CD19, a B-lymphocyte antigen (CD19), acts as a co-peptide of the B-cell antigen receptor complex (BCR) on B lymphocytes. CD19 is a biomarker for normal and neoplastic B cells, as well as follicular dendritic cells. CD19 establishes intrinsic B-cell signaling thresholds by regulating both B-cell receptor (BCR)-dependent and -independent signaling. CD19 plays a crucial role in the treatment of relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
CD19 expression distribution
CD19 is primarily expressed in B cells and plasma cells. It is also expressed in germ cells, such as early spermatocytes. It is not expressed in T cells. Unlike CD20, CD19 is expressed at all stages of B cell maturation.
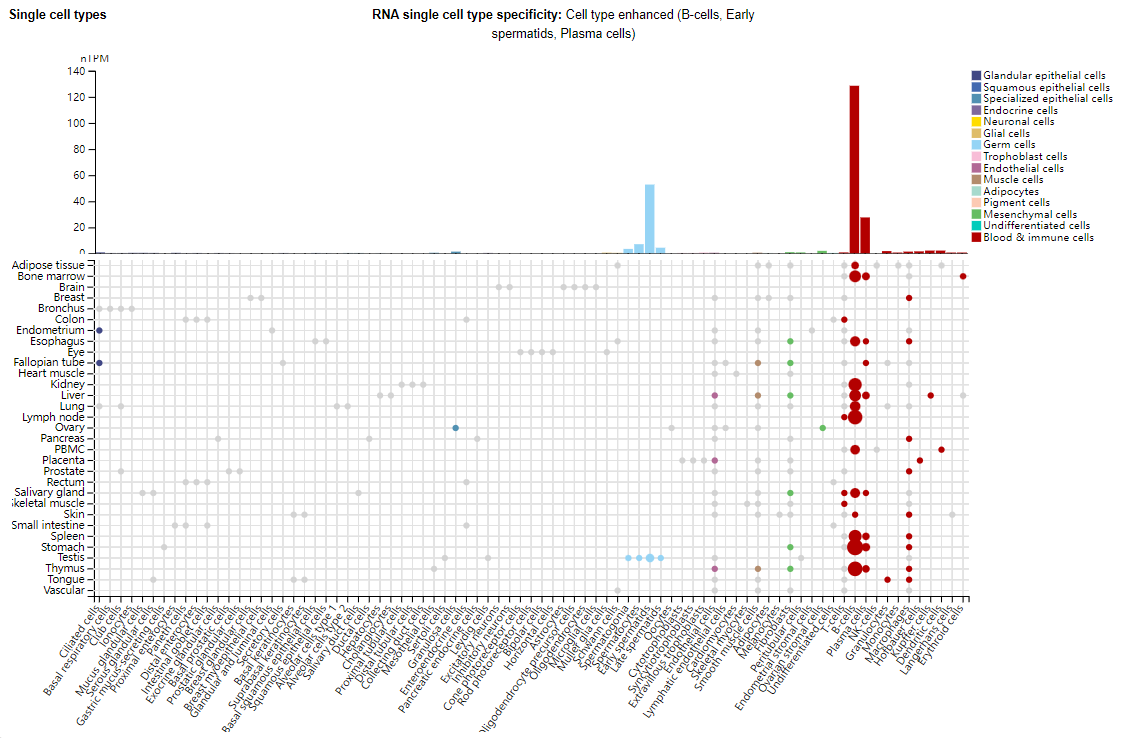
(Data source: Uniprot)
The structure of CD19
CD19 is a membrane protein encoded by the CD19 gene located on chromosome 16p11.2. It consists of 556 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 95 kDa. It has a single transmembrane domain, an intracellular C-terminus, and an extracellular N-terminus. The extracellular element contains two C2-type immunoglobulin-like domains separated by a smaller, potentially disulfide-linked non-immunoglobulin-like domain and an N-linked carbohydrate binding site. The intracellular C-terminal domain has multiple tyrosine residues.

(Data source: uniprot)
Function and targeted therapy of CD19
CD19 serves as a key co-receptor for BCR signaling. It forms a signaling complex with CD21, CD81, and CD225. Because BCR signaling requires protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) activation, CD19 recruits and amplifies the activation of SRC family protein tyrosine kinases, such as Lyn and Fyn. Following BCR activation, CD19 also enhances BCR-induced signaling by recruiting and activating PI3K and the downstream Akt kinase. CD19 signaling is crucial for normal B cell function, including B cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation into plasma cells and memory B cells. It also plays a role in antibody production and maintaining immune homeostasis.
The expression of CD19 in most B-cell malignancies makes it an ideal target for lymphoma treatment. Currently available CD19-directed therapies for the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (R/R DLBCL) include tafasitamab, loncastuximab tesirine, and CAR-T products, which have different mechanisms of action.

Tafasitamab is an Fc-enhanced humanized anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody that exerts its immunotherapy effects by mediating antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis. Tafasitamab can be used in combination with the immunomodulator lenalidomide, which has anti-tumor, anti-angiogenic, and erythropoietic properties. In the Phase II L-MIND study, the overall response rate (ORR), complete response rate (CRR), and median progression-free survival (mPFS) of patients treated with tafasitamab were 60%, 43%, and 12.1 months, respectively.
Loncastuximab tesirine is an antibody-drug conjugate that, when evaluated in the Phase II LOTIS-2 trial, demonstrated an objective response rate (ORR) of 48.3%, with 24% of patients achieving a complete response (CR) and a median overall survival (mOS) of 9.5 months.
Tisa-cel is an anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy with a 4-1BB co-stimulatory domain. In the Phase II JULIET study, tisa-cel demonstrated an objective response rate (ORR), complete response rate (CRR), and median overall survival (mOS) of 52%, 40%, and 8.3 months, respectively. Similar results were obtained in the long-term JULIET analysis. In the Phase III BELINDA trial, tisa-cel was found to be non-superior to standard of care (SOC), with a median event-free survival (mEFS) of 3 months in both arms.
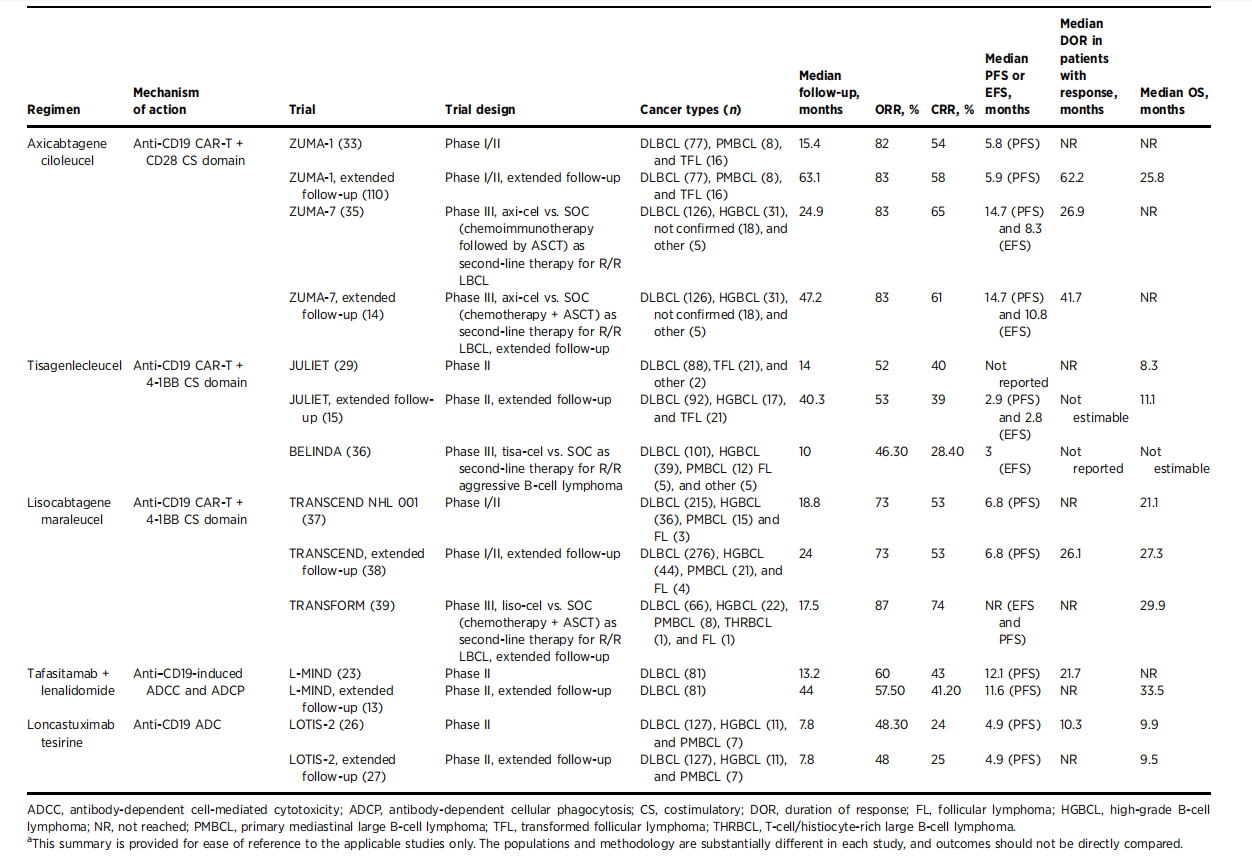
(Data source: Lownik J, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2024)
