Background
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is a transmembrane glycoprotein consisting of extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular domains. HER2 overexpression is associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer and suppresses immune cell activity, thereby inhibiting anti-tumor immunity. Trastuzumab (DB00072) is a humanized, recombinant, full-size antibody that binds to the HER2 extracellular domain IV and has diagnostic and therapeutic efficacy in breast cancer. However, its long blood retention and slow tumor penetration limit its application in certain settings.
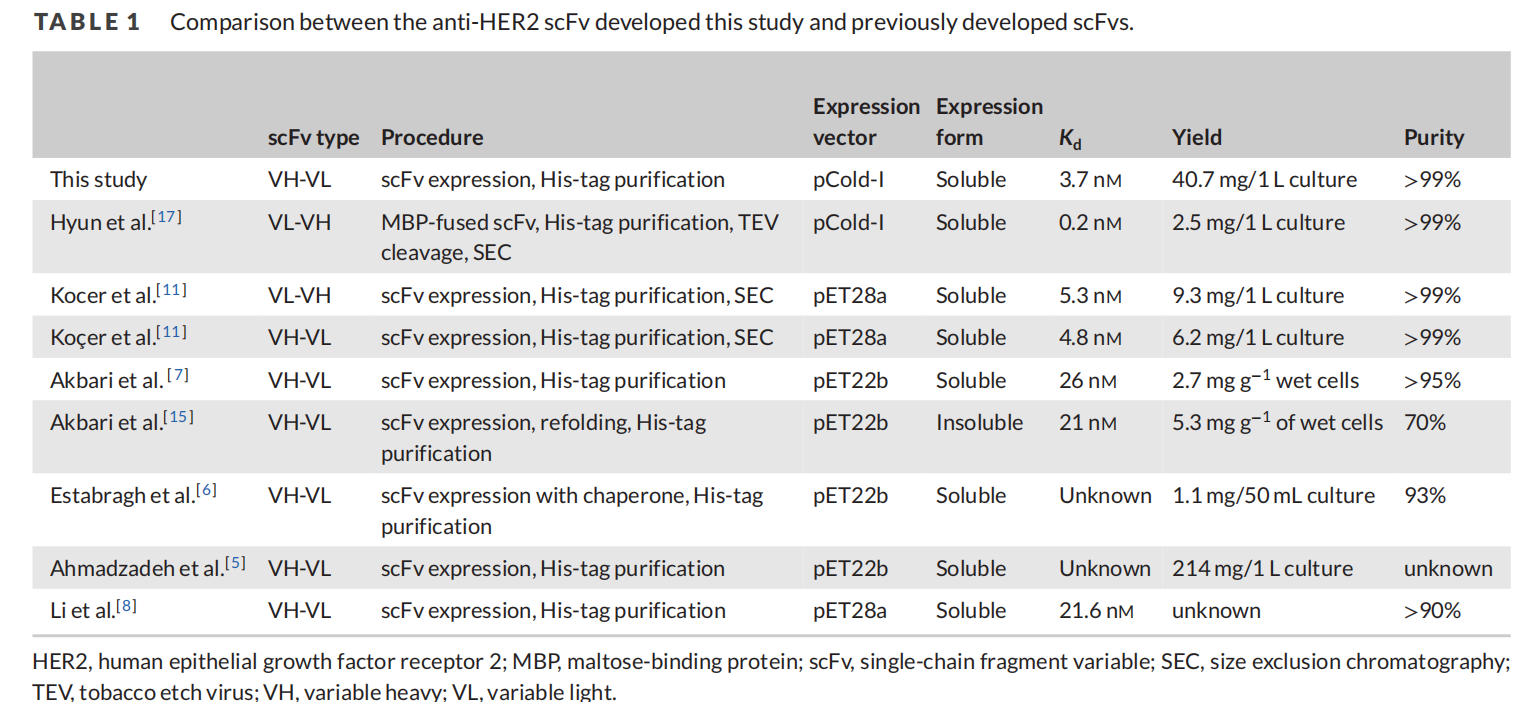
On July 16, 2024, researchers published a study titled "Efficient generation of recombinant anti-HER2 scFv with high yield and purity using a simple method" in the Biotechnology journal. The study developed a method for producing a soluble form of a single-chain fragment (scFv) targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in Escherichia coli. By optimizing the orientation of the variable heavy domain (VH) and variable light domain (VL) as well as the His tag, an HL-His type antibody with the highest HER2 binding activity was identified.

Construction of scFv plasmids
Based on the importance of domain orientation of monoclonal antibody scFv for yield and HER2 binding efficiency and the fact that the position of the His tag can affect the three-dimensional structure, solubility and function of the protein, four scFvs with different variable domain orientations and His tag positions were constructed, and four plasmids were designed: LH-His, His-HL, HL-His and His-HL.
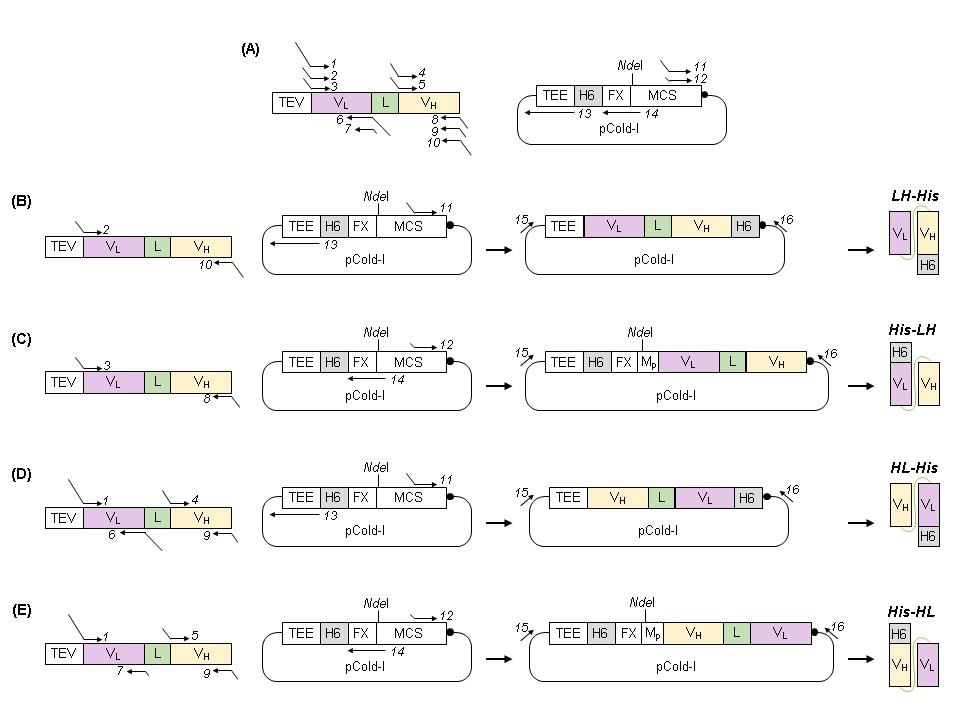
Expression and purification of scFv
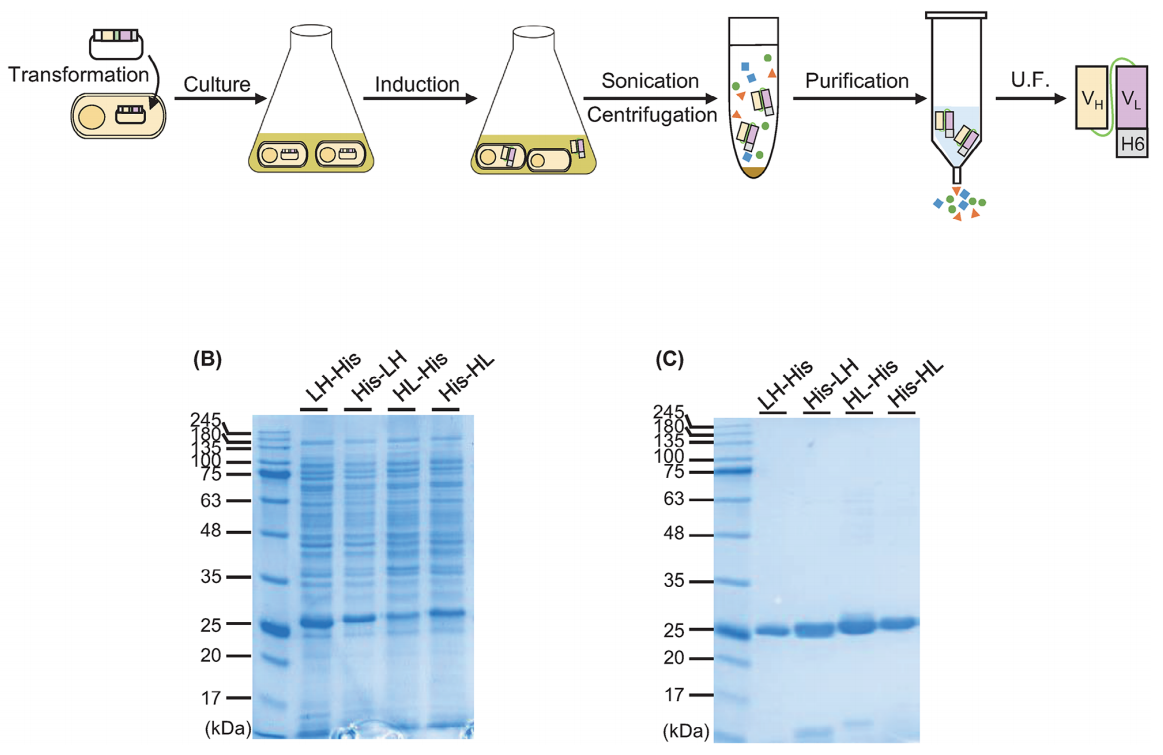
Using BL21 (DE3) E. coli cells for expression, the scFvs were expressed in a soluble form. The expected sizes of LH-His, His-HL, HL-His, and His-HL were 27.5, 28.2, 27.5, and 28.2 kDa, respectively. The yields of LH-His, His-HL, HL-His, and His-HL in 1 L of culture were 20.3, 40.8, 40.7, and 36.9 mg, respectively. Furthermore, after Ni-NTA purification alone, the purity of all four proteins reached over 99%, eliminating the need for further purification steps such as size exclusion chromatography or additional IMAC techniques.
Binding of HER2 protein to scFvs
An ELISA using HER2 protein as an antigen verified the antigen-binding efficiency of scFvs with different His-tag orientations. LH-His, HL-His, and His-HL exhibited antigen concentration-dependent absorbance signals, with no observed signal enhancement for His-LH. HL-His exhibited the highest affinity of the four scFvs. This may be because the N-terminal His-tag is close to the antibody binding site, hindering the interaction between the antibody and the antigen, or because although the scFv binds to the antigen, the secondary antibody (HRP-labeled anti-His-tag antibody) is unable to bind to the His-tag.

Simplifying scFv production
The entire process used to generate purified scFv includes protein expression, purification, and ultrafiltration, and lasts for 5 days. To expedite the process, the scFv was used directly for ELISA without purification or UF steps. After 20% glycerol was frozen and stored at -20°C, the antigen binding efficiency of the scFv did not change significantly, and it remained stable during freezing cycles. The addition of glycerol did not adversely affect the antigen binding efficiency of the scFv, and high protein concentrations were required when using glycerol for storage. Both unpurified scFv and His-tag purified scFv maintained antigen binding, indicating that the washing steps in the ELISA process can remove additional proteins and reagents without affecting the antigen-antibody binding efficiency.

Binding of scFv to breast cancer cells
Fluorescently labeled scFvs were used to visualize the binding activity of scFvs to HER2+ breast cells, and the results showed that the generated HL-His had binding efficacy to HER2 on the cell surface. This highlights the potential of fluorescent scFvs in accurately detecting HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells, thereby providing a promising method for accurately identifying HER2+ breast cancer cells in patients.


Summarize
In this study, the authors developed an anti-HER2 scFv expressed in Escherichia coli, a C-terminal His-tagged HL format with high HER2 binding efficiency. The entire scFv production process can be completed in 4-5 days, and the process is simple, not requiring multiple purification steps. The yield exceeds that of other previously published anti-HER2 scFvs with the same variable domain sequence. The anti-HER2 scFv produced in this study has broad applications and has the potential to improve the accuracy of on-site breast cancer diagnosis. This scFv, produced through a simple process and exhibiting high HER2 binding activity, has great potential in immunoassays, as a diagnostic agent for detecting HER2-positive breast cancer, and as a breast cancer-specific drug in immunotherapy.