Tumor necrosis factor TNFa Necrosis Factor-alpha is a cytokine that was originally discovered to be associated with anti-tumor activity and has been identified as a major regulator of inflammatory responses, participating in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
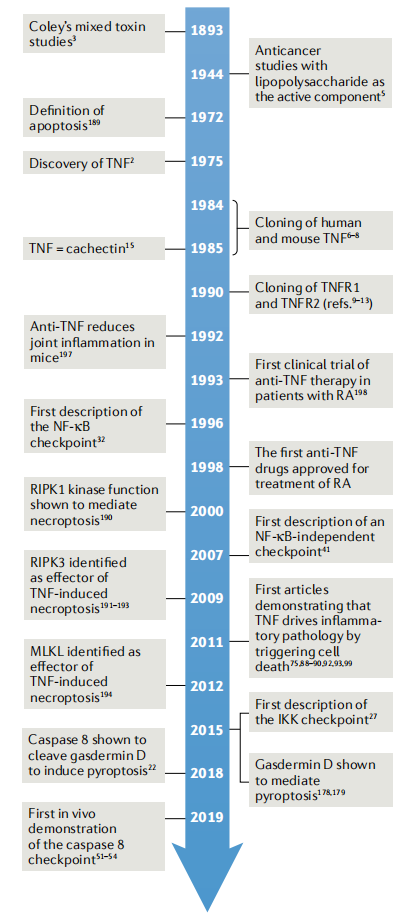
(Data source: vanLooG,et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023)
Definition and structure of TNFa:
TNFα is mainly composed of a 233-amino acid long type II transmembrane protein to form a stable homotrimeric arrangement, called the transmembrane form (mTNFa). Its soluble form (sTNFa) is produced by the cleavage of mTNFa by the metalloproteinase TNFα converting enzyme. mTNFa is mainly present on monocytes/macrophages.
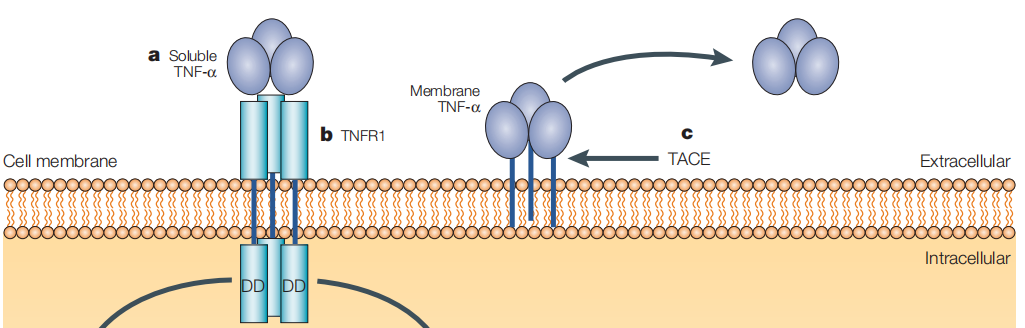
(Data source: Palladino MA,et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003.)
Cell Signaling:
sTNFα selectively binds to TNFR1, while mTNFα binds to both TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNFα binding to TNFR1 is irreversible, while binding to TNFR2 is reversible. TNFR1 signaling tends to be proinflammatory and apoptotic, while TNFR2 signaling is anti-inflammatory and promotes cell proliferation.
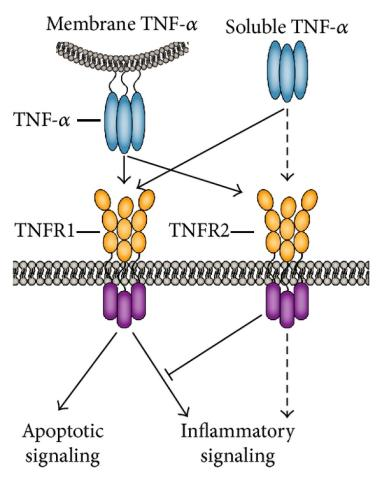
(Data source: https://biosci.mcdb.ucsb.edu/)
Immunomodulation:
Most of the information on TNFα signaling comes from TNFR1, which can initiate three pathways:
I. NF-κB mediates the transcription of a large number of proteins related to cell survival and proliferation, inflammatory response and anti- apoptotic factors.
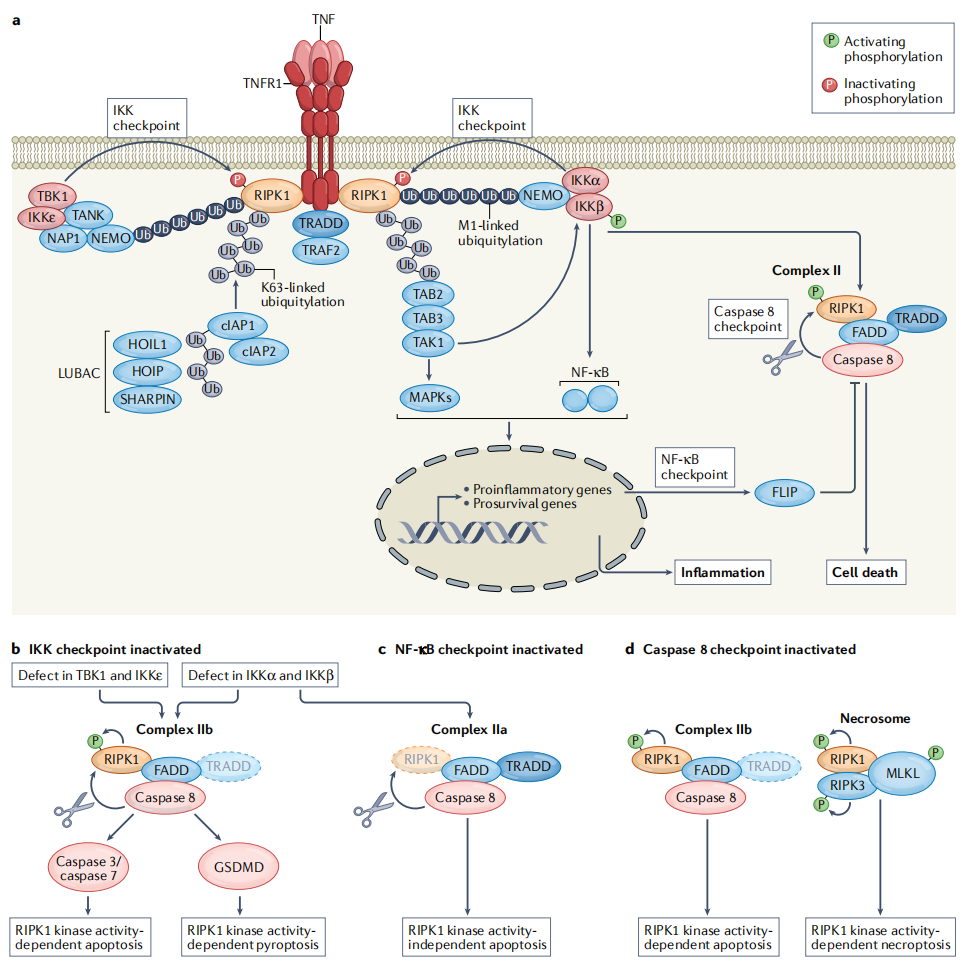
(Data source vanLoo G,et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023)
II. Activation of the MAPK pathway is involved in cell differentiation , proliferation, and is often pro- apoptotic.
III. Induction of death signaling, recruitment of caspases Caspase-8 , high concentrations of caspase -8 induce its own proteolytic activation, followed by cleavage of effector caspases, leading to cell apoptosis.
Clinical treatment:
TNFα signaling is a crucial component of the immune system, inhibiting tumorigenesis, preventing viral replication, and acting as an endogenous pyrogen that induces fever and apoptosis. Dysregulation of this pathway has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, Alzheimer's disease, and depression. Several anti-TNF drugs have been approved for the treatment of inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, and psoriasis.

(Data source: Steeland S,et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018)
