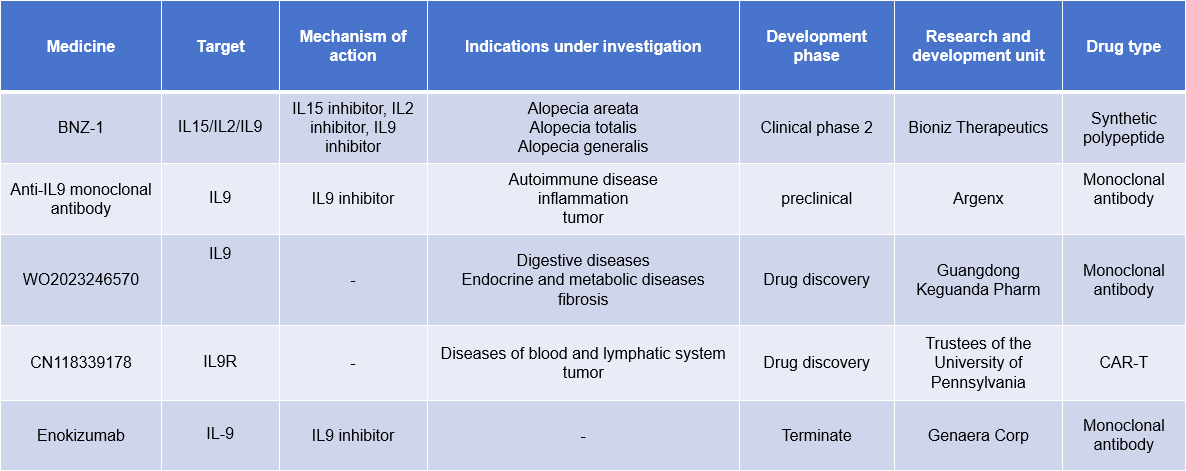
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
