Neurotensin receptor 3 (NRT3), also known as glycoprotein 95 (Gp95) or sorting protein (SORT1), functions as a sorting receptor within the Golgi apparatus and a clearance receptor on the cell surface. It is required for the transport of proteins from the Golgi apparatus to lysosomes via a pathway independent of the mannose-6-phosphate receptor (M6PR). Its genetic polymorphism is significantly associated with plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels and the risk of myocardial infarction. SORT1 has become a promising new target for the treatment of metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and various cancers.
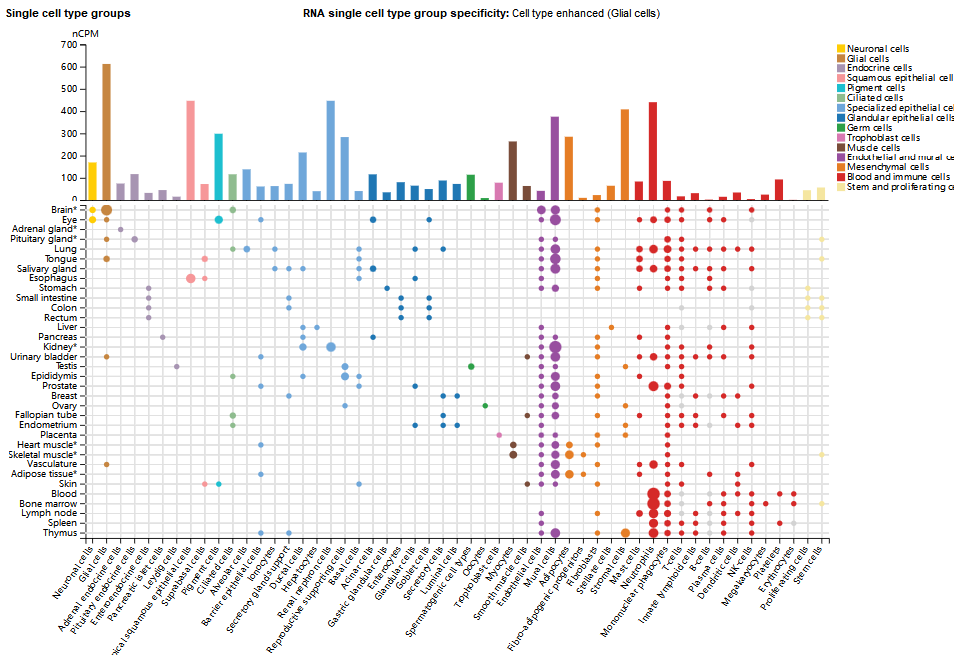
SORT1 expression distribution
SORT1 is most highly expressed in the brain, spinal cord, heart, skeletal muscle, thyroid, placenta, and testes. At the cellular level, SORT1 is widely expressed in many cells, mainly in glial cells, and also in adipocytes, specialized epithelial cells, monocytes, cardiomyocytes, and thyroid gland cells.

(Data source: unprot)
The structure of SORT1 and its receptor
SORT1 is a type I transmembrane protein composed of 831 amino acids and consists of a signal peptide, an extracellular region, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic region.
VPS10 domain: Located in the extracellular region, it is a key region for recognizing and binding numerous ligands, including neurotrophic factor precursor (proBDNF , proNGF), neurotensin (NTS), lipoprotein lipase (LPL), and granocyte protein precursor (GRN).
Cytoplasmic tail region: Contains motifs that interact with adaptor proteins such as GGA1 and GGA2, as well as the retrotranscription complex (Retromer), and is responsible for regulating the circulation and transport of SORT1 between the Golgi apparatus, endosomes, and plasma membrane.
Post-translational modifications: Phosphorylation at Ser-825 promotes interaction with GGA1; in addition, SORT1 can undergo palmitoylation, which helps it to localize to specific endosome membrane microregions and bind to the reverse transcription complex, thereby completing the reverse transport from endosomes to the Golgi apparatus.

(Data source: Nykjaer A, et al. Trends Neurosci. 2012)

(Data source: Rodríguez FD, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023)
SORT1 Function
Sortilin is widely distributed in neuronal membranes and vesicles, and after being cleaved by ADAM10/17, it produces soluble fragments . In the trans-Golgi network (TGN), Sortilin binds to BACE1 and guides its round-trip transport, regulating the degradation or reuse of BACE1, thereby affecting Aβ production. In the cell membrane (PM) , Sortilin can both deliver APP into lysosomes for degradation and promote BACE1 cleavage of APP, increasing the sAPPβ/Aβ ratio.
Sortilin and p75NTR form a receptor complex that transmits proNGF/proBDNF pro-apoptotic signals; Aβ oligomers upregulate Sortilin, enhance the formation of this complex and internalize AβO, and exacerbate neurotoxicity.
Sortilin can also endocytose and degrade ApoE, reducing the ApoE-Aβ complex and exerting a neuroprotective effect, but whether it can directly clear the ApoE-Aβ complex remains to be confirmed.
Sortilin participates in AD through multiple pathways: regulating APP processing, mediating neurotrophic factor apoptosis signals, and clearing ApoE and Aβ. Its specific effects depend on subcellular localization and expression levels, and it has both pro-pathogenic and neuroprotective potential.

(Data source: Salasova A, et al. Mol Neurodegener. 2022)
SORT1-targeted therapy
Latozinemab (AL001) is a monoclonal antibody targeting SORT1. Latozinemab blocks the interaction between Sortilin and PGRN, reducing Sortilin surface expression, preventing PGRN degradation, and ultimately increasing extracellular PGRN levels. It was primarily developed for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Its highest development stage was Phase 3 clinical trials, which are currently terminated.

(Data source: Boylan MA, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023)
Nivisnebart is an antibody targeting SORT1, developed by Alector, for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia, and is currently in phase 2 clinical trials.
