RGMA plays multiple functions in the developmental and adult nervous systems. It regulates cephalane tube closure, inhibits neurite growth and cortical neuronal branching, and promotes the formation of mature synapses. RGMA can activate downstream signaling pathways after binding to receptors NEO1/neogenin and BMP. RGMA plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal regeneration and survival, and is associated with diseases such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, and spinal cord injury.
RGMA expression distribution
RGMA is highly expressed in the central nervous system, especially in neurons of the spinal cord, cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum.
It is expressed in glial cells, Ledich cells, stromal cells, and fibroadipogenic progenitor cells.
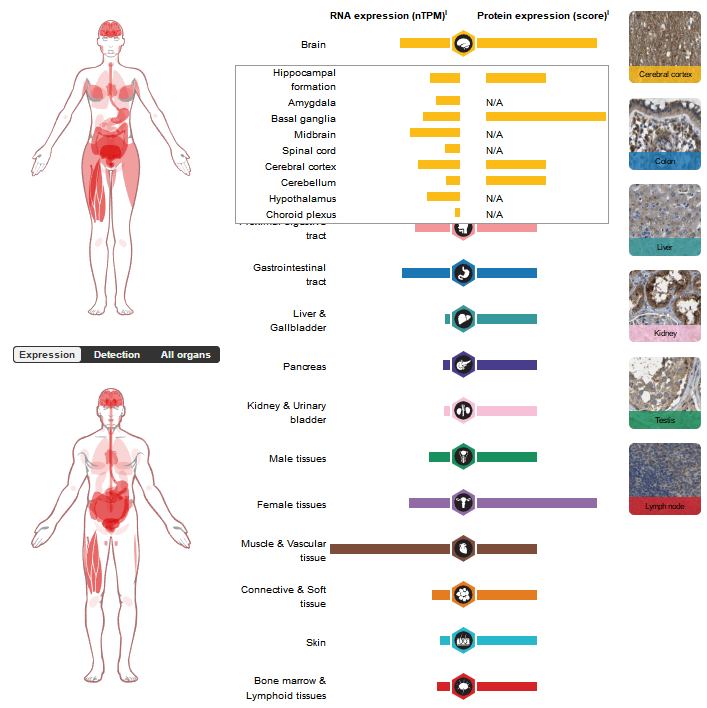
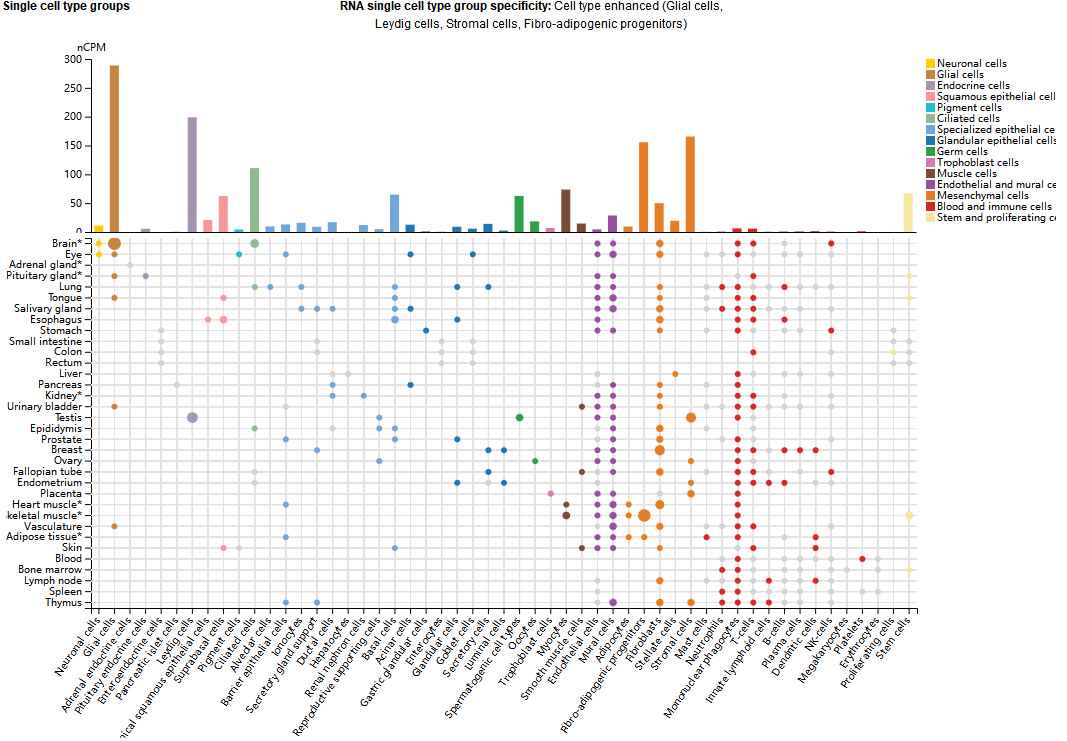
(Data source: uniprot)
The structure of RGMA and its receptor
RGMA is a membrane-associated glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchoring protein, possessing an N-terminal signal peptide, an RGD motif (RGMa and RGMc), and a partially von Willebrand D-type (vWFD) domain. The RGM domain is central to its function, responsible for binding to downstream receptors. The partially von Willebrand D-type domain may be involved in protein stability and oligomerization.
N-terminal domain (N-RGM) of the RGM contains a triple-helix bundle with the " RGD " motif, while the C-terminal domain (C-RGM) forms a tight β-sandwich structure and contains a GDPH cleavage site, mediating its own proteolytic activity. The C-RGM is the major high-affinity interaction site for Neogenin, while the N-RGM contains a Neogenin binding site. RGMs are key activators of BMP signaling, exhibiting high affinity for BMP ligands, and the N-RGM is the high-affinity interaction site for BMP ligands.

(Data source: Siebold C, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2017)
RGMA signaling pathways and regulation
BMP signaling pathway: RGMA acts as a co-receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), potentially transmitting signals via SMAD1, SMAD5, and SMAD8. In the nervous system, activation of BMP signaling is involved in regulating cell differentiation and survival, and under certain conditions, promotes apoptosis. In tumors, the BMP signaling pathway is complex, but the involvement of RGMA may affect tumor cell proliferation and microenvironment remodeling.
Neogenin signaling pathway: After RGMA binds to its receptor NEO1/neogenin, it activates the RHOA-ROCK1/rho kinase signaling pathway via the UNC5B-ARHGEF12/LARG-PTK2/FAK1 cascade, leading to collapse of the neuronal growth cone and inhibition of neurite growth. This makes RGMA a potential therapeutic target for promoting neural regeneration and repair after spinal cord injury. Furthermore, RGMA binding to NEO1/neogenin inactivates the HRAS by affecting the HRAS-ptk2/FAK1-AKT1 pathway.
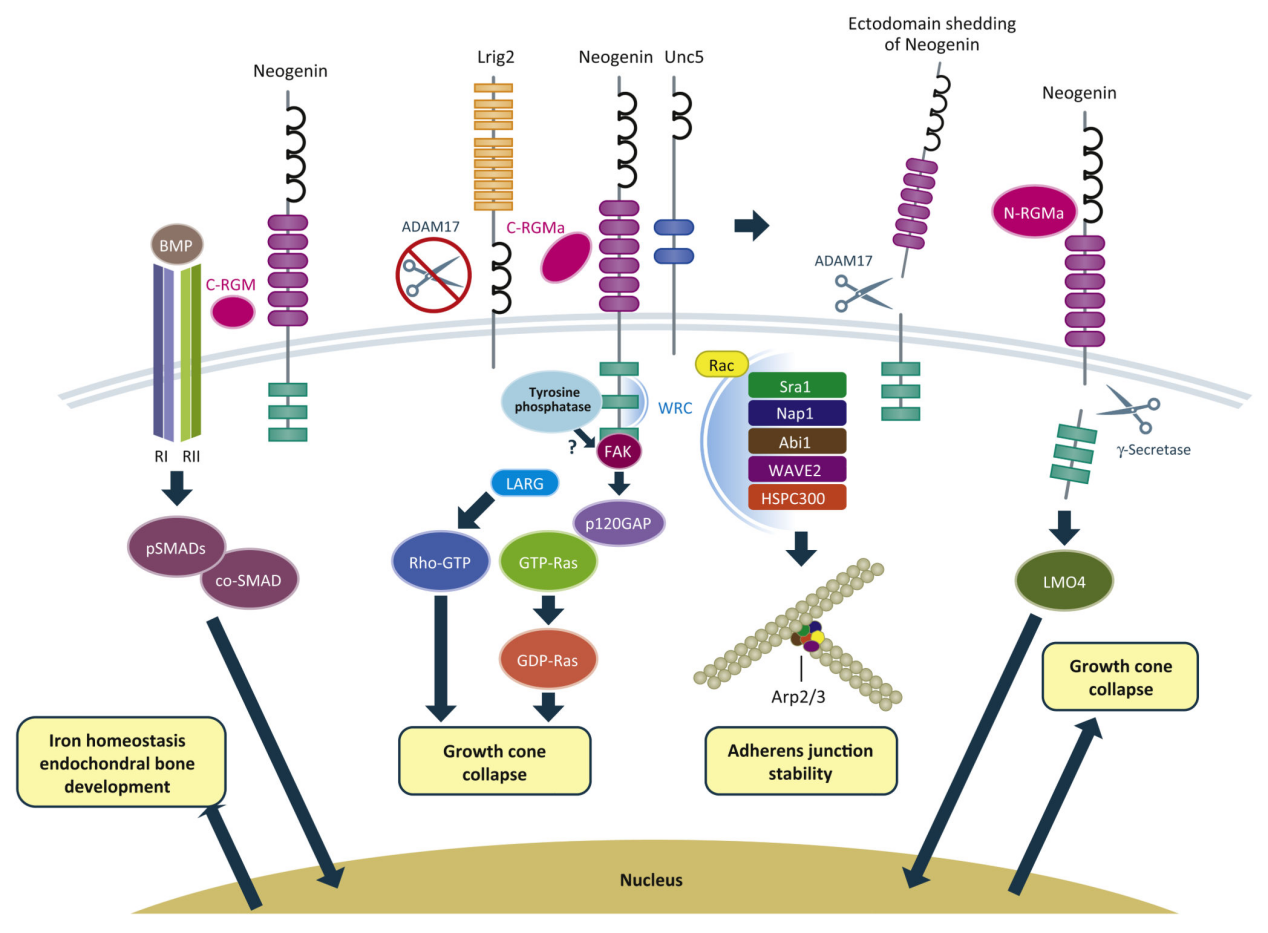
(Data source) Siebold C, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2017)
Targeted therapy for RGMA
Unasnemab (MT-3921) is a monoclonal antibody targeting RGMA, jointly developed by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Osaka University (Japan) for the treatment of spinal cord injury and HTLV-1-related spinal cord disease.

(Data source: Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma official website)
Elezanumab (ABT-555) is a monoclonal antibody targeting RGMA developed by AbbVie for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke and acute spinal cord injury. It is currently in phase 2 clinical trials.

(Data source: AbbVie official website)
