ANGPT2, also known as ANG-2, is an angiopoietin that binds to TEK/TIE2, competing for ANGPT1 binding sites and modulating ANGPT1 signaling. Ang2 binds to the TIE2 receptor with the same affinity, inducing its antagonistic effects, but does not bind to TIE1. ANGPT2 is widely involved in angiogenesis, bone physiology, adipose tissue physiology, and pathological conditions such as inflammation, cardiac hypertrophy, rheumatoid arthritis, and tumors.
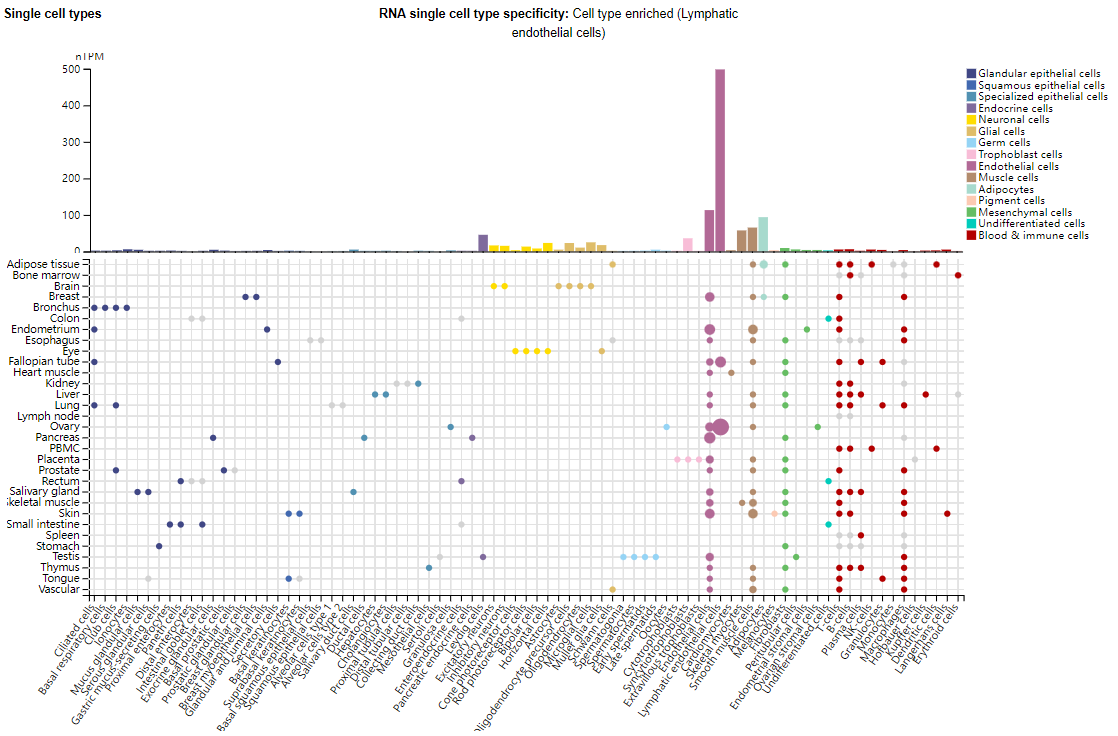
ANGPT2 expression distribution
ANGPT2 is mainly expressed in lymphatic endothelial cells, and is also expressed in muscle cells, adipocytes, and endocrine cells.
(Data source: Uniprot)
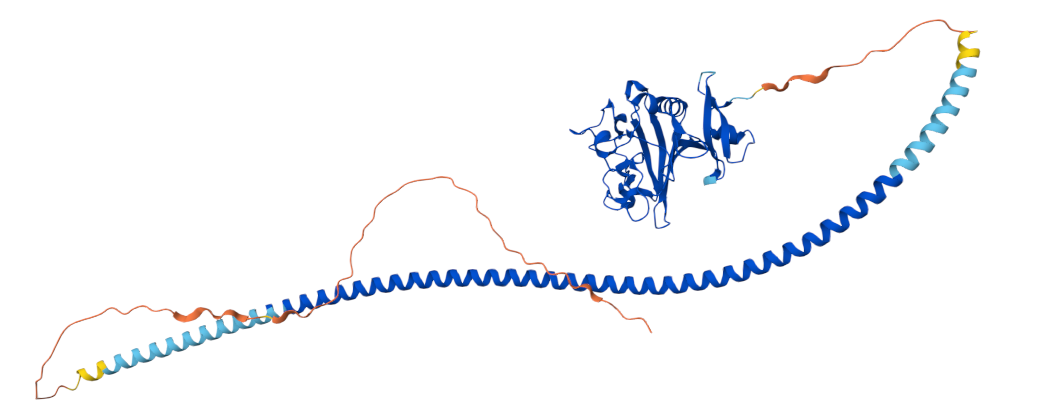
Structure of ANGPT2
ANGPT2 is a secreted protein composed of 496 amino acids that shares approximately 60% amino acid identity with Ang1 and lacks one of the nine cysteines found in mature Ang1. An N-terminal coiled-coil domain, also present in ANGPT1, may play a role in protein dimerization or multimerization. A C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain is crucial for ANGPT2 binding to the TIE2 receptor.
(Data source: Alphafold)
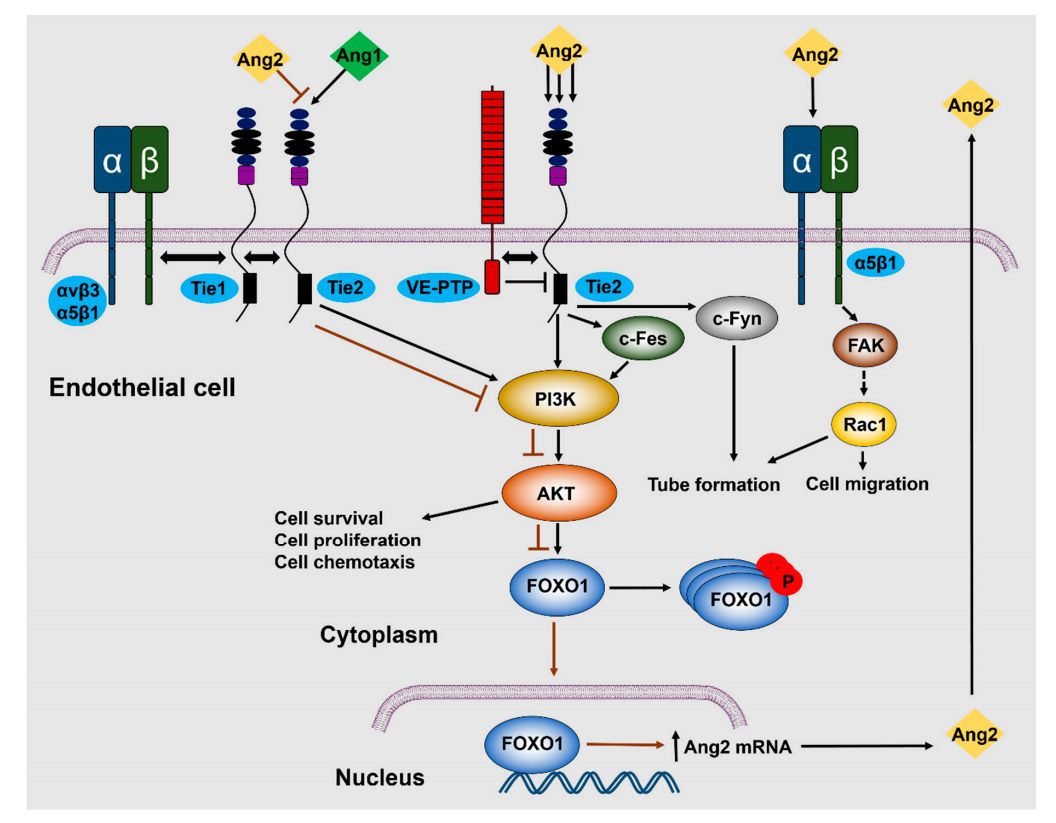
Regulation of ANGPT2 signaling
At high concentrations, ANGPT2 interacts with TIE2 , acting as both an antagonist and an agonist . In the absence of ANGPT1, ANGPT2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of TEK/ TIE2 , thereby activating the p85 subunit of PI3K and phosphorylating Akt at Ser473, ultimately promoting cell survival and proliferation. In the absence of angiogenic inducers such as VEGF, ANGPT2-mediated loosening of cell-matrix contacts may induce endothelial cell apoptosis, leading to vascular regression. ANGPT2, acting synergistically with VEGF, promotes endothelial cell migration and proliferation, acting as a permissive angiogenic signal and participating in the regulation of lymphangiogenesis.
(Data source: Akwii RG, et al. Cells. 2019)
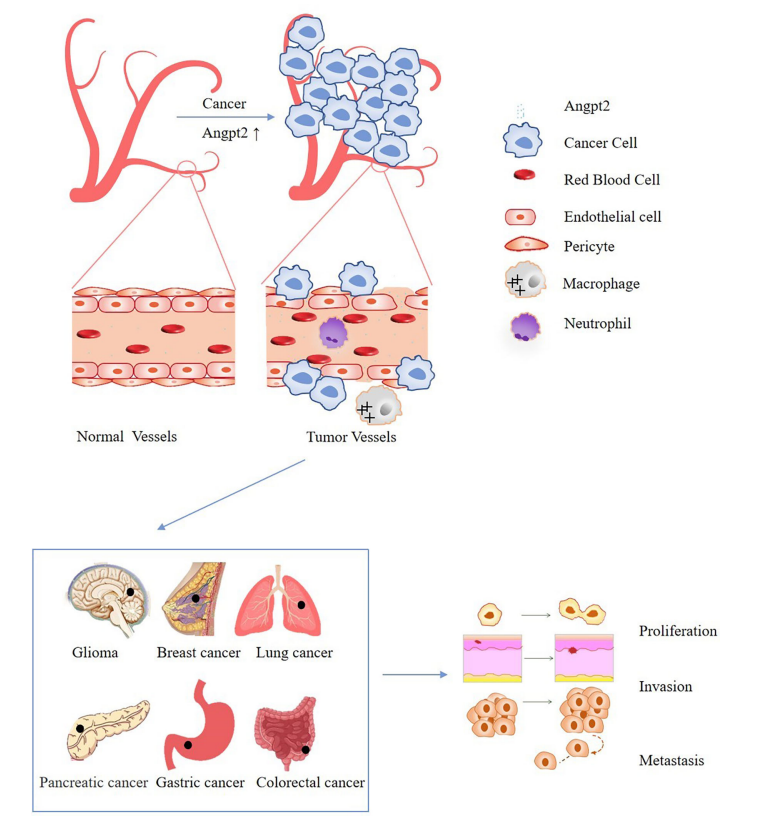
ANGPT2 and cancer
Elevated Ang2 levels in cancers lead to vascular instability, increased vascular permeability, and restricted immune cell trafficking, ultimately promoting cancer proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Examples include gastric cancer, lung cancer, glioblastoma, and colorectal cancer.
(Data source: Liu N, Liu M, Fu S, et al. Front Immunol. 2022)
Targeted therapy for ANGPT2
Current therapeutic strategies targeting ANGPT2 primarily rely on ANGPT2 inhibitors. Faricimab, a bispecific antibody currently on the market, targets Ang2/VEGF-A. By blocking VEGF-A, it inhibits abnormal angiogenesis and leakage. Simultaneously, neutralizing Ang-2 helps stabilize blood vessels and reduce inflammation. It is primarily used to treat conditions such as retinal vein occlusion, retinal vein occlusion-associated macular edema, and age-related macular degeneration.
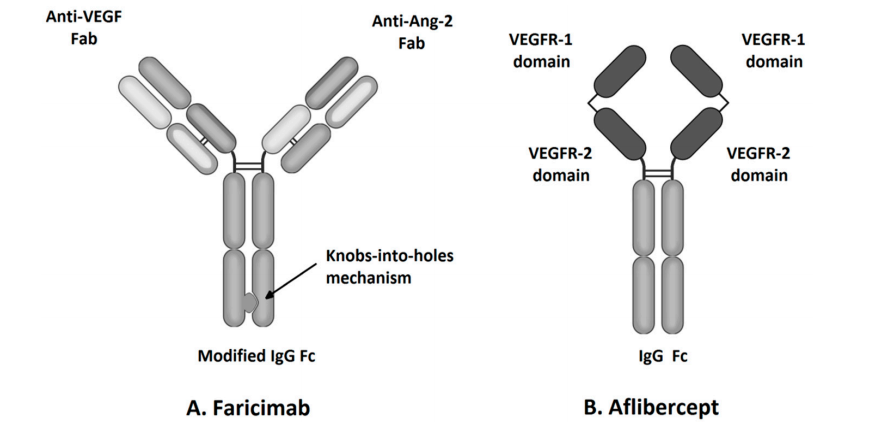

(Data source: Liberski S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022)
BI - 836880 was originally developed by Ablynx NV and later licensed to Boehringer Ingelheim for further development and clinical trials. BI - 836880 is a novel bispecific nanobody with VEGF- and Ang2-binding domains similar to those of Faricimab, as well as an albumin-binding domain for extended half-life. It is currently in Phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of advanced cancers, solid tumors, and wet age-related macular degeneration.
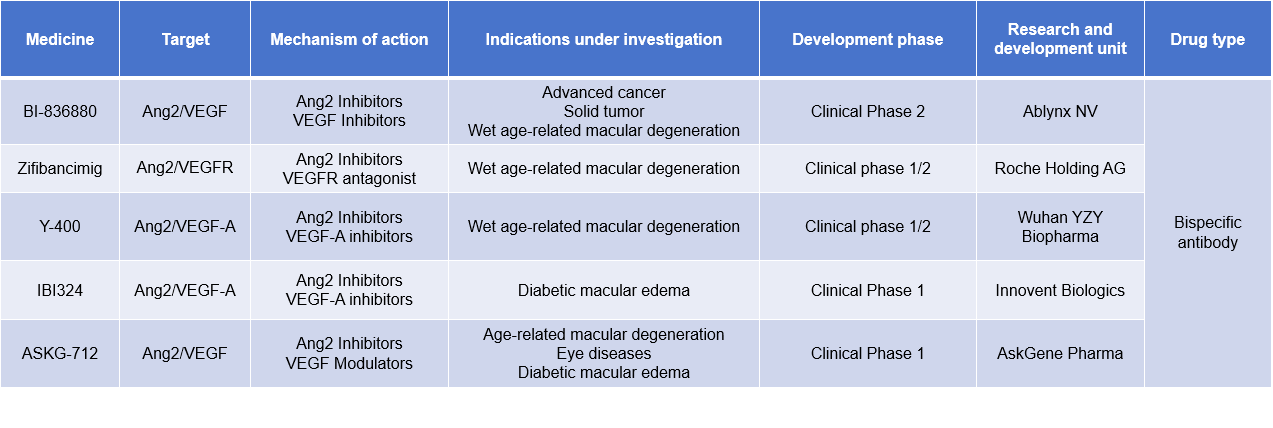
(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
