Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable hematologic disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth of plasma cells, primarily in the bone marrow. CD138 (Syndecan-1 or SDC1) is a transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan that is upregulated in malignant plasma cells . CD138 plays a key role in the pathogenesis of MM, promoting tumor cell survival and proliferation, making it an important tumor marker and therapeutic target.
Expression distribution of CD138
CD138 is expressed on plasma cells, hepatocytes, suprabasal keratinocytes, syncytiotrophoblasts, squamous epithelial cells, cholangiocytes, and type 1 pneumocytes).

(Data source: Uniprot)
Structure and function of CD138
CD138 is a 283-amino acid type I transmembrane protein composed of an N-terminal extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and a C-terminal intracellular domain. The extracellular domain contains modified sites for glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains, including heparan sulfate (HS) chains and possibly chondroitin sulfate (CS) chains. These GAG chains enable CD138 to interact with various growth factors, extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, and other ligands. The transmembrane domain anchors CD138 to the cell membrane and contains a conserved dimerization motif (GXXXG) that facilitates interactions between CD138 molecules. The intracellular domain contains two conserved regions (C1 and C2) that are involved in cytoskeletal organization and signaling. The C1 region associates with the actin cytoskeleton, while the C2 region can interact with proteins containing PDZ domains, participating in signaling and intracellular trafficking.
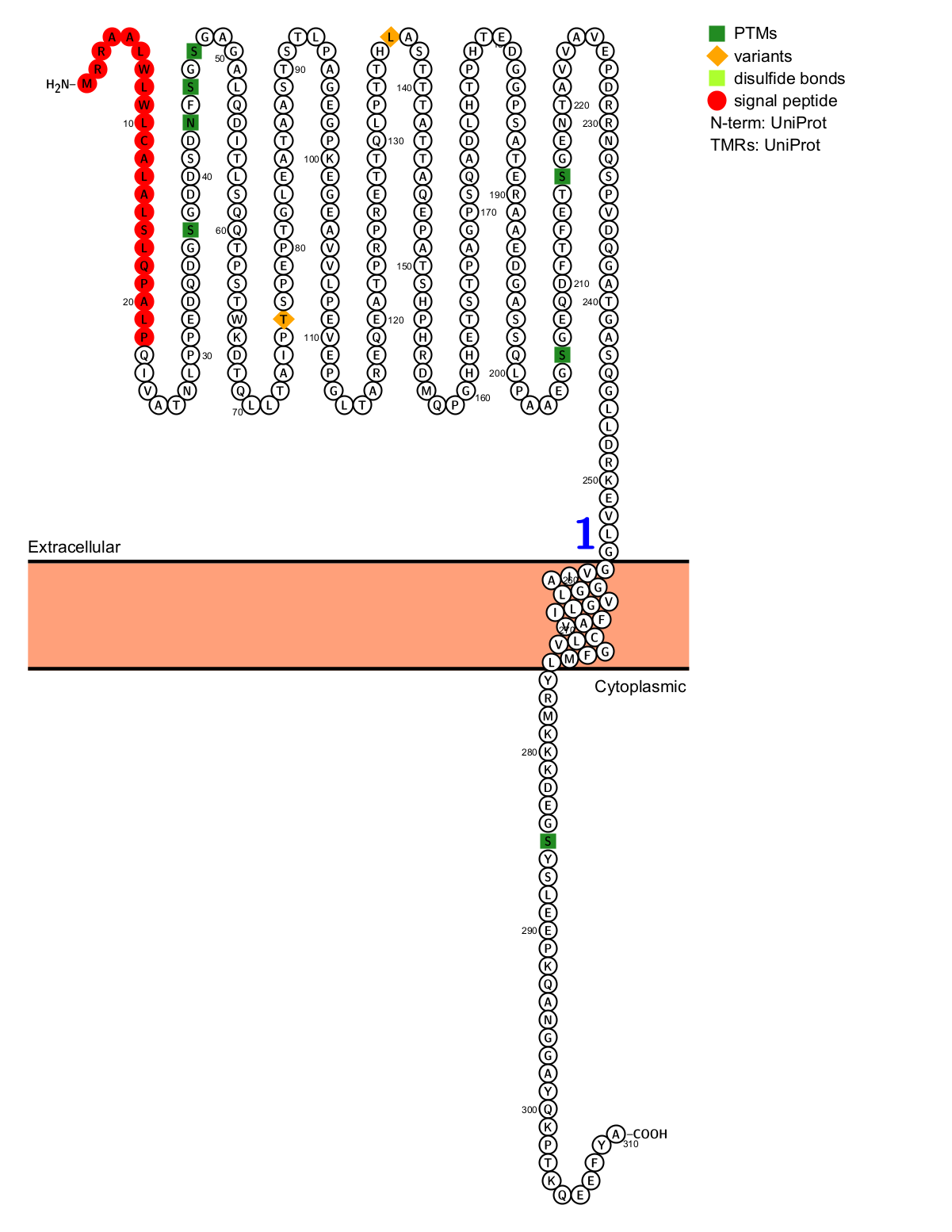
(Data source: Uniprot)
SDC1 interacts with various extracellular matrices and proteins, such as laminin and fibronectin, promoting adhesion and migration. It acts as a co-receptor in various interactions, stabilizing the formation of complexes between GF receptors and α4β1 integrin, activating pathways related to cell proliferation and survival. Its extracellular domain can be cleaved by proteases and released into the extracellular environment; it also acts as a co-receptor on other cells and activates paracrine signaling. CD138 activates multiple factors through its transmembrane domain, including those involved in exosome biogenesis. On endothelial cells, it promotes the interaction between VEGF and VEGFR2, activating angiogenic signaling pathways.
The extracellular domain of SDC1 can be shed from the cell surface and released into the extracellular space, where it enters the circulation as soluble SDC1. Soluble SDC1 acts as a decoy receptor, competing with intact SDC1 and reducing intracellular signaling; soluble SDC1 can also act as an agonist to promote signaling. In multiple myeloma, the HS chain of soluble SDC1 binds to HGF to enhance downstream signaling, including Met, PI3K/PKB, and RAS/MAPK, and promote myeloma cell survival and proliferation.

(Data source: Yang Z, Chen S, Ying H, Yao W. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022)
CD138-targeted therapy
CD138 plays multiple key roles in multiple myeloma and is a crucial regulator of tumor cell growth, survival, invasion, and immune escape. Currently, therapies targeting CD138 primarily include monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and CAR-T cell therapy.

Monoclonal antibodies
VIS832 is a focused humanized IgG monoclonal antibody derived from the B-B4 clone. This monoclonal antibody demonstrates potent and dose-dependent effects on CD138 against MM cell lines and patient-derived MM cells, as well as on-target ADCC mediated by NK cells and macrophages against MM cell lines and autologous patient cells. VIS832 demonstrated significant anticancer activity in MM xenograft mouse models, with both agents synergizing their therapeutic activity, whether used alone or in combination with Len or Btz.
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs)
Indatuximab ravtansine, or BT062 (Biotest AG), is an ADC composed of a chimeric anti-CD138 IgG4 mAb (clone B-B4) conjugated to the maytansine DM4 (or ravtansine) via a disulfide linker. BT062 has demonstrated significant anticancer activity in preclinical testing, inhibiting tumor growth and prolonging host survival in xenograft mouse models as a monotherapy and in combination with Len and Len/Dex in in vitro and in vivo mouse MM xenograft models. Building on this promising progress, a Phase I clinical trial is investigating the efficacy and optimal dose of BT062 as a monotherapy in patients with RRMM (NCT00723359).

Bispecific antibodies
STL001 is a bispecific anti-CD138/CD3 antibody composed of two single-chain variable fragment (scFV) arms with IgG1-Fc region sequences. This bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) can target immune T cells and NK cells, as well as MM cell co-cultures, and has demonstrated enhanced anti-tumor activity in vitro compared to a combination of single anti-CD138 and anti-CD3 mAbs. Notably, STL001 achieved 90.1% MM cell lysis, significant T cell activation efficiency, and in vitro interaction with NK cells. Furthermore, administration of STL001 in a human MM xenograft mouse model resulted in a significant 75% reduction in tumor volume compared to a negative control.
CAR-T cell therapy
CART-138 is a modified CAR-T cell composed of an anti-CD138 scFv fused to the T cell activation domain 4-1BB. In the Phase I/II clinical trial NCT01886976, autologous CART-138 was tested as a treatment option in five chemotherapy-refractory MM patients. Data collected in this study showed that four infused patients returned to a stable disease state within more than three months, and one patient with advanced plasma cell leukemia had a significant reduction in MM cells in the peripheral blood. In addition to the clinical results, the treatment regimen was generally safe and well tolerated, with no serious adverse reactions.

(Data source: Riccardi F, et al. Front Oncol. 2024)
