HER3 is a human epidermal growth factor receptor (ERBB3). HER3 protein belongs to the ErbB/HER receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family and is expressed in many types of tumors. HER3 also promotes cell proliferation and is a potential target for tumor treatment.
HER3 expression
HER3 is expressed in a variety of cell types, including epithelial cells, glial cells, trophoblast cells, and some cancer cells, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, melanoma, head and neck cancer, cervical cancer, and prostate cancer.

(Data source: uniprot)
HER3 structure and activation
HER3 is encoded by the ERBB3 gene, located on human chromosome 12q13. It is a type I transmembrane protein of approximately 180 kDa. HER3 consists of a large extracellular domain (ECD), a hydrophobic transmembrane segment, and an intracellular domain, which includes a juxtamembrane region, a tyrosine kinase segment, and a tyrosine-rich carboxyl-terminal tail. The extracellular domain is composed of four subdomains, designated subdomains I-IV. Physiological activation of HER3 is triggered by interaction with neuregulin (NRG). In the absence of ligand, direct intramolecular interactions between subdomains II and IV maintain an inactive (closed or tethered) conformation of HER3. Ligand binding to subdomains I and III induces structural changes in the extracellular domain of the receptor, resulting in an open conformation that exposes the dimerization arm. Consequently, the receptor can dimerize with another member of the ERBB family in an open conformation (heterodimerization) or with another identical receptor (homodimerization).

(Data source: Gandullo-Sánchez L, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022)
HER3 signaling pathway and regulation:
Binding of NRG1-2 to HER3 induces conformational changes, leading to its preferential heterodimerization with EGFR and HER2. This leads to further conformational modifications in the intracellular domain, resulting in transphosphorylation of the C-terminal tail, and ultimately activates downstream intracellular signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT, MAPK, JAK/STAT, and SRC, regulating multiple cellular processes including cell division, proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, and tumor progression.

(Data source: Uliano J, et al. ESMO Open. 2023)
The role of HER3 in different cancers
Dimerization of HER3 with HER2 or EGFR is involved in resistance to multiple drugs in targeted cancer therapies. HER3 is also involved in multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and radiotherapy.

(Data source: Zeng H, et al. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024)
HER3-targeted therapy
There are many therapies targeting HER3, such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), bispecific antibodies (bAbs), antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and other therapies, such as HER3 vaccines.

(Data source: Gandullo-Sánchez L, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022)
Monoclonal antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies can inhibit ligand binding on the HER3 extracellular domain, block the kinase activity of the HER3 dimerization partner or its ability to dimerize with HER3, inhibit HER3 expression on the cell surface, or lock HER3 in an inactive conformation. Most HER3-targeting mAbs are currently being studied in preclinical and clinical trials. So far, multiple mAbs targeting HER3 have been discovered, with patritumab, seribantumab, and lumretuzumab being the most studied.
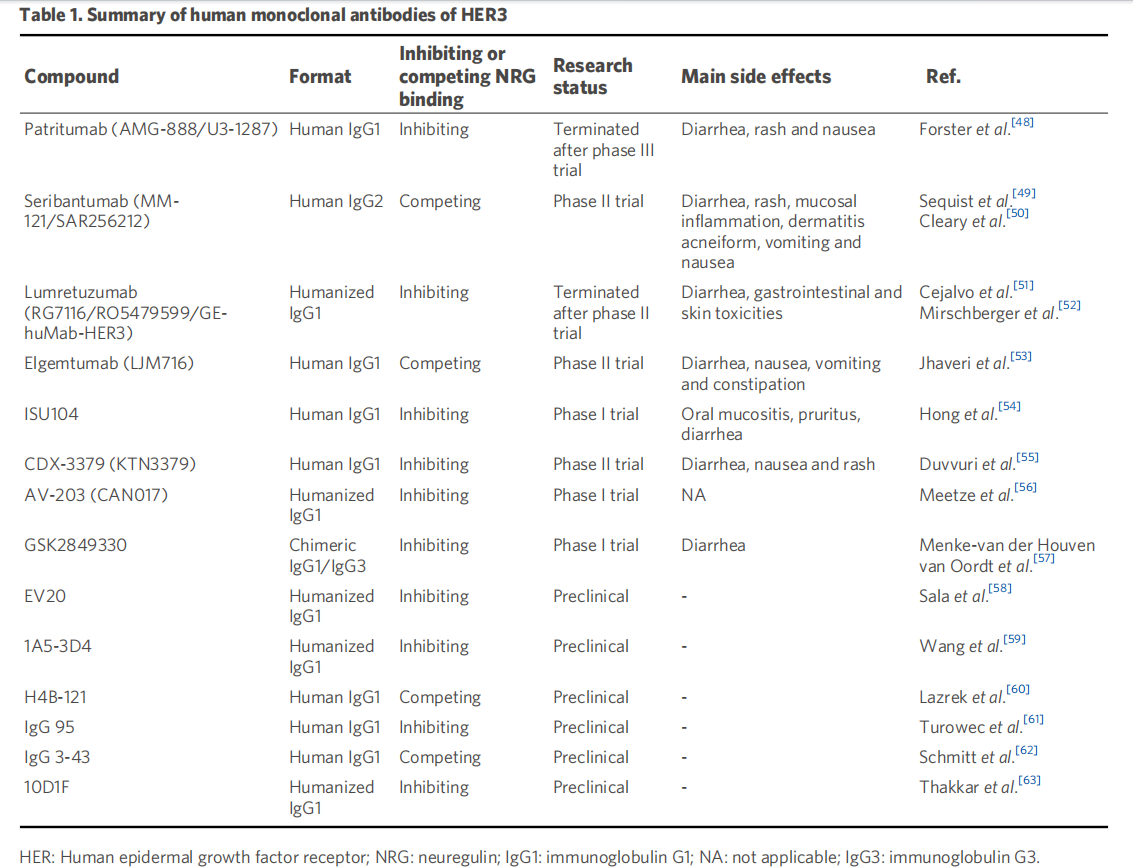
(Data source: Zeng H, et al. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024)
Bispecific antibodies: To overcome limitations and resistance to mAbs, various HER3 bsAbs are being studied in preclinical and clinical trials. Zenocutuzumab is a bispecific humanized IgG1 with two distinct Fab arms, one targeting domain I of HER2 and the other domain III of HER3. Duligotuzumab is a humanized IgG1 bsAb with two binding sites, one for EGFR or the other for HER3 subdomain III. Duligotuzumab has been shown to effectively block ligand binding and downstream signaling of EGFR and HER3, and to mediate ADCC.
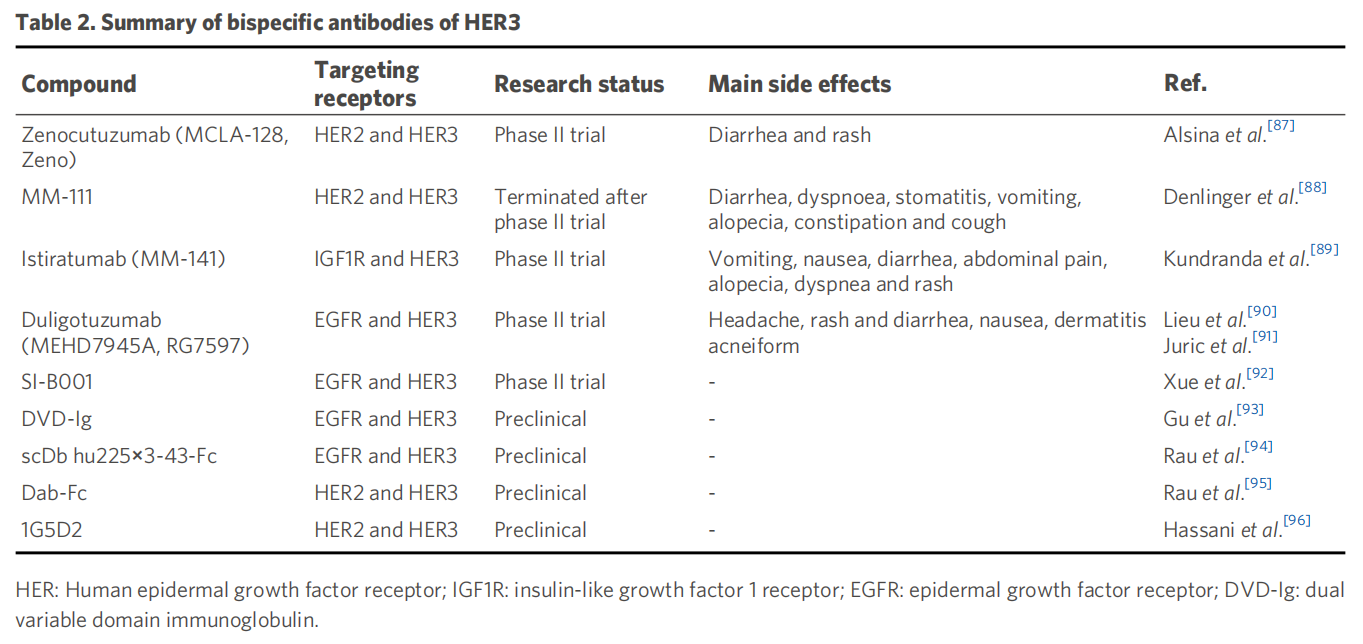
(Data source: Zeng H, et al. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024)
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs): ADCs utilize antigen-specific antibodies, offering tumor selectivity and efficacy unmatched by standard drugs. ADCs can promote receptor internalization and destruction, leading to cancer cell death. HER3-targeted ADCs have emerged as a promising candidate and have demonstrated potent anti-tumor efficacy in preclinical and clinical trials. U3-1402 is a HER3-targeted ADC composed of patritumab, a cleavable maleimide-GGFG peptide linker, and the topoisomerase I inhibitor deruxtecan (DXd) as a payload. U3-1402 is efficiently internalized, induces HER3 degradation, and exhibits growth inhibitory activity in HER3+ breast, gastric, and colorectal cancers.

(Data source: Zeng H, et al. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024)
HER3 vaccines: Studies have found that vaccines can trigger long-lasting anti-tumor immune responses that can be regularly enhanced. Therefore, vaccination may be an effective treatment for cancer. Several vaccines targeting HER3 have been developed, two of which are currently being tested in clinical trials. pING-hHER3FL is a circular DNA fragment that encodes the entire HER3 protein. Currently, pING-hHER3FL is in Phase I studies as an immunotherapy for HER3-positive malignancies. NCT04348747 uses a dendritic cell vaccine targeting HER2/HER3 in combination with pembrolizumab to boost the immune system, enhance tumor immune responses, and help shrink cancer. This vaccine has been shown to be effective in treating TNBC or HER2+ BC with brain metastases in Phase II clinical trials.
