The gain of function (GOF) CTNNB1 mutations (CTNNB1GOF) have been shown to be associated with immune rejection in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), leading to primary resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in HCC patients. In these cases, a suppressive tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) is characterized by T cell exclusion, lack of dendritic cell recruitment, and altered cytokine profiles.

(Data source: doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-331342)
In December 2023, Zhang Wanguang's team from Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology published a research paper titled "Targeting MMP9 in CTNNB1 mutant hepatocellular carcinoma restores CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumour immunity and improves anti-PD-1 efficacy" in the BMJ journal Gut. The study revealed that MMP9 is a promising therapeutic target for CTNNB1GOF, providing an effective combined immunotherapy strategy for enhancing immune activation and anti-PD1 efficacy. Wuhan Mabnus Bio was responsible for the development of the MMP9 blocking antibody in the article.

(Article publication information)
MMP9 expression is upregulated in CTNNB1GOF HCC:
By constructing three different spontaneous liver tumor HCC models, RNA-seq was performed on the three groups of models. The Venn diagram showed three upregulated genes (MMP9, PROCR, ZFP287). The immune score and stromal score were analyzed using the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) screened identified five genes (CXCL5, MMP9, PLAUR, CLEC5A, ITGB6) , thus locating the MMP9 gene.

MMP9 inhibits the activation and migration of CD8+ T cells:
By eliminating CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells or macrophages respectively, we identified specific immune cell subsets regulated by MMP9, confirming that inhibition of CD8+ T cells is essential for MMP9 to promote tumor progression; in vitro co-culture studies showed that the tumor cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells was dose-dependently weakened under MMP9 stimulation, revealing the effect of MMP9 on CD8+ T cell activation.
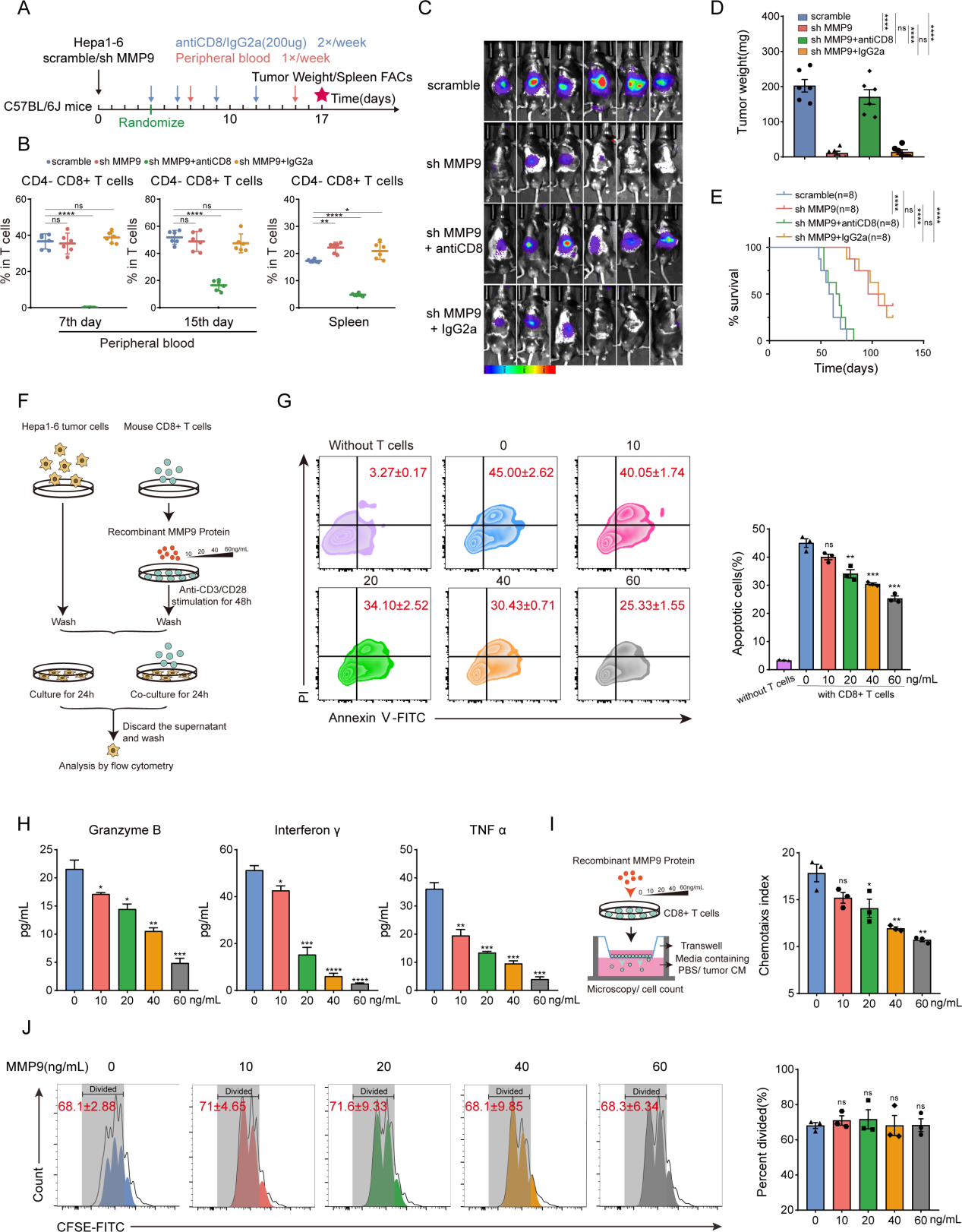
Blockade of MMP9 improves time to cure and enhances anti-PD1 efficacy in CTNNB1GOF HCC:
PD1-based immunotherapy has been widely used in HCC treatment, and tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells have been reported as a biomarker for anti-PD1 therapy. By introducing MMP-9-in-1 (a specific MMP9 inhibitor that selectively targets hemoglobin (PEX)) in combination with anti-PD1 therapy in the CTNNB1GOF HCC model, the combination therapy resulted in more significant tumor regression and prolonged survival compared to either MMP-9-in-1 or anti-PD1 monotherapy.

MMP9 inhibits the infiltration of CD8+ CXCR3+ T cells in CTNNB1GOF HCC:
The researchers further explored the mechanism of MMP9 in reshaping TIME through single-cell RNA-seq: MMP9 gene knockout mainly affected the infiltration and function of CD8+ CXCR3+ T cells (CD8+ CXCR3+ T cells specifically enriched G protein-coupled chemokine receptor activity, regulated T cell activation, leukocyte migration and cell adhesion).

CXCR3-mediated GPCR intracellular signaling by proteolytically shedding SSH1 from CD8+ T cells:
Proteomics identified 26 downregulated proteins in CD8+ T cells after MMP9 stimulation, which were enriched in GTPase activity, GDP phosphatase activity, regulation of cytoplasmic calcium ion concentration and cell migration: gene set enrichment analysis further demonstrated that MMP9 stimulation was related to multiple membrane transport processes, and MMP9 inhibited CXCR3-mediated ERK and AKT phosphorylation in CD8+ T cells. In addition, under MMP9 stimulation, SSH1, which promotes directional cell migration and T cell response to antigen stimulation, was significantly reduced in CD8+ T cells.

Summary:
Combining the above data results, the researchers developed a new anti-MMP9 rabbit monoclonal antibody and evaluated the potential therapeutic value of immunotherapy in preclinical practice. Combined with PD1 treatment, it produced more significant hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth inhibition and prolonged survival, paving the way for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with MMP9-targeted antibody drugs.

