Transmembrane protein with an EGF-like and two follistatin-like domains2/Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2) is a member of the EGF protein family. TMEFF2 is primarily expressed in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, hippocampus, and prostate. Its signaling pathways play complex roles in cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and tumorigenesis.
Expression distribution of TMEFF2
TMEFF2 is highly expressed in the adult and fetal brain, spinal cord, and prostate. It is expressed in all brain regions except the pituitary gland, with highest expression in the amygdala and corpus callosum. It is expressed in pericrypt myofibroblasts and other stromal cells of the normal colonic mucosa. It is expressed in prostate cancer. Its expression is downregulated in colorectal cancer. It is present (at the protein level) in Alzheimer's disease plaques. Isoform 3 is weakly expressed in the testis and highly expressed in the normal prostate and prostate cancer.
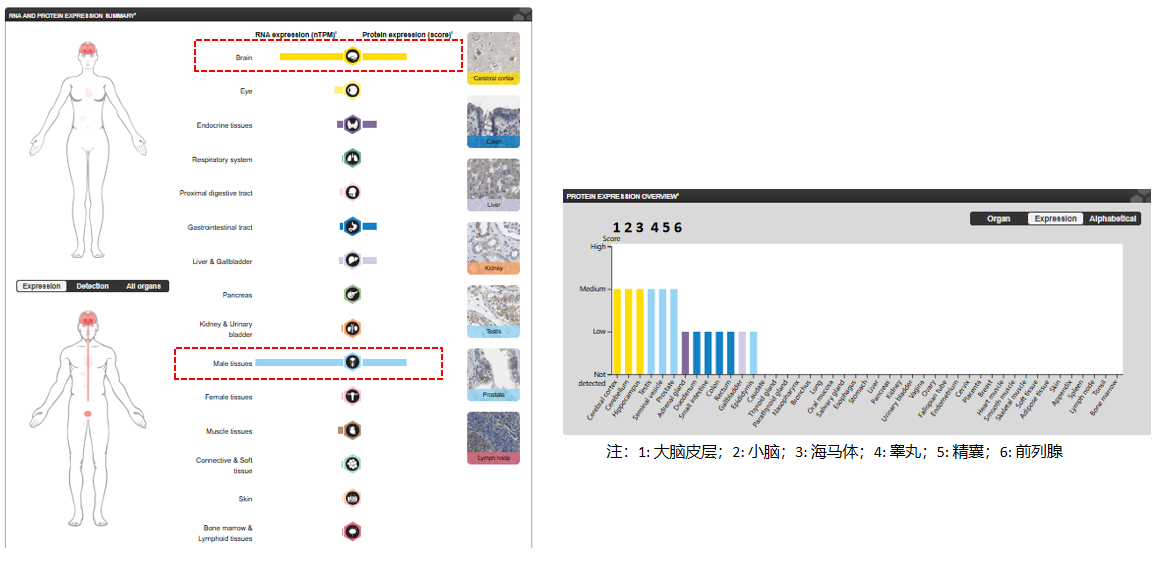
(Data source: Uniprot)
Function of TMEFF2
May act as a survival factor for hippocampal and midbrain neurons. Its shed form upregulates cancer cell proliferation, possibly by promoting ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
Structure of TMEFF2
TMEFF2 is a type I transmembrane protein with a length of 374 AA and a molecular weight of approximately 41.4 kDa , encoded by the TMEFF2 gene . It belongs to the EGF protein family.
Extracellular domain: a) EGF-like domain: contains 1 EGF-like domain, involved in intercellular signal recognition and intracellular signal transduction; b) Follistatin-like domain: contains 2 Follistatin-like domains, can bind to TGF-β family members (such as activin, bone morphogenetic protein) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), inhibit their receptor activation, and regulate cell proliferation and differentiation.
Intracellular domain: The cytoplasmic region contains potential G protein activation sequences, which may participate in G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-related signaling pathways and regulate intracellular signal transduction.

(Data source : Motasim Masood, et al. Cancers vol. 2020)
TMEFF2 signaling pathway
JAK-STAT-interferon pathway: TMEFF2 exerts its tumor suppressor effect by activating the JAK-STAT pathway. In gastric cancer models, high TMEFF2 expression can activate STAT1, inducing the expression of interferon-related genes (such as IRF1), thereby inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis.
ERK/MAPK pathway: The shed extracellular domain of TMEFF2 (TMEFF2-ECD) promotes ERK1/2 phosphorylation, activates the MAPK signaling pathway, and enhances prostate cancer cell proliferation. This process is dependent on ADAM proteases (such as ADAM17)-mediated cleavage of the extracellular domain. 59 In contrast, full-length TMEFF2 may inhibit ERK activation, reflecting its bidirectional function.
Integrin-RhoA pathway: Full-length TMEFF2 interacts with integrins (such as αvβ3) through the basic amino acid sequence in the intracellular region, inhibiting RhoA activation, thereby reducing the migration and adhesion ability of prostate cancer cells .
SHP-1-dependent tumor suppressor pathway: In gastric cancer, TMEFF2 binds to the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 , inhibiting downstream pro-oncogenic signaling (such as PI3K/AKT) through dephosphorylation , inducing cell cycle arrest ( G1/S phase) and apoptosis. TMEFF2 and SHP-1 expression are positively correlated, and patients with high expression of both TMEFF2 and SHP-1 have a better prognosis.
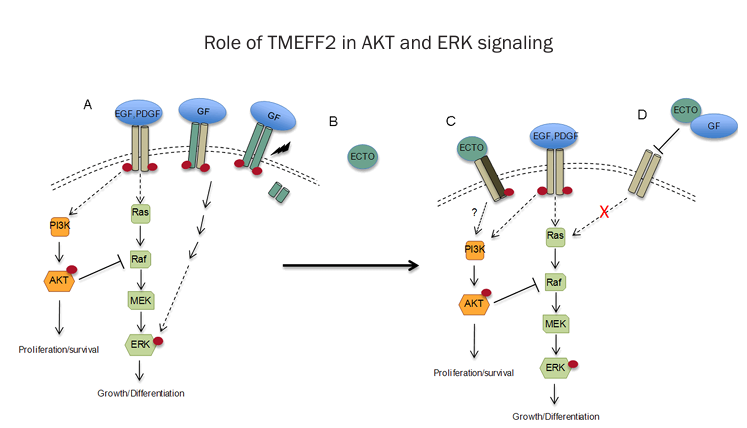
(Data source: Xiaofei Chen , et al. Int J Biochem Mol Biol . 2013)
TMEFF2 and disease
Abnormal neurodevelopment : Animal experiments have shown that TMEFF2 gene knockout mice have growth retardation and die during the weaning period, suggesting that it is essential for neuronal survival and development.
Endometrial cancer (EC) : TMEFF2 protein expression is significantly decreased in EC tissue , while methylation levels are elevated (methylation index reaches 24.53 vs. 4.58 in normal tissue). Methylation levels at the CpG1 site of the TMEFF2 gene can differentiate between endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma (AUC = 0.933), becoming a diagnostic indicator second only to BMI .
Prostate cancer: High expression in normal prostate and androgen-dependent cancers may contribute to tumorigenesis as the disease progresses. Full-length TMEFF2 inhibits tumor invasion by binding to sarcosine dehydrogenase, reducing sarcosine levels. The shed extracellular domain (TMEFF2-ECD) activates the ERK or PI3K/AKT pathways to promote tumor proliferation.
Gastric Cancer : a ) Tumor Suppressor Effect: Reduced expression in gastric cancer tissues is positively correlated with patient prognosis. Overexpression of TMEFF2 inhibits the PI3K/AKT pathway by binding to the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 , inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest ( G1/S phase). b) Epigenetic Silencing Mechanism: Promoter hypermethylation mediated by the STAT3-DNMT1 axis leads to loss of expression, accelerating carcinogenesis.

(Data source: Tiantian Sun , et al. Clin Cancer Res . 2014)
Targeted therapy for TMEFF2
JNJ-70218902 is a bispecific T cell engager targeting TMEFF2 and CD3, developed by Janssen Research & Development LLC . Its primary mechanism of action is as a CD3 stimulator and TMEFF2 inhibitor. By binding to TMEFF2 on prostate cancer cells and CD3 on T cells, it promotes T cell-mediated tumor cell killing. It is intended for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and B-cell lymphoma. It was approved for Phase 1 clinical trials in the United States on July 10, 2020.

(Data source: Emiliano Calvo, et al. The oncologist, vol. 20-25)
Ciduvectamig is a bispecific T cell engager targeting TMEFF2 and CD3ε , developed by Janssen Biotech, Inc. Its mechanism of action is as a CD3ε inhibitor and a TMEFF2 inhibitor, targeting tumor cells by inhibiting CD3ε and TMEFF2 signaling pathways. Its current clinical stage and indication are unknown.
JNJ-8902 , a bispecific T cell engager developed by Johnson & Johnson , targets TMEFF2 and CD3. Its primary mechanism of action is similar to that of JNJ-70218902 and is intended for the treatment of prostate cancer. The first Phase 1 clinical trial in the United States was approved on April 25, 2022, but is currently terminated.
huPr1-vcMMAE, developed by PDL BioPharma, Inc., is an ADC targeting TMEFF2 and tubulin (microtubule protein). Its primary mechanism of action is as a TMEFF2 and tubulin inhibitor, delivering cytotoxic drugs through TMEFF2 for the treatment of prostate cancer. It is currently in the preclinical stage.
