B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) both belong to the natriuretic peptide (NP) family. Concentrations of NT-proBNP and BNP increase in heart failure (HF). They are the most widely used biomarkers in the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure (HF) and cardiac dysfunction.
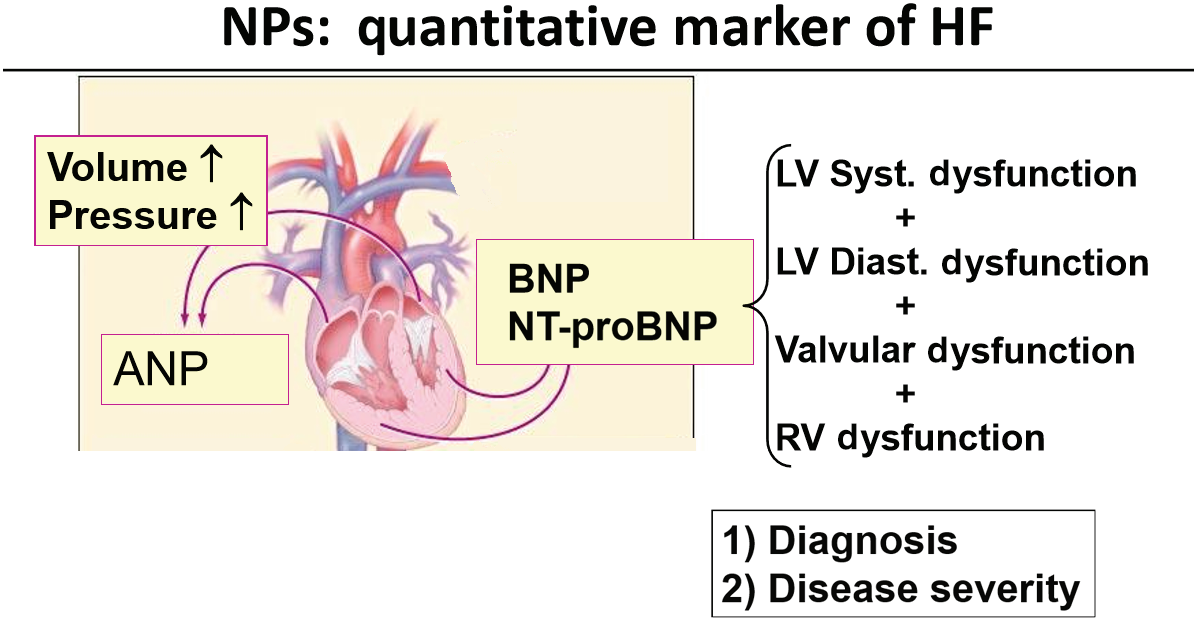
(Data source: Mueller C, et al. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019)
NT-ProBNP and BNP production
When myocardial cells are stimulated (such as mechanical stretching of the ventricles), they produce B-type natriuretic peptide (pre-proBNP), a protein containing 134 amino acids. 26 amino acids will then be shed to form a BNP precursor (proBNP) containing 108 amino acids. The BNP precursor is cleaved by endonucleases into NT-proBNP containing 76 amino acids and BNP containing 32 amino acids.

(Data source: Kim YS, et al. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019)
NT-ProBNP and BNP functions
NT-proBNP and BNP are both different splice forms of the proBNP polypeptide. Levels of both can reflect changes in cardiac function and can be used to assist in the diagnosis of heart failure, but their specific functional characteristics differ. BNP has a relatively short half-life of approximately 20 minutes; NT-proBNP has a relatively longer half-life of approximately 120 minutes and can rise continuously, resulting in higher concentrations in peripheral blood compared to BNP. BNP has biological activity, promoting sodium excretion and urination, reducing volume overload, lowering blood pressure, and exhibiting a strong vasodilatory effect. However, no biological activity has been demonstrated for NT-proBNP. BNP is unstable in vitro, while NT-proBNP is relatively stable.
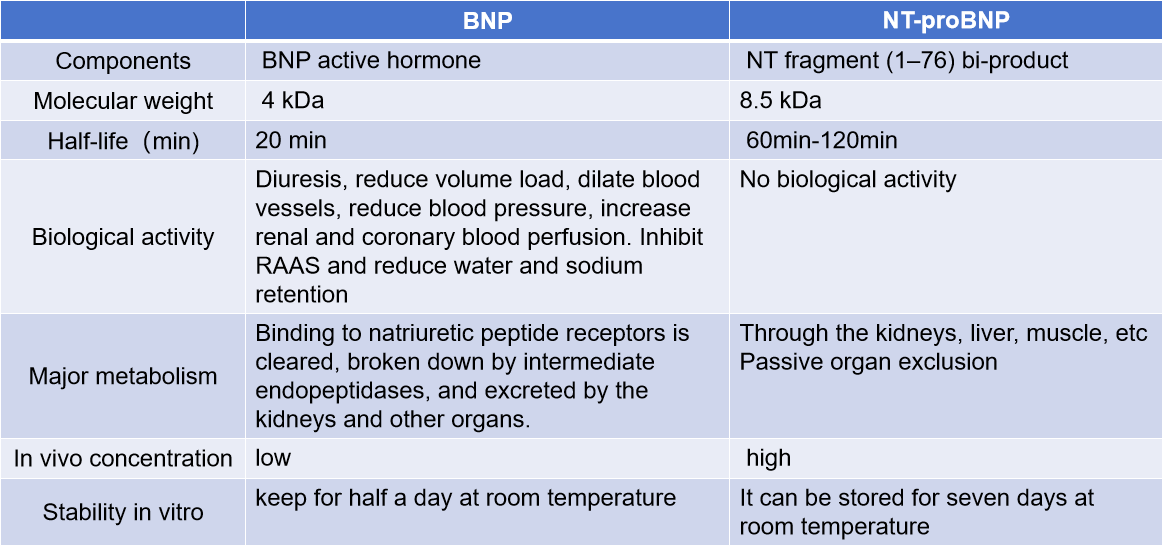
In addition, they are affected differently by heart failure treatment drugs. BNP is affected by neprilysin inhibitors (sacubitril/valsartan), and BNP levels may increase; after treatment with sacubitril/valsartan or the initial treatment phase of B-receptor blockers, BNP concentrations increase, and BNP results are affected by recombinant BNP in the body. NT-proBNP is not a substrate of neprilysin, and its concentration rarely increases after treatment with neprilysin inhibitors. It is also less affected by human recombinant BNP.
Clinical value
Clinical diagnosis of heart failure: BNP>100 pg/mL and NT-proBNP>300 pg/mL are the optimal cutoff values for diagnosing heart failure. BNP and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) concentrations in patients with asymptomatic heart failure tend to be higher than in healthy controls, but still lower than in patients with symptomatic heart failure. The use of NPs as diagnostic markers requires caution, as their concentrations also depend on other factors, including age, body mass index, or other conditions such as the presence of renal failure or inflammatory lung disease.

(Data source: Janjusevic M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021)
Prognostic assessment: NT-ProBNP and BNP levels are closely related to the severity of heart failure and the patient's prognosis. High levels of NT-ProBNP and BNP may indicate a poor prognosis.
Treatment of heart failure: Recombinant BNP is currently used in clinical practice to treat heart failure by exerting its diuretic, vasodilation, and RAAS inhibition effects.
Application in other diseases: In addition to heart failure, NT-ProBNP and BNP can also be used to diagnose and monitor other cardiovascular diseases, such as pulmonary hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and acute coronary syndrome.

(Data source: Cavalcante PN , et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023)
