IL23A is the α subunit of interleukin-23 , also known as IL-23p19. It combines with IL12B to form the proinflammatory cytokine IL-23, which plays distinct roles in innate and adaptive immunity. Released by antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells and macrophages, it binds to a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R. The IL-23 signaling pathway drives chronic human diseases and is crucial to the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases, including ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn's disease (CD), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Expression distribution of IL23A
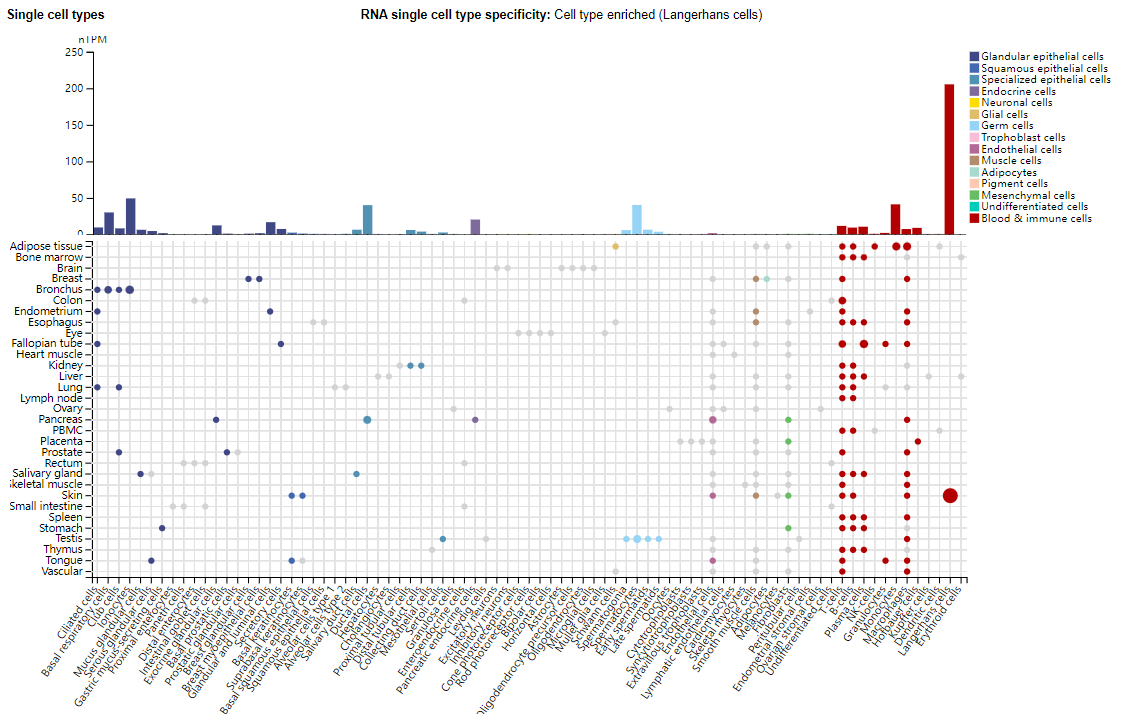
IL23A is mainly expressed in macrophages, dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, and is also expressed in glandular epithelial cells and specialized epithelial cells.
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of IL23A
IL23A is a secreted protein composed of 189 amino acids and four α-helices. It forms a dimer with the IL-12p40 subunit through disulfide bonds to form IL23. The IL-23 receptor complex consists of IL-23R and IL-12Rβ1. The IL-12p40 subunit binds to IL-12Rβ1, while the IL-23p19 subunit binds to IL-23R, initiating intracellular signaling.

(Data source: Glassman CR, et al. Cell. 2021)
IL23 signaling pathway and regulation
IL23 binds to the receptor complex, activating JAK2 and TYK2. These receptors then phosphorylate to form docking sites, leading to the phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT4. The IL23 signaling pathway promotes the proliferation and differentiation of T helper 17 (Th17) cells, which produce IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22, tumor necrosis factor ( TNF ) α, IFNγ, and IL-26. These cells are key players in autoimmunity and play a crucial role in the development of autoimmune diseases.

(Data source: Jairath V, et al. Lancet. 2024)
Targeted therapy for IL23A
Blocking IL-23A can reduce the activation and proliferation of Th17 cells, which play a key role in autoimmune responses. Currently, four monoclonal antibody drugs targeting IL23A (IL23p19) have been approved for marketing: Mirikizumab, ABBV 066 ( Risankizumab-RZAA ), Tildrakizumab-ASMN, and Guselkumab. Numerous inhibitors targeting IL23p19 are also in clinical development.
Guselkumab (TREMFYA), developed by Johnson & Johnson, was first approved in the United States in July 2017 for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and in July 2020 for the treatment of adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis. TREMFYA is the first and only approved fully human bispecific monoclonal antibody that blocks IL-23 and simultaneously binds to the receptor CD64 on IL-23-producing cells.

(Data source: Tremfyahcp)
Mirikizumab (Omvoh) is a humanized IgG4 anti-human IL-23p19 monoclonal antibody approved for marketing in 2023. It selectively targets the p19 subunit of IL-23 and inhibits the IL-23 pathway for the treatment of ulcerative colitis.

(Data source: Lilly)
Picankibart ( IBI112 ), a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-23p19 developed by Innovent Biologics, has received acceptance for its National Drug Application (NDA)/BLA by the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) of the China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. The study successfully met its primary and all key secondary endpoints in May 2024, demonstrating that the proportion of subjects achieving skin clearance and improved quality of life in the Picankibart group was significantly higher than in the placebo group. Picankibart demonstrated an overall favorable safety profile during the study period, with no new safety signals identified. IBI112 has the potential to provide a more effective, longer-dose treatment option for patients with psoriasis, ulcerative colitis, and other autoimmune diseases.
JNJ 4804 is a combination therapy of TNF antibody Glolimumab and IL-23 antibody Guselkumab for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease and is currently in Phase 2 clinical trials.

(Data source: New Drug Intelligence Database)
