Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is a secreted serine protease primarily synthesized in the liver. It primarily binds to the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) to promote its degradation, thereby reducing the clearance of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). In addition to the LDL-R, PCSK9 also binds to Toll-like receptors (TLRs) to mediate inflammatory responses and to SR-B receptors to promote platelet activation (PA) and thrombosis. PCSK9 inhibitors are primarily used clinically to treat hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis (AS), and related ischemic cardiovascular diseases.
Distribution of PCSK9
PCSK9 is expressed in type 2 alveolar cells, hepatocytes, pancreatic cells, neuroepithelial cells, and Kupffer cells. Under different physiological and pathological conditions, the expression level and activity of PCSK9 may change, thereby affecting an individual's lipid metabolism and risk of cardiovascular disease.
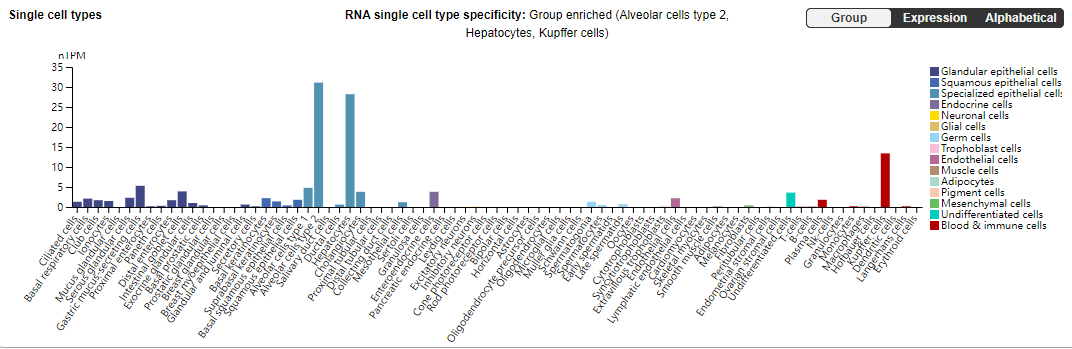
(Data source: uniprot )
Structure of PCSK9
PCSK9 consists of 692 amino acids and has three distinct domains: the prodomain (31–152 aa), the catalytic domain (153–421 aa), and the C-terminal Cys/His-rich domain (CHRD; 453–692 aa), each of which plays an important role in governing the biological functions of PCSK9 and its trafficking within the cell.

(Data source: Bao X, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024)
Function of PCSK9
Low-density lipoproteins are crucial for controlling low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in the blood. LDL-C is removed from the circulation through regulation. When PCSK9 is secreted from hepatocytes and binds to the LDLR on the cell surface, LDLR recycling to the cell surface is impeded. Due to the conformational change induced by PCSK9, LDLR cannot be recycled from endosomes back to the cell surface. Instead, the PCSK9-LDLR-LDL-C complex is transported to lysosomes for degradation. By promoting LDLR degradation, PCSK9 reduces cell surface LDLR levels and increases serum LDL-C.
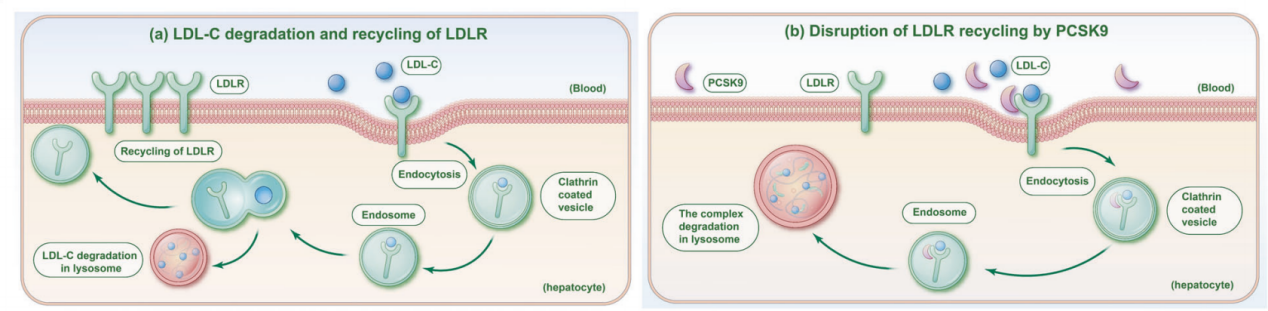
(Data source: Bao X, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024)
PCSK9 and diseases:
PCSK9 plays an important role in many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, liver disease, infection, autoimmune disease, neurocognitive disorders and cancer.
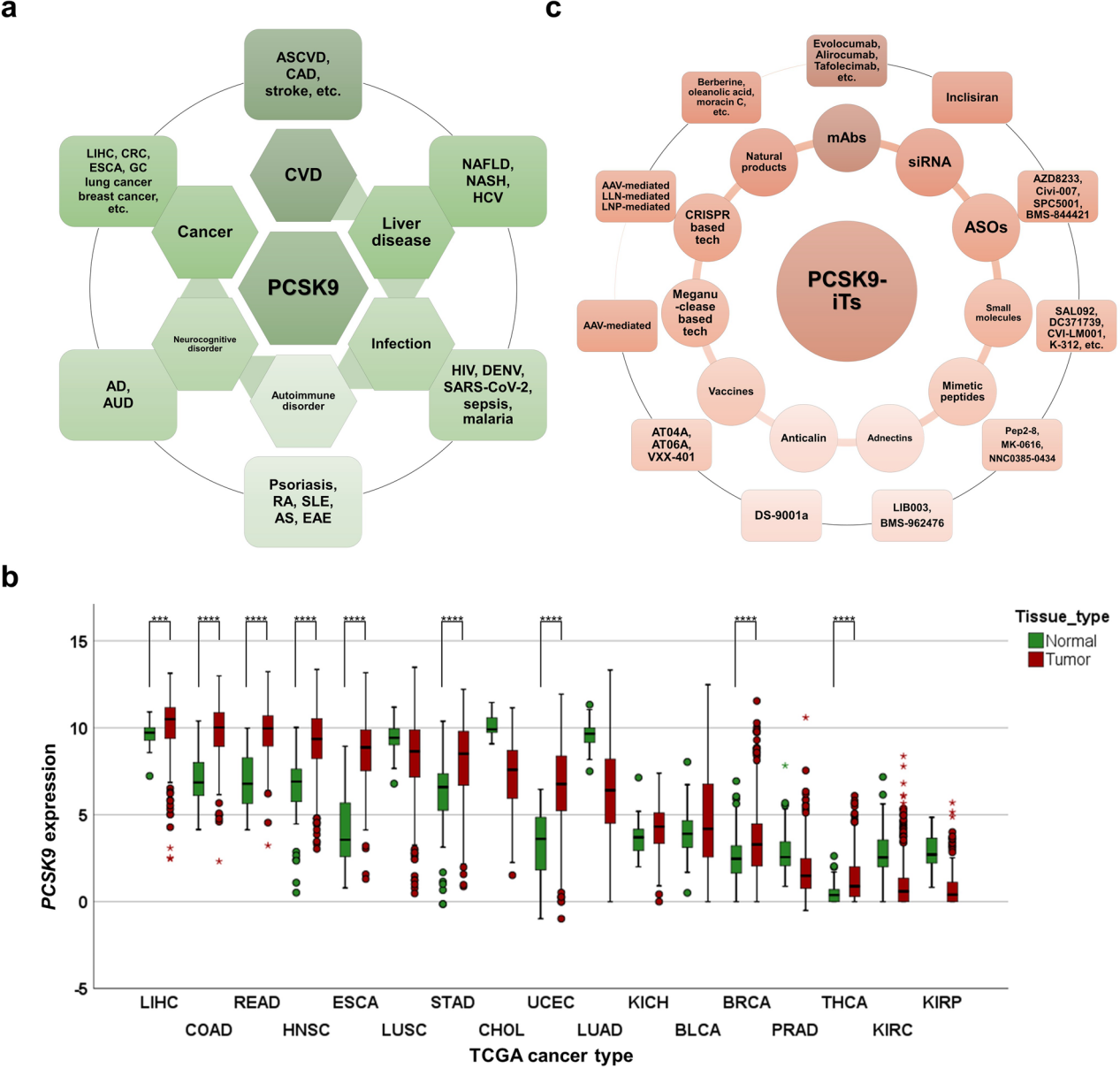
(Data source: Bao X, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024)
PCSK9 inhibitors
Since PCSK9 and its inhibitors were first discovered in 2003, a large number of preclinical and clinical studies have been conducted to investigate the function of PCSK9 in the past 20 years, culminating in the approval of three specific PCSK9 inhibitors, including three monoclonal antibodies (evolocumab and alirocumab, tafolecimab) and one RNA interference (RNAi).

(Data source: Bao X, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024.)
PCSK9 inhibitors are mainly divided into four categories: McAb inhibitors, nucleic acid drugs, small molecules, vaccines and drugs. The mechanisms of action of these inhibitors vary.
McAb inhibitors: PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies block the interaction between PCSK9 and LDL-R, inhibiting LDL-R degradation and lowering LDL-C levels. Similar peptides exert their inhibitory effects by blocking the binding of PCSK9 to the EGF-A domain of LDL-R.
Nucleic acid drugs: Such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), siRNAs, and CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing systems. ASOs are designed to target PCSK9 mRNA, thereby inhibiting intracellular protein translation and PCSK9 protein synthesis through the mechanism of RNase H1 occupying or cleaving the targeted mRNA.
Small molecules: Such as BMS-962476, block the biological activity of PCSK9 by preventing LDL-R binding, leading to disruption of subsequent sorting and degradation steps and increasing receptor recycling and LDL uptake.
Vaccine drugs: Such as L-IFPTA+ vaccine, can inhibit the activity of PCSK9 in the circulation.

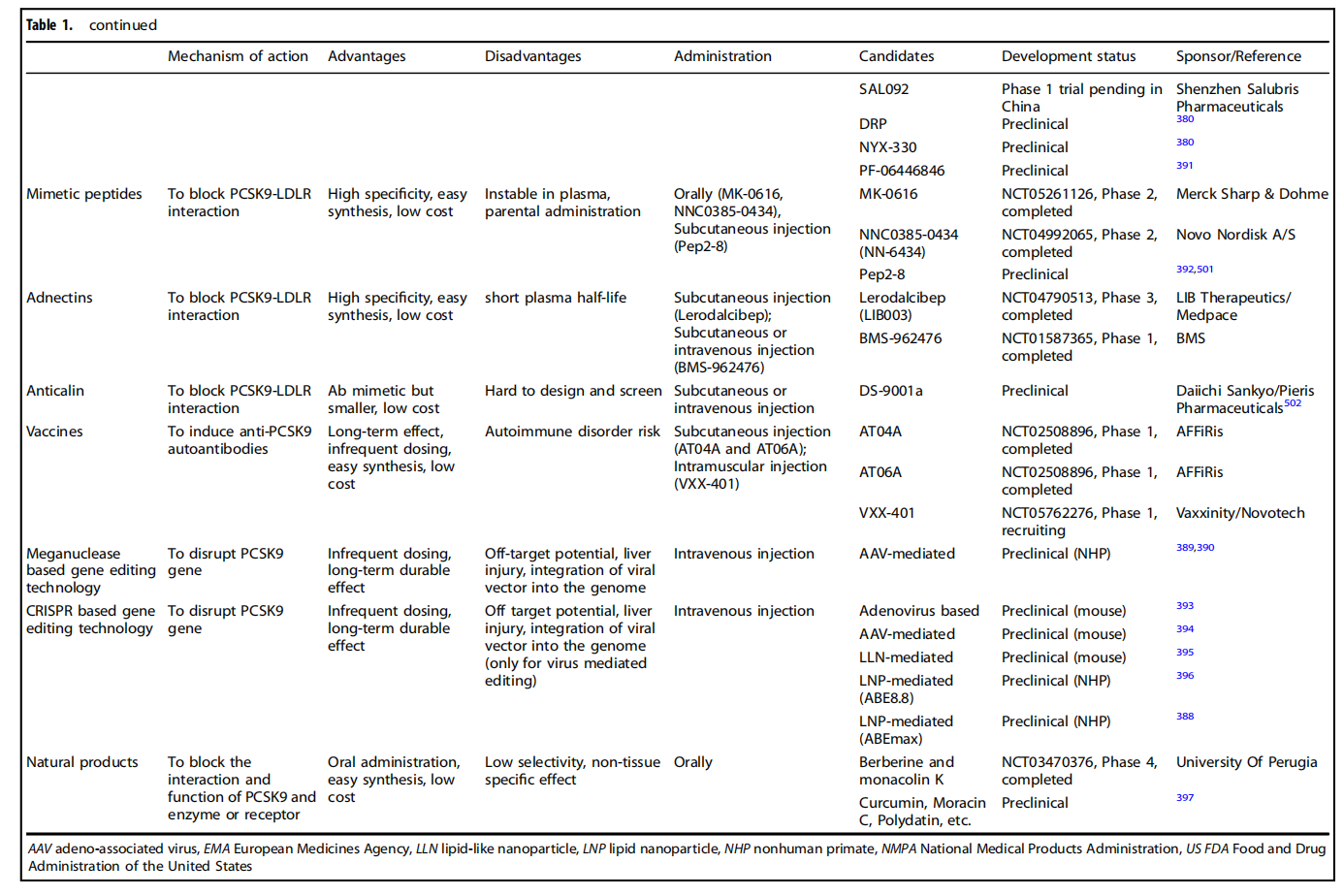
(Data source: Bao X, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024.)
