Activin receptor type 2B serine/threonine kinase receptor (ACVR2B) is a type II transmembrane protein. ACVR2B is activin A receptor type 2B, a type II receptor serine/threonine kinase belonging to the TGF-β superfamily. It is primarily expressed in the brain, testes, and thyroid gland, playing a key role in muscle development and neural function.
Expression distribution of ACVR2B
ACVR2B is widely distributed in various tissues, with prominent expression in the brain, testis, and muscle, and is conserved across species. Its expression level is closely correlated with ligand affinity (such as Activin) and downstream signaling regulation (such as the TGF-β pathway), playing a key role in muscle development and neural function.
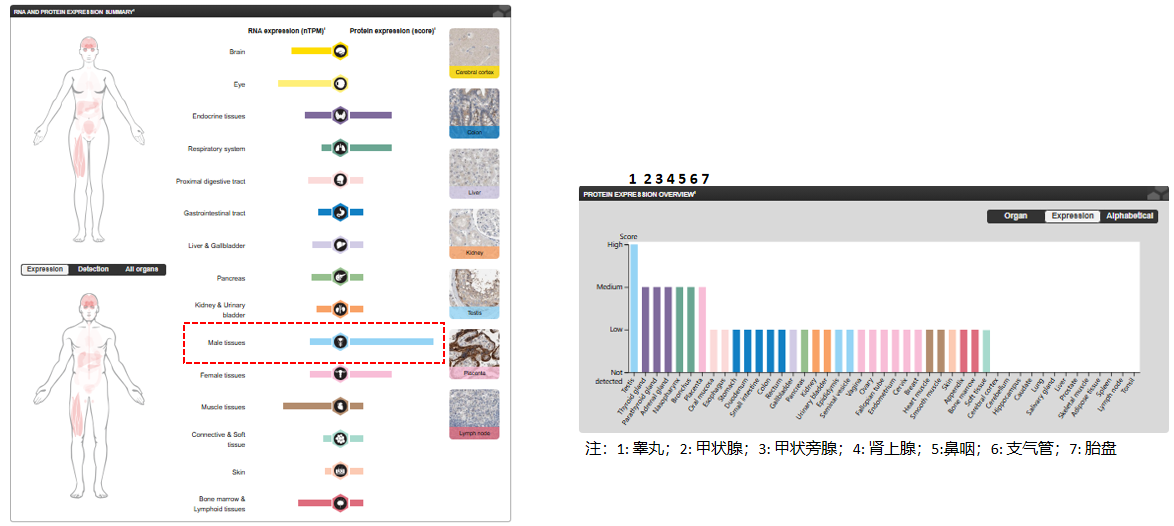
(Data source: Uniprot)
Features of ACVR2B
1. ACVR2B is a transmembrane serine/threonine kinase receptor that binds to type 1 receptors (such as ACVR1B) to form a complex, mediating the transmission of activin signals from the cell membrane into the cell interior. This signaling pathway regulates numerous key physiological processes, including neuronal differentiation and survival, hair follicle development, pituitary FSH secretion, wound healing, immunosuppression, carcinogenesis, and ovarian follicle development.
2. In this complex, ACVR2B is the primary ligand-binding receptor (recognizing activin A/B and inhibin A), while type 1 receptors (such as ACVR1B) are responsible for downstream signal transduction. Activin binding to ACVR2B activates its kinase activity, which in turn phosphorylates and activates type 1 receptors. Activated type 1 receptors subsequently phosphorylate the C-terminal serine residues of SMAD2/3 proteins.
3. Phosphorylated SMAD2/3 dissociates from the receptor, forms a complex with SMAD4 in the cytoplasm, and is transported into the nucleus, ultimately mediating activin-induced gene transcription.
4. ACVR2B signaling is regulated by two factors: a) Inhibitory SMAD7 is recruited to ACVR1B via FKBP1A, preventing SMAD2/3 from binding to the receptor; b) Inhibitory B binds to ACVR2B via the co-receptor IGSF1, antagonizing activin signaling.
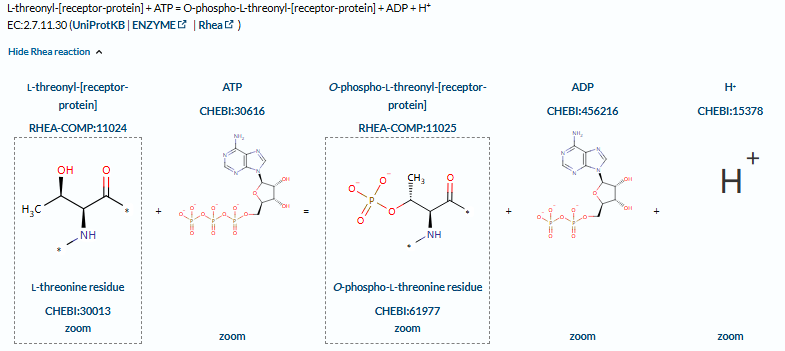
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of ACVR2B
ACVR2B is a type II serine/threonine kinase receptor transmembrane protein encoded by the ACVR2B gene with a length of 512 AA and a molecular weight of approximately 57.7 kDa. It contains extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular domains.
Extracellular domain: has a characteristic ligand binding domain that specifically recognizes ligands such as activin A/B and inhibin A.
Intracellular kinase domain: Contains conserved serine/threonine kinase activity and can phosphorylate type I receptors (such as ACVR1B).
Receptor complex formation: It needs to form a heterodimer complex with type I receptors (such as ACVR1B) to initiate downstream signal transduction

(Data source : AlphaFold)
ACVR2B signaling pathway
Classical SMAD2/3 signaling pathway: ACVR2B phosphorylates the GS domain of the type I receptor, activating its kinase activity. The type I receptor further phosphorylates the downstream transcription factors SMAD2/3 . Phosphorylated SMAD2/3 binds to SMAD4 to form a complex, which translocates to the nucleus and regulates the expression of target genes (such as the myogenic genes MyoD and Myogenin), affecting cell differentiation, proliferation, or hypertrophy.
Non-classical signaling pathways: a) MAPK pathway: ACVR2B can transmit signals independently of SMAD by activating MAPK (such as ERK and p38), participating in cell stress response and migration; b) SMAD1/5/8 pathway: Under pathological conditions (such as fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, FOP ), ACVR2B binds to mutant ALK1 (such as ALK2-R206H), abnormally activates SMAD1/5/8 , and leads to heterotopic ossification; c) NOX4-ROS axis: In osteoarthritis, the Activin A-ACVR2B axis produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) by activating NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4), amplifying SMAD2/3 signaling and exacerbating cartilage destruction.
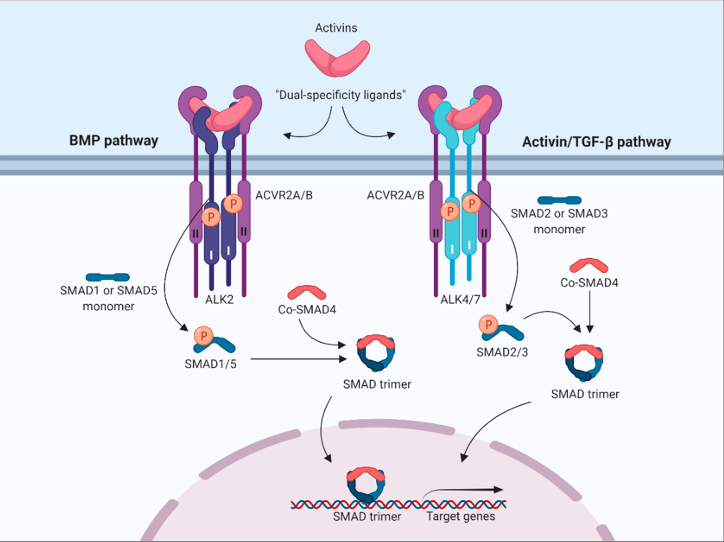
(Data source OddrunElise O , et al. Biomolecules vol. 2020)
ACVR2B and disease
Bone and joint diseases: Osteoarthritis: Activin A-ACVR2B signaling amplifies the SMAD2/3 pathway through the NOX4-ROS axis , exacerbating cartilage destruction. Blocking this signaling can slow joint degeneration.
Muscular dystrophy: a) Muscular Dystrophy: ACVR2B is the primary receptor for myostatin, which inhibits muscle growth. Blocking this signaling with a soluble ACVR2B - Fc decoy receptor significantly increases muscle mass and strength (up to 61% increase in muscle mass in mice ). b) Cancer cachexia and chemotherapy-induced amyotrophy: ACVR2B inhibitors (such as sACVR2B-Fc) can prevent muscle loss and improve muscle function.
Obesity and Metabolic Disorders: a) Fatty Liver Disease (MASLD): Inhibiting ACVR2B signaling improves Western diet-induced metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis, reduces hepatic fat deposition and fibrosis, and lowers total cholesterol levels. b) Type 2 Diabetes : Bimagrumab (targeting ACVR2A/B) has demonstrated dual effects in clinical trials—reducing body fat (average -20.5%) while increasing lean body mass (+3.6%) and improving insulin sensitivity and glycemic control .
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH): Imbalanced ACVR2B signaling promotes vascular remodeling. The FDA -approved drug, Sotatercept ( ACVR2A-Fc fusion protein), restores the balance of the BMP/ activin pathway by capturing ligands , improving pulmonary vascular resistance and patients' exercise capacity .
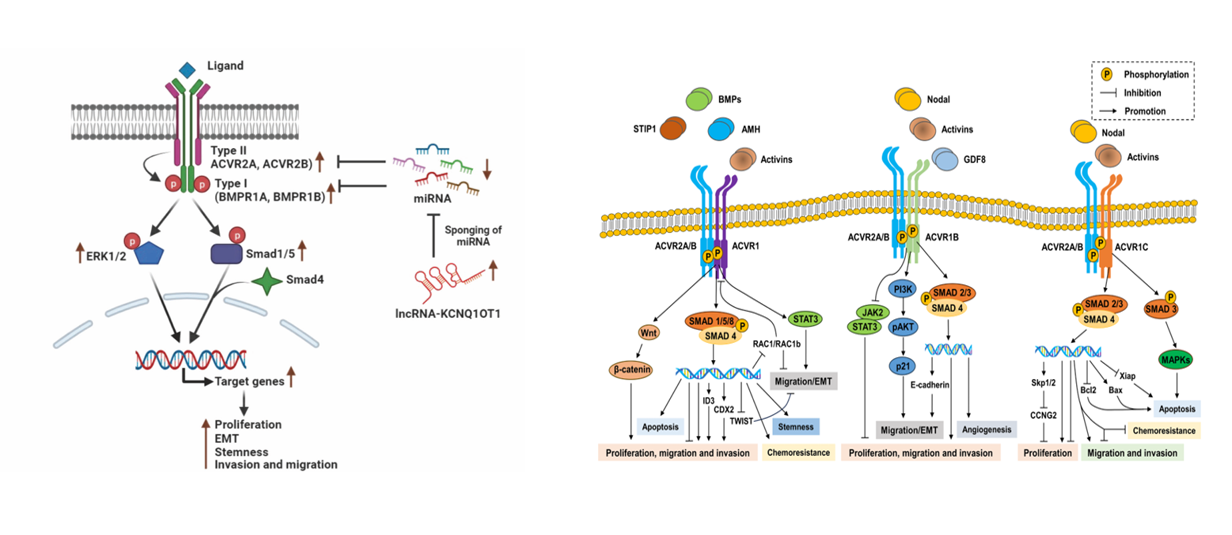
(Data source Left: Swagata M , et al. Cell death discovery vol. 2024
Right: Ruochen Du, et al. Biochemical pharmacology vol. 2024)
ACVR2B-targeted therapy
Luspatercept is an Fc fusion protein drug developed by Acceleron Pharma, Inc. that targets ACVR2B and GDF11. Its primary mechanism of action is as an ACVR2B and GDF11 inhibitor, promoting erythrocyte maturation by inhibiting the ACVR2B signaling pathway (Smad2/3 signaling). It is used to treat non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia. It was approved for marketing in the United States on November 8, 2019, and in China on January 25, 2022.
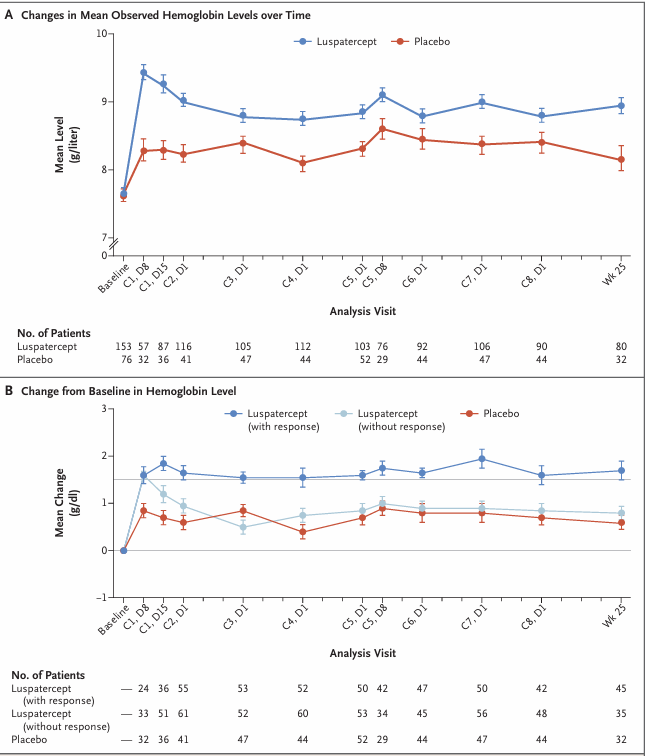
(Data source: Pierre F , et al. N Engl J Med. 2020)
Bimagrumab, developed by MorphoSys AG, is a monoclonal antibody targeting ACVR2B and ACVR2A. Its primary mechanism of action is as an ACVR2B inhibitor and ACVR2A modulator, blocking ACVR2B signaling to increase lean body mass for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Bimagrumab was approved in the United States on September 26, 2013, to begin Phase 2 clinical trials.
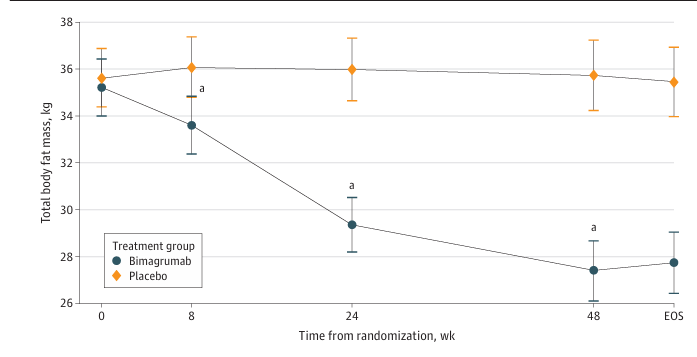
(Data source: Steven BH , et al. JAMA Network Open. 2021)
Cibotercept (RKER-012), developed by Keros Therapeutics, Inc., is an Fc fusion protein targeting ACVR2B and TGF-β. Its primary mechanism of action is as an ACVR2B regulator and TGF-β inhibitor, selectively inhibiting TGF-β ligands (such as GDF8/11), improving pulmonary vascular lesions and intended for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. It received approval to begin a Phase 2 clinical trial in the United States on October 27, 2023.
BIIB-110 , a recombinant protein drug developed by AliveGen USA, Inc., targets ACVR2B. Its primary mechanism of action is as an ACVR2B inhibitor, modulating the ACVR2B signaling pathway for the treatment of muscle atrophy. It was approved for Phase 1 clinical trials in the United States on March 18, 2024.
LAE-103 , developed by Shanghai Laekna Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., is a monoclonal antibody targeting ACVR2B. Its primary mechanism of action is as an ACVR2B modulator, inhibiting ACVR2B to reduce muscle atrophy and is intended for the treatment of liver cirrhosis and muscle fibrosis. The first clinical trial application was filed on June 30, 2025.
