IL-15 is a potent immunostimulatory cytokine that enhances T and NK cell immune responses. IL-15 promotes tissue protection by promoting the clearance of infected cells. IL-15 dysregulation plays a pathological role in organ-specific autoimmune diseases, including celiac disease. IL-15 can enhance the anti-tumor activity of immune cells. IL-15 shares the same receptor subunits as IL-12 (Shared β and γ chains), activating similar signaling pathways and exhibiting similar biological activities. Due to the severe side effects and toxicity of IL-2 therapy, its clinical application remains limited. IL-15, similar in function to IL-2 and offering additional benefits, has emerged as an alternative to IL-2.
(Data source: Cai M, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023)
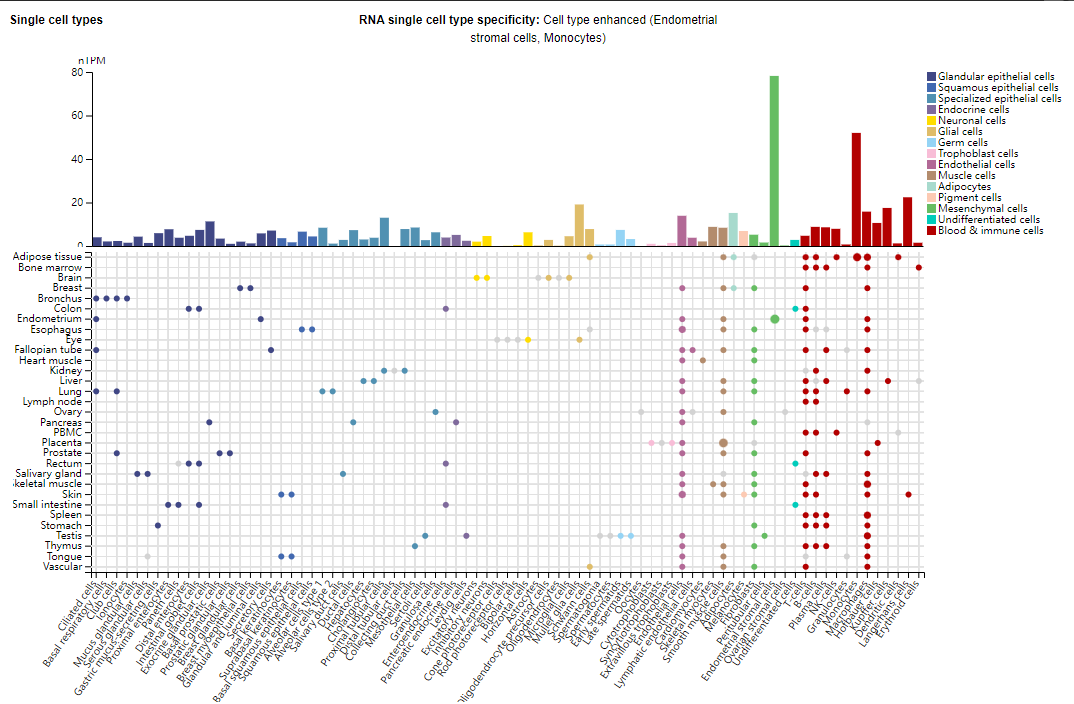
IL-15 expression distribution
IL-15 is ubiquitously expressed and is present in both hematopoietic cells (such as monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells) and non-hematopoietic cells (such as keratinocytes, fibroblasts, neurons, skeletal muscle, and epithelial cells).
(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure of IL-15 and its receptor
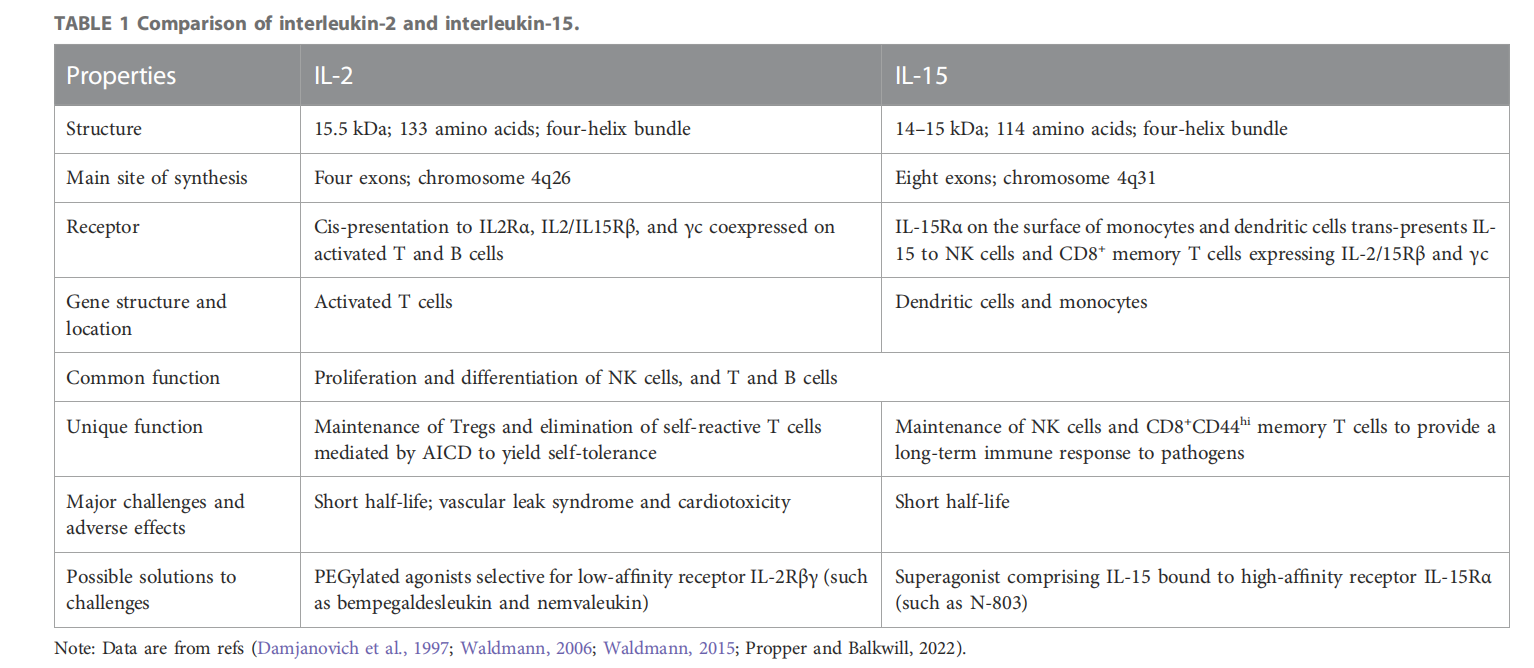
IL- 15, structurally similar to IL-2, is a 4-alpha-helical glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 14-15 kDa and located on human chromosome 4q31. The IL-15 receptor is mainly composed of three subunits: α, β, and γ. The α chain is the unique high-affinity receptor for IL-15, IL-15α. The β chain is shared with the IL-2 receptor, termed IL-2/IL-15Rβ; also known as CD122. The γ chain (γc; also known as CD132) is shared with the receptors for IL-2, IL-7, IL-4, IL-9, and IL-21. IL-15Rα is an atypical cytokine receptor with hydrophilic residues surrounding a hydrophobic core of four α-helices. IL-15 and IL-15Rα can form a stable complex. IL-15Rα exists not only as a membrane-bound receptor but also in a soluble form, generated by transmembrane receptor cleavage, which may serve as a protective mechanism against excessive IL-15 activity.

(Data source: Ring AM, et al. Nat Immunol. 2012)
IL-15 signaling pathway and regulation:
IL-15 binds to the high-affinity IL-15Rα subunit expressed on antigen-presenting cells and is trans-presented to the IL-2/IL-15Rβγ heterodimer on NK or CD8 T cells. IL-15 binds to the IL-2/IL-15Rβ/γc heterodimer, inducing JAK1 activation, which phosphorylates STAT3 via its β chain. JAK3 then phosphorylates STAT5 (STAT5A, STAT5B) via its γ chain, activating downstream signaling pathways through three pathways.
Pathway 1: Activation of JAK1/3/STAT3/5, phosphorylated STAT proteins form dimers and are transported to the nucleus for transcriptional activation;
Pathway 2: The adaptor protein Shc binds to the phosphotyrosine residues on IL-2/IL-15Rβ, leading to the activation of the Shc, Grb2, GAB2, P13K and AkT signaling pathways.
Pathway three: IL-15 signaling is associated with the activation of Grb2 and SOS, forming a Grb2/SOS complex, activating the RAS-RAF MAPK pathway, and participating in cell proliferation.

(Data source: Waldmann TA, et al. J Exp Med. 2020)
Targeted therapy of IL-15
IL-15 inhibitors can prevent IL-15 from binding to its receptor. Commonly used IL-15 inhibitor drugs mainly target soluble IL-15Rα, IL-15 mutants, specific antibodies against IL-15 or IL-2/IL-15Rβ, mutation modifications of IL-2 (BNZ-1 and 2, H9-RETR) to block the interaction between IL-15 and its receptor, and JAK inhibitors.
BNZ-1 is a targeted IL-15 inhibitor. It is a polypeptide that binds to the IL-15 co-receptor γ chain (γc), preventing the formation of heterodimers between IL-15 and its receptor complex (including IL-2/IL-15Rβ and γc), thereby inhibiting the biological function of IL-15.

( Data source: Waldmann TA, et al. J Exp Med. 2020)
IL-15 agonists: Because IL-15 typically does not exist as a monomer but often binds to IL-15Rα to form a heterodimer, the development of IL-15Rα-targeting agonists is crucial. ALT-803 (N-803) is a fusion protein targeting IL-15Rα , consisting of a higher-affinity IL-15 variant (IL-15N72D) and a human IL-15Rα sushi domain-Fc fusion protein. It was approved for marketing in April 2024 for the treatment of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, and platinum-resistant ovarian cancer.
IL-15 can be used in combination with other drugs. IL-15, combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies) and other cytokines , can enhance the anti-tumor activity of NK cells and CD8+T cells.

(Data source: Ma S, et al. Trends Immunol. 2022)
