Transforming growth factor β (TGF - β, TGFB) is a multifunctional cytokine. TGF-β signaling is a key pathway in embryogenesis, tissue homeostasis, and cancer progression. TGF-β includes three isoforms: TGF-β1, TGF-β2, and TGF-β3 . TGF-β1 is the most extensively studied isoform. Only activated TGF-β can bind to the TGF receptor complex and induce both canonical and noncanonical TGF-β signaling pathways.
Expression distribution of TGFB
TGFB is mainly expressed in extravillous trophoblasts, NK cells, dendritic cells, T cells, and monocytes, and is also expressed to a lesser extent in B cells, plasma cells, macrophages, and Langerhans cells.

(Data source: Uniprot)
Biosynthesis and activation of TGFB
Each TGF-β polypeptide monomer is initially synthesized as a precursor polypeptide. In the endoplasmic reticulum, the TGF-β precursor loses its signal peptide and dimerizes via disulfide bonds. The dimers are then transported to the Golgi apparatus, where they are cleaved by the protease furin into mature cytokine fragments and latency-associated peptides (LAPs), forming small latent complexes (SLCs). Secreted SLCs can further associate with latent TGF-β binding proteins (LTBPs), which target SLCs to the extracellular matrix (ECM) for storage, or with glycoprotein A repeat-dominant protein (GARP) or leucine-rich repeat protein 33 (LRRC33), anchoring SLCs to the cell surface. A variety of factors, including acids, bases, reactive oxygen species (ROS), thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), certain proteases, and integrins, can release mature cytokines from the latent complexes, hence their termed TGF-β activators.

(Data source Deng Z, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024)
Signaling pathway and regulation of TGFB
Activated after LAP release, TGF-beta-1 exerts its effects by binding to TGF-beta receptors (TGFBR1 and TGFBR2), which transmit signals. Activated TGF- beta -1 acts through SMAD- dependent and/or SMAD- independent pathways.
SMAD -dependent pathway: After TGF- β1 binds to specific cell surface receptors, phosphorylated TbR-I recruits and phosphorylates SMAD2 and SMAD3. Phosphorylated SMAD2 and/or SMAD3 bind to SMAD4 to form a trimeric complex that regulates gene expression in the nucleus.
Non- SMAD -dependent pathway: After TGF- B1 binds to the receptor, phosphorylated TbR-I recruits and phosphorylates signaling molecules such as PI3K-AKT, p38 MAPK, NF-kB, and ERK, participating in the regulation of gene expression.

(Data source: Tie Y, et al. Mol Biomed. 2022)
Function of TGFB in disease
TGF-β signaling plays a key role in regulating the TME and has complex effects on cancer progression . TGF-β has a dual role in tumor progression, acting as a tumor suppressor in the early stages of cancer and as a tumor promoter in later stages of cancer such as breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, lung cancer and pancreatic cancer . TGF-β inhibits the proliferation of immunosuppressive myeloid cells, especially in early cancers. In advanced tumors, TGF-β produced by myeloid cells suppresses anti-tumor immunity, thereby promoting tumor metastasis. Tumor cells, endothelial cells, mesenchymal stem cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts and macrophages can induce the production and secretion of TGF-β in the TME. TGF-β suppresses tumor immune responses by regulating multiple functions of immune cells in the TME.
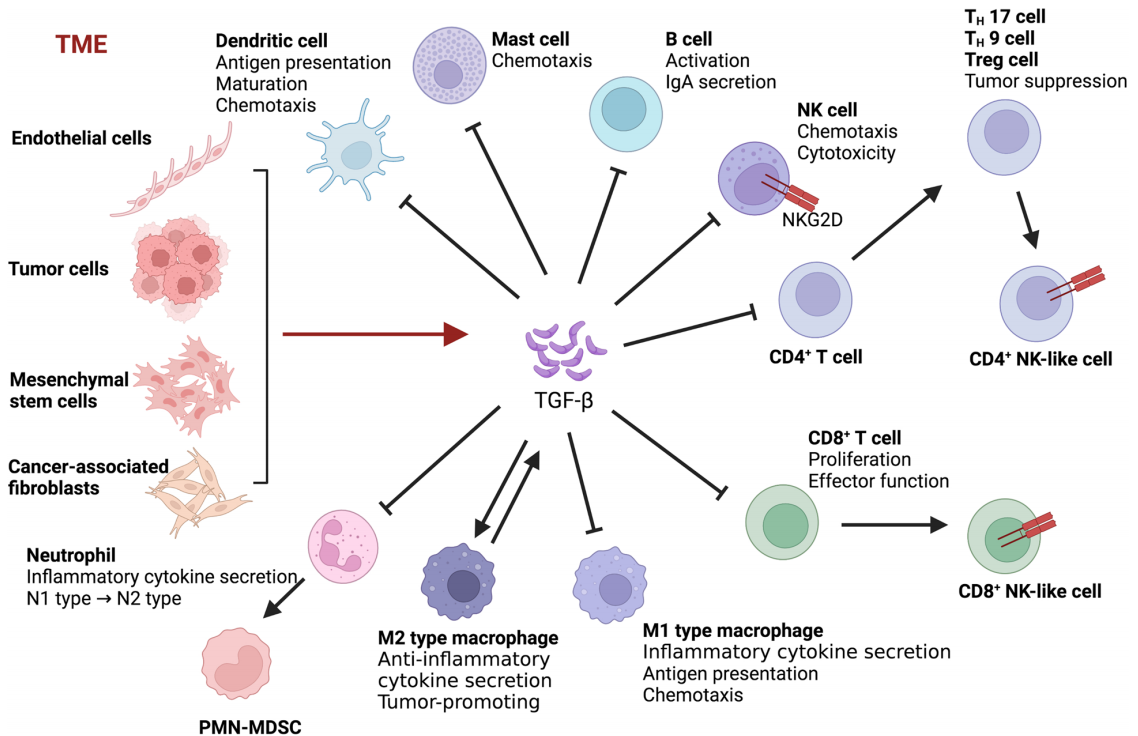
(Data source: Tie Y, et al. Mol Biomed. 2022)
Overexpression of TGF-β is associated with the development and progression of fibrosis in fibrotic diseases, such as pulmonary fibrosis, hepatic fibrosis, renal fibrosis, cardiac fibrosis, and systemic sclerosis. TGF-β is crucial in regulating the recruitment and function of macrophages within fibrotic lesions. It acts as a chemotactic factor for macrophages, leading to their recruitment to fibrotic lesions. In turn, TGF-β induces macrophages to secrete profibrotic cytokines, thereby enhancing TGF-β activity. Furthermore, TGF-β stimulates macrophages to express ECM proteins.

(Data source: Tie Y, et al. Mol Biomed. 2022)
Targeted therapy for TGFB
TGFB , such as altering TGFβ synthesis, targeting TGFβ mRNA, and targeting furin. They can also alter TGFβ activation, targeting the latent TGFβ complex, targeting GARP, and targeting αV integrin. They can also alter TGFβ signaling , such as targeting TGFβ receptors and SMADs.
SRK-181 is an antibody that selectively binds to latent TGFβ1, inhibiting its activation. In mouse models, SRK-181, when combined with an anti-PD-1 antibody, induced significant anti-tumor responses and survival benefits without the adverse effects of pan-TGFβ inhibitors, such as heart valve disease.
In a phase 1 study (NCT02947165), another anti-TGFβ monoclonal antibody called NIS793 was well tolerated in patients with advanced solid tumors, alone or in combination with an anti- PD -1 antibody. Treatment-related adverse events in all patients in the study were primarily skin toxicity and gastrointestinal events, and no dose-limiting toxicities were observed during dose escalation.
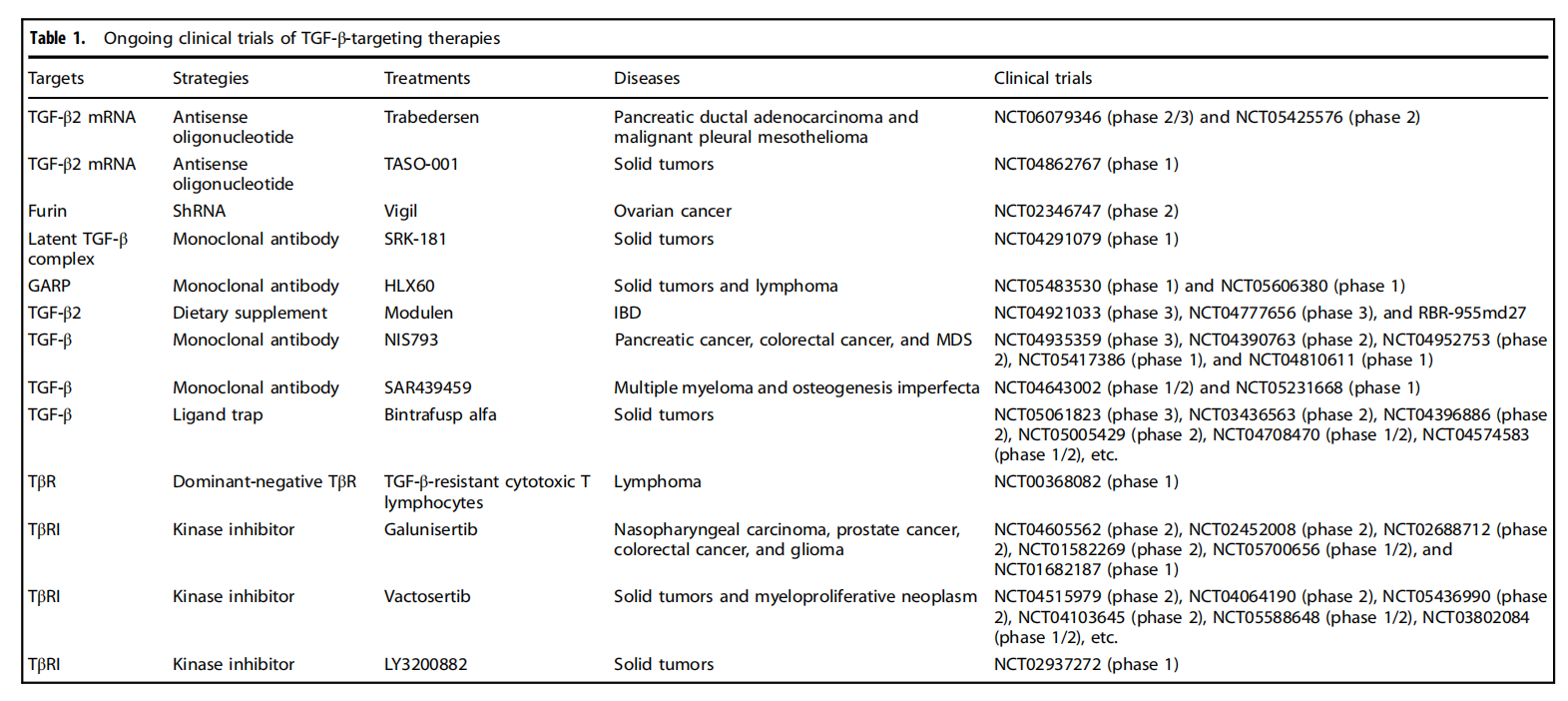
(Data source:Deng Z, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024)
