Interleukin-1α (IL1A) is a major alarmin cytokine that triggers and enhances inflammatory responses. It plays a crucial role in inflammation and bridges the innate and adaptive immune systems. After binding to its receptor IL1R1 along with the accessory protein IL1RAP, it forms a high-affinity interleukin-1 receptor complex. Signaling involves the recruitment of adaptor molecules such as MYD88, IRAK1, or IRAK4. IL-1α is a unique cytokine that can be localized in the cytosol, membranes, and nuclei, and can also be secreted extracellularly.
(Data source: Chiu JW, et al. Cells. 2021)
IL1A expression distribution
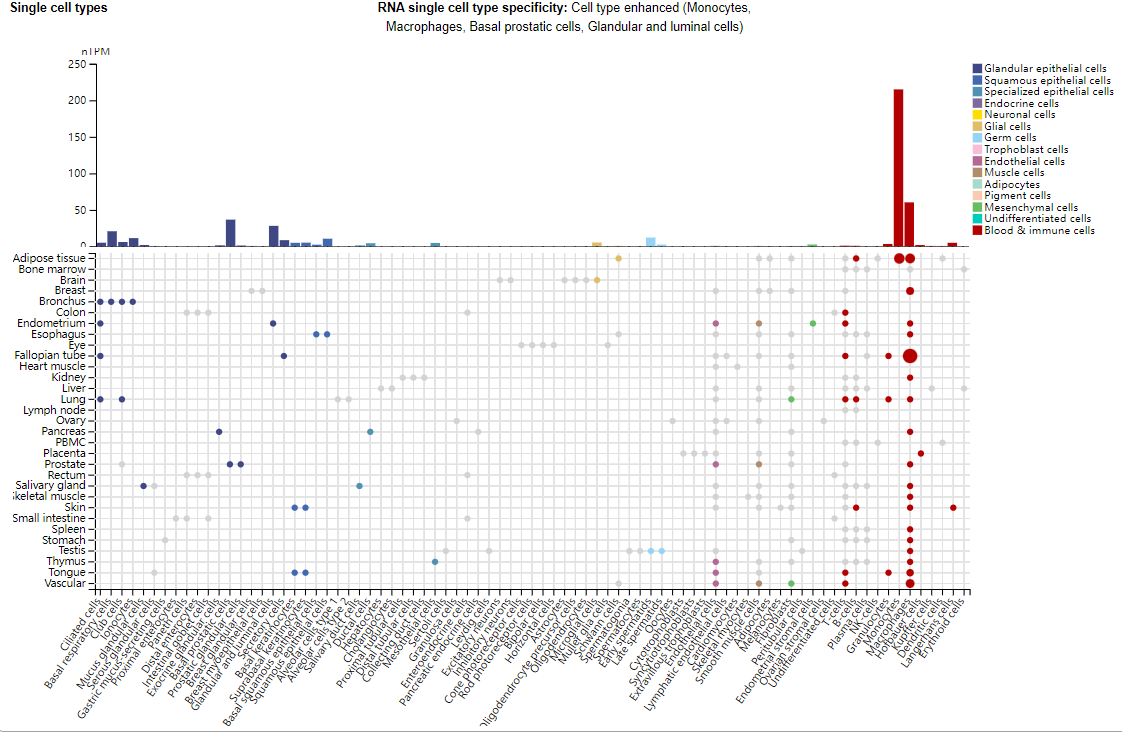
IL1A is primarily expressed in monocytes, macrophages, prostate basal cells, glandular and luminal cells. Endothelial and epithelial cells are the main sources of IL1A under both physiological and pathological conditions.
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of IL1A and its receptor
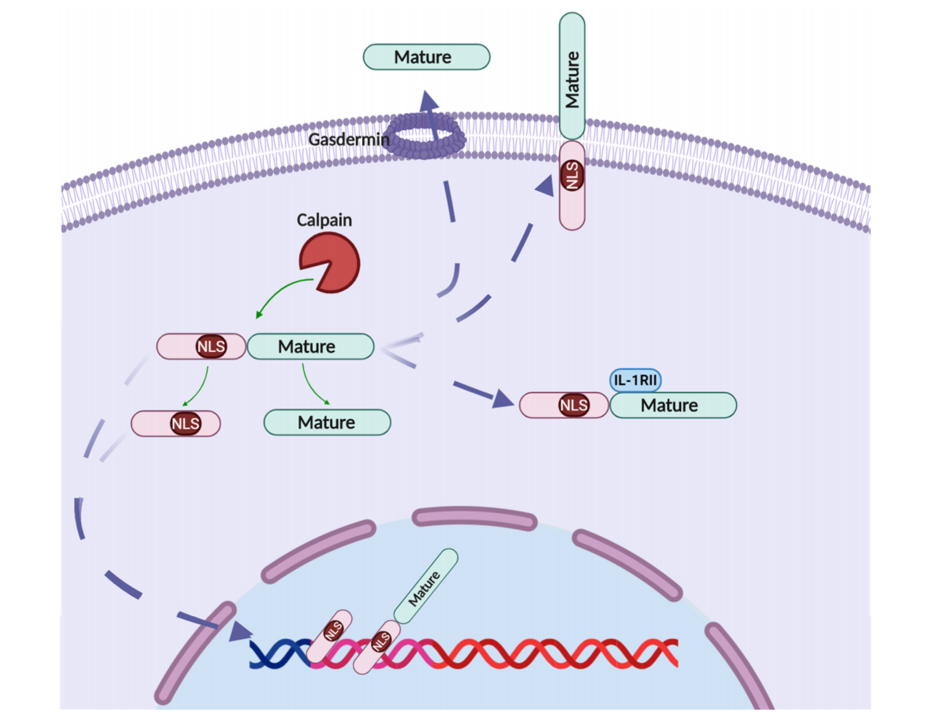
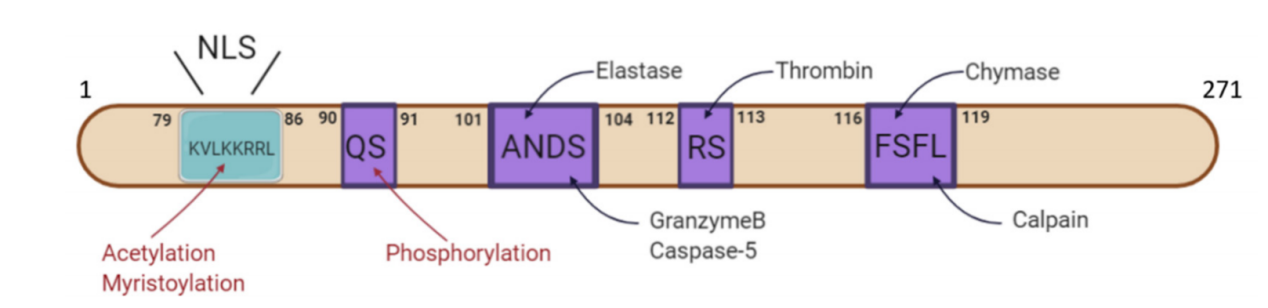
The precursor form of IL-1A (pro-IL-1α). Pro-IL-1α contains a nuclear localization signal (NLS) site, which directs its translocation into the cell nucleus. Pro-IL-1α can be cleaved by pro - IL-1α proteases into a 17-kDa mature form and a 16-kDa N-terminal form. The mature form of IL -1α possesses greater biological activity. IL-1α can be cleaved by various proteases, including elastase, granzyme B, caspase-5, thrombin, basophil gelatinase, and calcineurin.
(Data source: Chiu JW, et al. Cells. 2021)
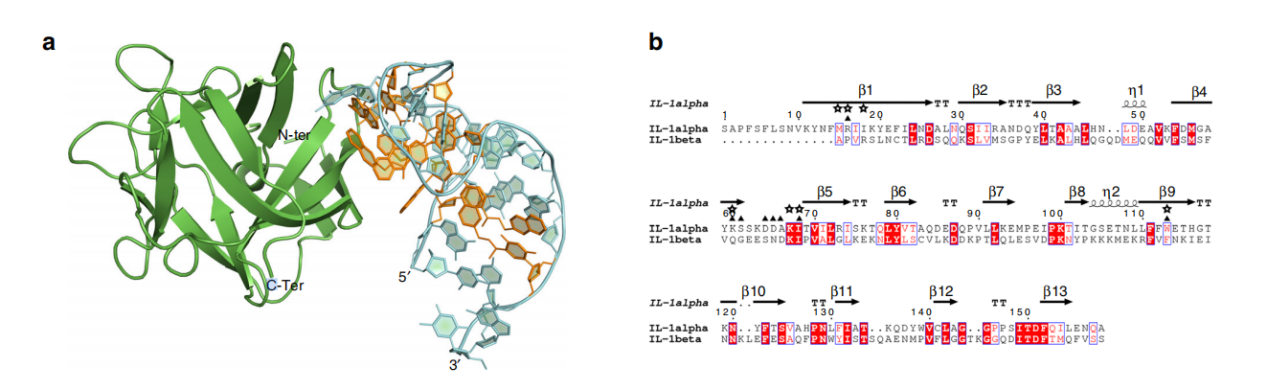
As a member of the β-trefoil protein family, IL-1α's secondary structure is composed almost entirely of β-strands and one α-helix. The core of this structure is a six-stranded β-barrel, with another six strands forming three hairpins that serve as the base of the barrel. Unlike IL-1β and IL-1Ra, two cytokines that contain 12 β-strands, IL-1α has an additional β-strand at the N- terminus, which forms hydrogen bonds with the S5 strand and the long loop L8-9, further stabilizing the overall protein structure.
(Data source: Ren X, Gelinas AD, von Carlowitz I, Janjic N, Pyle AM. Nat Commun. 2017)
IL1A signaling pathway and regulation
Binding of IL-1α to IL-1RI leads to receptor dimerization at the TIR domain and recruitment of IL-1RAcP. The IL-1α/IL-1RI/IL-1RAcP complex recruits the adaptor protein MyD88 and IRAK to initiate downstream signaling cascades. IRAK phosphorylates IRAK1 and IRAK2 and recruits TRAF6 to form the IRAK1-IRAK2-TRAF6 complex. Subsequently, TRAF6 binds to TAK1-TAB1-TAB2 to phosphorylate TAK1. Phosphorylated TAK1 dissociates from the TRAF6-TAK1-TAB1-TAB2 complex, initiating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways and regulating the expression of downstream proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and cyclooxygenase 2.

(Data source: Chiu JW, et al. Cells. 2021)
The role of IL1A in cancer
IL1A is a dual-function cytokine that exerts both anti-tumor and pro-tumor effects in various cancers. For example, in breast cancer, IL1A can promote cancer progression by increasing cell proliferation and inducing TSLP expression in tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells, thereby enhancing cancer survival and metastatic spread. It also increases NF-κB and STAT3 activation to generate and maintain cancer stem cells. However, IL1A inhibits cell growth in the G0/G1 phase and, through IL-1R, suppresses cell proliferation, thereby exerting a cancer-suppressing effect.
In HCC , IL1A promotes cancer development by activating inflammation and compensatory proliferation in the liver and suppresses cancer by promoting the activation of T cells and NK cells.
In pancreatic cancer, IL1A can consistently activate NF-κB to induce metastatic behavior and maintain the expression of inflammatory factors in the tumor microenvironment, which is beneficial to tumor survival.


(Data source: Chiu JW, et al. Cells. 2021)
Targeted therapy for IL1A
Current targeted therapies for IL1A primarily include monoclonal antibodies, small molecule inhibitors, bispecific antibodies, and fusion proteins. Currently, only one fusion protein has been approved for marketing, while other drugs are still under clinical investigation.
Rilonacept is a fusion protein targeting IL-1α and IL-1β for the treatment of recurrent pericarditis. It was approved by the FDA in 2008. On December 10, 2024, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) website announced that rilonacept for injection, produced by Sino-US Huadong Medicine, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Huadong Medicine, had received approval for a new indication for the treatment of recurrent pericarditis (RP) in adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older, as well as for reducing the risk of recurrence. The drug was first approved for marketing in China in November 2024.
Lutikizumab is a bispecific antibody developed by AbbVie that targets IL-1α and IL-1β for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa, psoriatic arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It is currently in Phase 3 clinical trials.
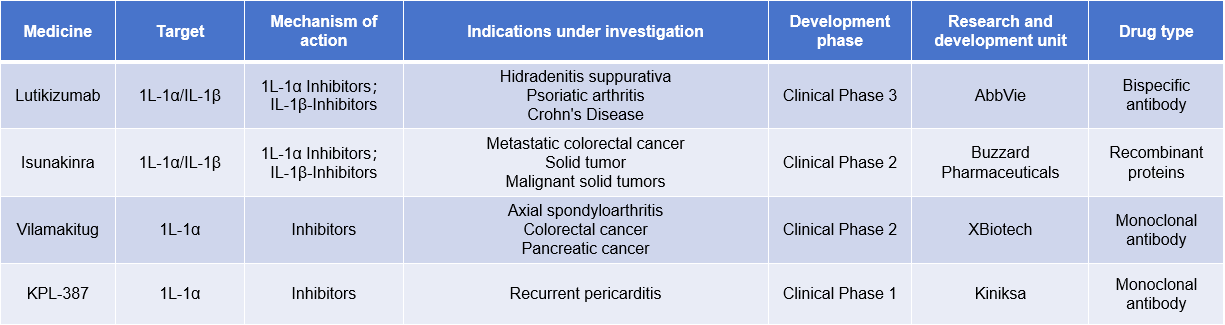
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
