CD200 is an OX-2 membrane glycoprotein, also known as MOX1 and MOX2. It can synergistically stimulate T cell proliferation and may regulate myeloid cell activity in various tissues. CD200 is an immune checkpoint molecule that interacts with the specific receptor CD200R to guide signal transduction. CD200 exerts its immunosuppressive effects by inhibiting natural killer (NK) cell activation, cytotoxic T cell function, and M1-polarized macrophage activity, while promoting the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and Tregs.
Expression distribution of CD200
CD200 expression has been detected in a variety of immune cells and normal tissues, including human thymocytes, neurons, activated T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, vascular endothelial cells, glomeruli, epithelial keratinocytes, and trophoblasts.
CD200R is highly expressed on macrophage-associated macrophages (TAMs), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), and tumor-associated dendritic cells (TADCs) in the tumor microenvironment (TME).
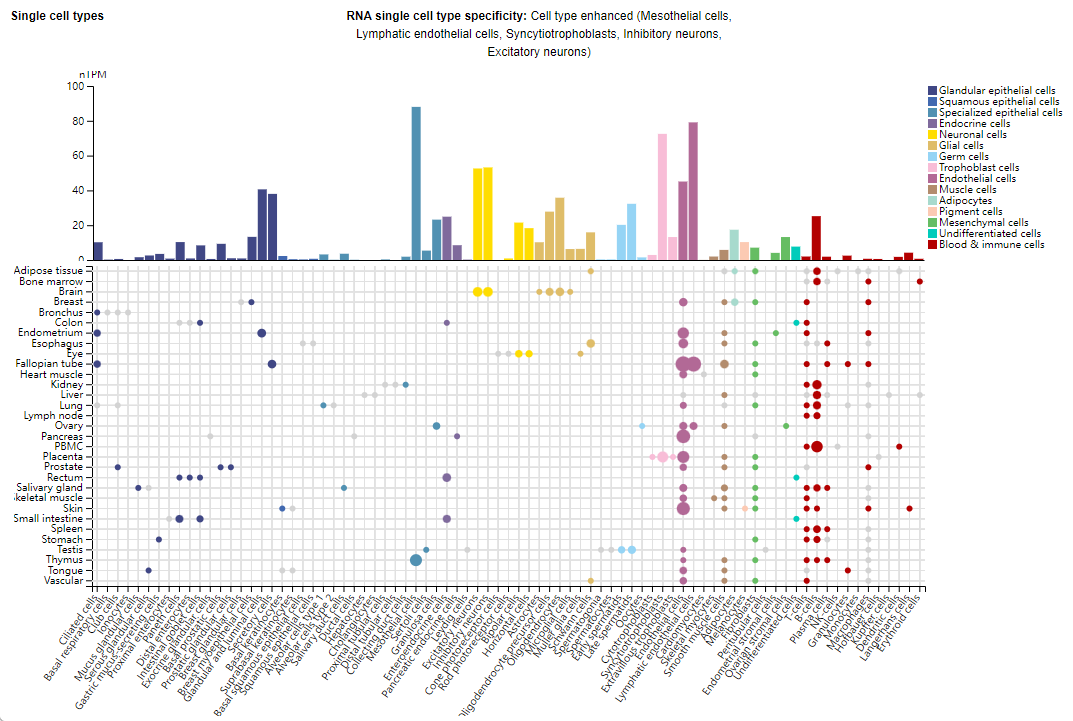
(Data source: Uniprot)
The structure of CD200 and its receptor
CD200 is a single-pass transmembrane type I membrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) of proteins. It comprises two extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains, a transmembrane domain, and a 19-amino acid cytoplasmic "tail." The V-like domain, located at the NH2 terminus of CD200, is the primary region for interaction between CD200 and CD200R. It contains a short α-helix located within the EF loop. The C2-like domain, located downstream of the V-like domain, is not directly involved in the interaction with CD200R but may play a role in maintaining the overall structure and stability of CD200.
CD200R is also an IgSF protein, containing two extracellular Ig-like domains. However, its cytoplasmic 67-amino acid "tail" has three phosphorylated tyrosine residues that participate in intracellular signaling.

(Data source: Hatherley D, Lea SM, Johnson S, Barclay AN. Structure. 2013)
Regulation of CD200 signaling pathway
CD200 signaling has both canonical and non-canonical pathways. In the canonical pathway, CD200 exerts its downstream immunosuppressive effects after interacting with its receptor, CD200R. This leads to the recruitment of the adaptor proteins Dok1, Dok2, SHIP, and RasGAP—and inhibition of Ras/MAPK signaling. CD200 also participates in an "atypical" intracellular pathway that promotes a pro-tumor phenotype independent of signaling through CD200R.
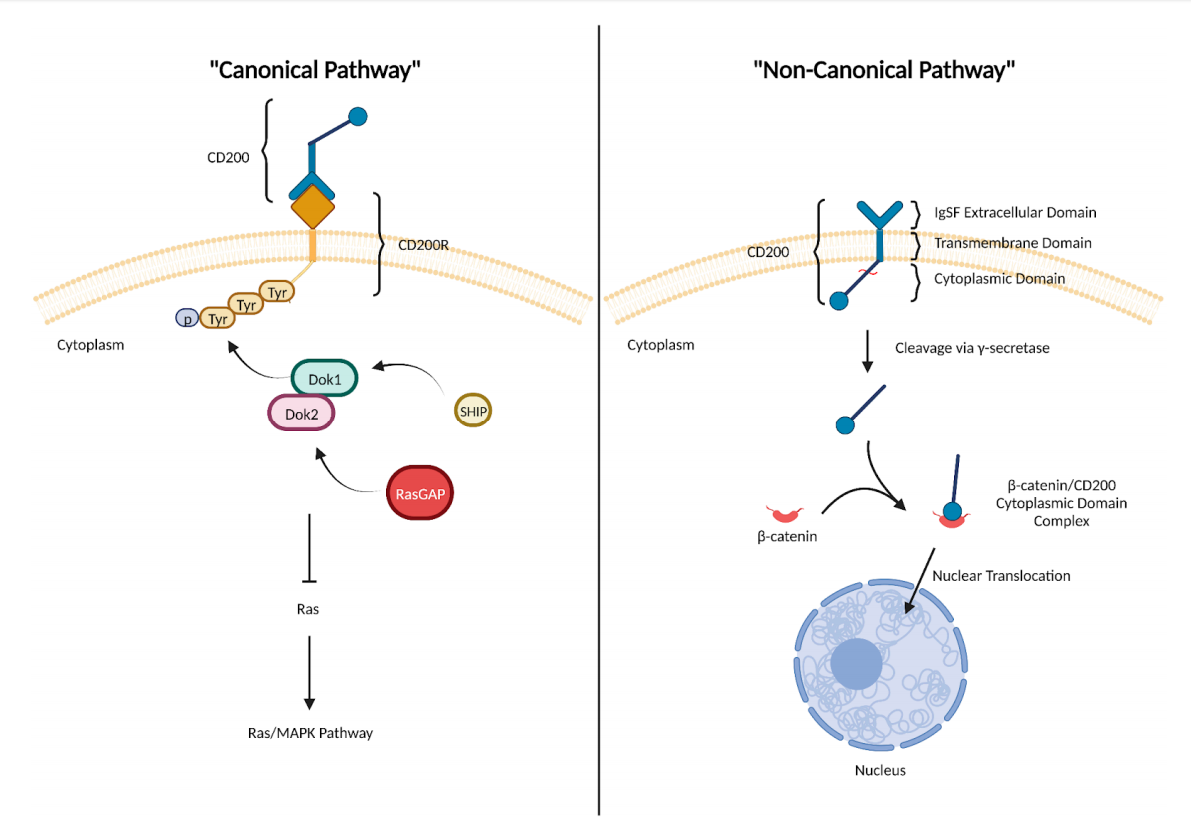
(Data source: Nip C, et al. Biomedicines.2023)
Dual roles of CD200/CD200R signaling in cancer
The CD200/CD200R axis plays a critical role in maintaining immune tolerance and protecting healthy tissues from unwanted immune damage. It regulates the levels of activated myeloid cells under normal and pathological conditions, preventing chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases. It also plays a central role in balancing appropriate immune surveillance, inflammatory responses, and pathogen clearance, while maintaining tissue homeostasis. However, CD200 expression has also been implicated in the pathogenesis of solid tumors and hematological malignancies by mediating immunosuppression of both innate and adaptive immune responses.
CD200/CD200R signaling promotes cancer progression
CD200/CD200R signaling inhibits NK cell activation by reducing NKp44 and NKp46 expression, reduces MAPK/STAT3-mediated Th1 cytokine production, blocks metabolic signaling within T cells, leading to an inactive T cell phenotype, inhibits DC-mediated T cell activation, promotes the expansion of Tregs and MDSCs, differentially regulates the production of chemokines involved in immune cell recruitment, such as CXCL2, CXCL3, CCL3, CCL24, and CCL8, by inhibiting ERK and p38 MAP kinase, and drives M-CSF-mediated M2 macrophage polarization by increasing β-catenin/S100a4-RAGE/NF-κB/M-CSF signaling. Furthermore, CD200/CD200R signaling stimulates cancer cell invasion and metastasis by increasing the expression of Ctsk and genes associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
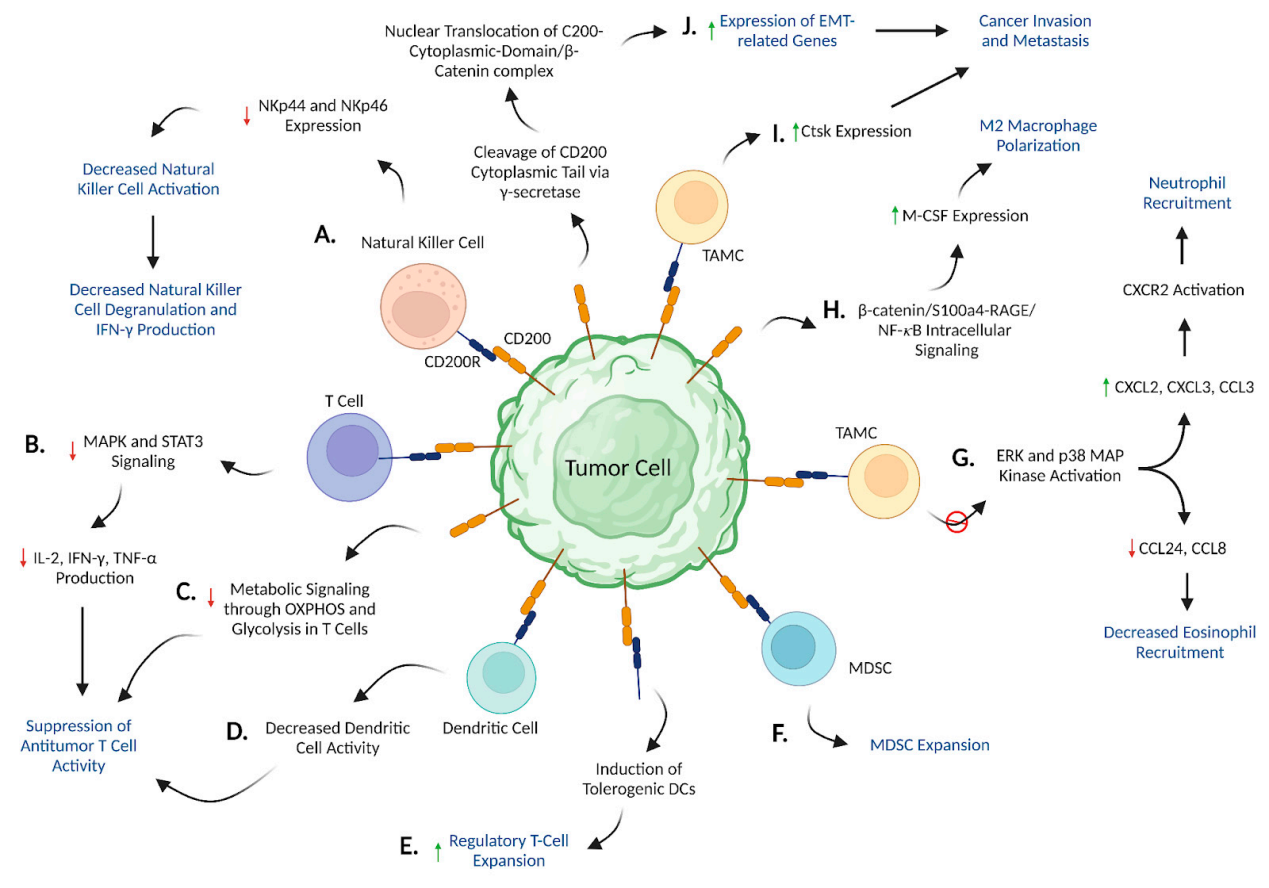
(Data source: Nip C, et al. Biomedicines. 2023)
CD200/CD200R inhibits tumor growth and metastasis
CD200/ CD200R signaling in breast cancer and melanoma. In breast cancer, the CD200/CD200R axis prevents tumor-promoting inflammation by reducing tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and decreasing the production of IL-6 and TNF-α.
In melanoma, CD200/CD200R signaling inhibits the expansion of TAMCs, suppresses VEGF-, HIFα-, and MIF-mediated tumor angiogenesis, promotes the infiltration of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells into tumors by increasing the production of CXCL9 and CXCL16, and polarizes macrophages to the M1 phenotype by reducing the release of IL-10.

(Data source: Nip C, et al. Biomedicines. 2023)
CD200 targeted therapy
Ucenprubart (LY3454738), a CD200R-targeting monoclonal antibody developed by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of moderate and severe atopic dermatitis, demonstrated a favorable safety and tolerability profile in a Phase 1 clinical study, with no serious adverse events reported. Although the primary efficacy endpoint was not met, significant improvements in EASI and SCORAD scores were observed in patients with atopic dermatitis, with some patients maintaining efficacy 12 weeks after discontinuation of treatment, demonstrating potential durability.
In February 2025, Eli Lilly announced in its financial report the termination of the Phase II clinical trial of Ucenprubart for atopic dermatitis, which became a major setback in its research and development process.
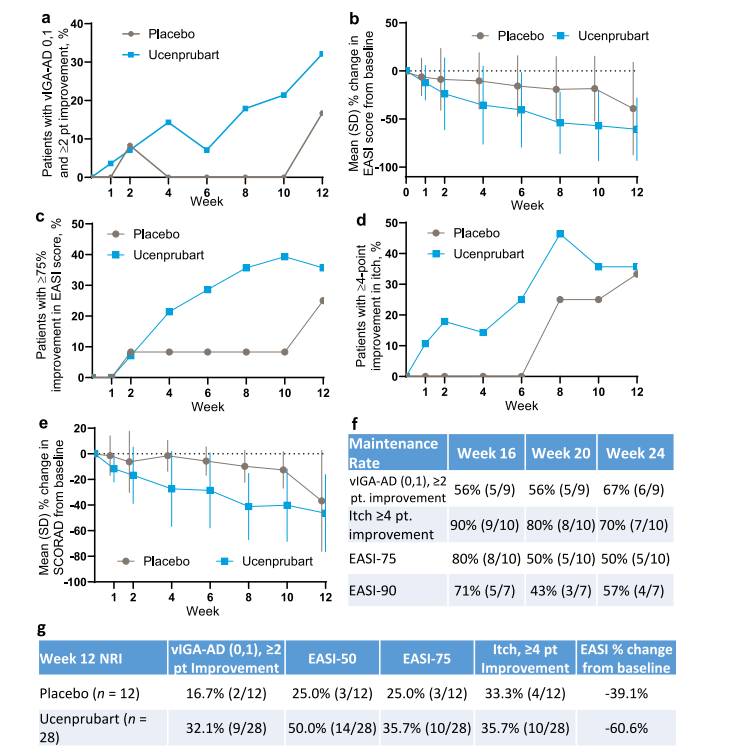
(Data source: Koester A, Witcher DR, Lee M, et al. Nat Commun. 2025)
Samalizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CD200, is being investigated for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. In a Phase I clinical trial (NCT00648739) sponsored by Alexion Pharmaceuticals, a team of researchers tested the efficacy, safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of samalizumab in patients with CLL and multiple myeloma (MM)-related tumors. Phase I study results suggest the drug has potential in treating cancers, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Although the clinical trial was terminated by Alexion Pharmaceuticals for administrative reasons, preliminary results from the study demonstrated the relative safety of samalizumab and its potential to reduce tumor burden associated with CLL.
23ME-00610 is a fully humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction between CD200R1 and its ligand CD200, thereby relieving the immunosuppressive state of the tumor microenvironment. Results from the Phase 1 portion of a Phase 1/2a trial of 23ME-00610 demonstrated acceptable safety and tolerability, favorable pharmacokinetic (PK) characteristics, and saturated binding to the CD200R1 target. Based on these Phase 1 data, 23andMe selected a dose of 1400 mg intravenously administered every three weeks to evaluate the drug's anti-tumor activity in the ongoing Phase 2a trial. In November 2024, 23andMe announced the closure of its therapeutic drug division and the termination of all clinical trials, including the development of 23ME-00610, due to a strategic restructuring.
