Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) is a transmembrane receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily, primarily expressed on microglia in the brain and macrophages in the periphery. TREM2 participates in a variety of biological functions, including cell maturation, cell proliferation, cell survival, phagocytosis, and inflammation regulation. It is a major pathology-induced immune signaling hub and plays a crucial role in neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and cancer.
The structure of TREM2
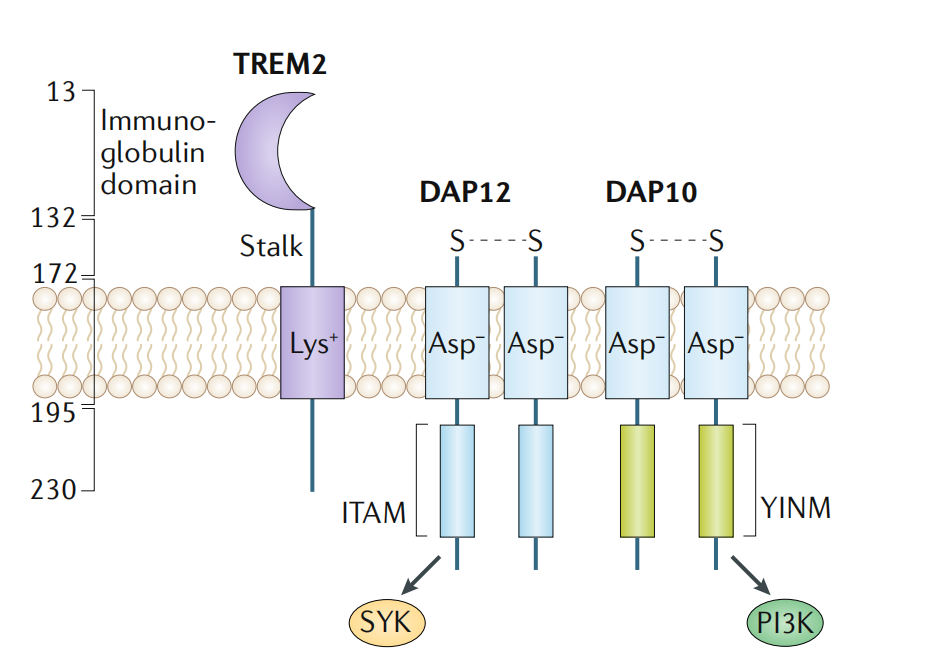
The TREM2 gene is located on human chromosome 6-P21 and consists of 230 amino acids. It is a single-pass transmembrane protein. The TREM2 extracellular region includes a V-type immunoglobulin domain and a short stalk region, followed by a transmembrane domain (containing charged lysine residues) and a short intracellular domain without a signal transduction motif.
TREM2 is cleaved at histidine 157-serine 158 by α-secretases (such as ADAM10 and ADAM17) to release sTREM2, and the resulting transmembrane fragment is further degraded by γ-secretase.
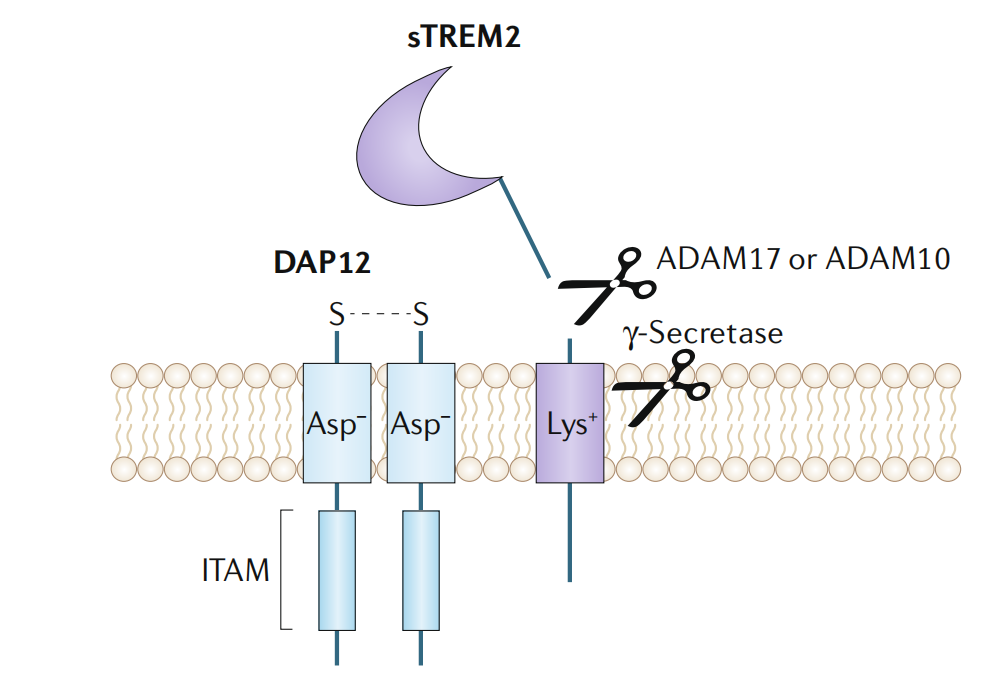
(Data source: Ulland TK, et al. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018)
TREM2 signaling pathways and regulation:
Upon binding of the TREM2 ligand to TREM2, TREM2 interacts with the adaptor proteins DNAX activating protein 12 (DAP12 ) and DAP10 through oppositely charged residues, forming the TREM2-DAP12/DAP10 heterodimer. TREM2 is induced through the interaction between lysine (Lys) in its transmembrane region and aspartic acid (Asp) in DAP12. The TREM2-DAP12 signaling pathway propagates through the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of DAP12, leading to the activation of the tyrosine protein kinase SYK. The primary kinase recruited by the ITAM region of DAP12 is spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK), which activates downstream signaling molecules such as PI3K, Akt, mTOR, ERK, and JNK, ultimately leading to cell activation, cell survival, and increased intracellular calcium levels.

(Data source: Qiu H, et al. Front Immunol. 2021)
TREM2 and disease
TREM2 is a known risk gene for Alzheimer's disease. Specific TREM2 variants, such as TREM2 R47H, are associated with an increased risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Under stress or pathological stimulation, microglia activate mTOR in a TREM2 -dependent manner to meet increased demands for energy and protein synthesis. TREM2 is crucial for controlling lipid homeostasis in microglia. TREM2 activation can enhance microglial phagocytosis, help reduce amyloid accumulation in the brain, and thus mitigate the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.

(Data source: Schlepckow K, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2023)
In the TME, TREM2 is highly expressed in myeloid cells such as DCs, immunosuppressive macrophages, and monocytes. Activation of TREM2 can promote the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive functions of TAMs, which may contribute to tumor immune escape and progression. Inhibition of TREM2 can induce DCs to produce more type I IFNs.
In terms of macrophage regulation, TREM2 deficiency and anti-TREM2 mAbs can promote the transformation of macrophages to the M1 phenotype, which has anti-tumor functions. They also significantly induce the secretion of IL-12, IL-6, IL-15, and TNF, and reduce the levels of IL-10, TGF-β, CXCL10, CXCR3, MMP-2, and MMP-9. TREM2 deficiency and anti-TREM2 monoclonal antibodies also significantly promote the proliferation and activation of CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells expressing PD-1, and may increase tumor responsiveness to anti-PD-1 treatment. TREM2 reshapes the TME, promotes tumor regression, and enhances the efficacy of immunotherapy.

(Data source: Qiu H, et al. Front Immunol. 2021)
TREM2 targeted therapeutic strategies
TREM2 has emerged as a key signaling hub in Alzheimer's disease (AD), metabolic syndrome, and cancer, which are among the most lethal and costly medical conditions in the Western world and for which effective treatments are urgently needed. There are many potential interventions targeting the TREM2 pathway as a therapeutic target.
Activating the TREM2 signaling pathway: By targeting the receptor's active domain, agonist monoclonal antibodies or small molecule drugs can activate TREM2, enhancing its downstream signaling, thereby improving the phagocytic function and anti-inflammatory effects of immune cells. This strategy has attracted much attention in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease .
Inhibition of the TREM2 signaling pathway: In cancer, blocking TREM2 signaling or depleting TREM2+ myeloid cells in the tumor microenvironment can allow the reactivation of T cell-mediated anti-tumor immune responses. Anti-TREM2 antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) or monoclonal antibodies that act as TREM2 antagonists are emerging promising directions for reversing the myeloid immune suppressive environment and cancer immunotherapy.
Regulatory TREM2 ligands: TREM2 ligands that are specific to specific conditions and/or tissues could help regulate TREM2 activity.
Intervention targeting the TREM2 cleavage process: TREM2 can be cleaved by ADAM protease family members such as ADAM10 and ADAM17 to produce sTREM2. By inhibiting this process, the level of TREM2 on the cell surface can be increased, which may enhance its signaling.
Intervention targeting downstream molecules of the TREM2 signaling pathway: Although TREM2 downstream molecules such as DAP12, DAP10, SYK, PI3K, Akt, and mTOR are also involved in many other signaling pathways, intervention targeting these molecules may help regulate the biological effects of TREM2.

(Data source: Deczkowska A, et al. Cell. 2020)
TREM2-targeted therapy
There are currently few antibody drugs targeting TREM2 in clinical development, and they are mainly focused on the treatment of neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.
VGL-101 is a human monoclonal antibody targeting TREM2 developed by Vigil Neuroscience for the treatment of rare microglial diseases.
AL-002 is a monoclonal antibody targeting TREM2 developed by Alector for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and is currently in Phase 2 clinical trials.
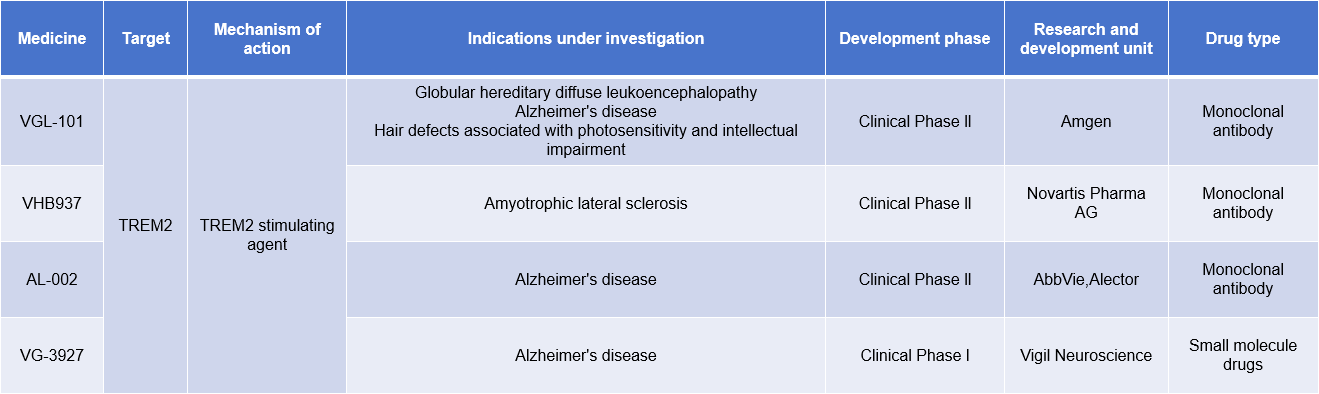
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
