ALCAM is an activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule, also known as CD166 and MEMD , mediating heterotypic cell contacts and homotypic cell contacts through its interaction with CD6, and promoting T cell activation and proliferation by interacting with CD6.
Expression distribution of ALCAM
ALCAM is expressed in oligodendrocytes, oligodendrocyte precursor cells, type I alveolar cells, and to a lesser extent in some immune cells (macrophages, Hofbauer cells, Kupffer cells, dendritic cells, and Langerhans cells).
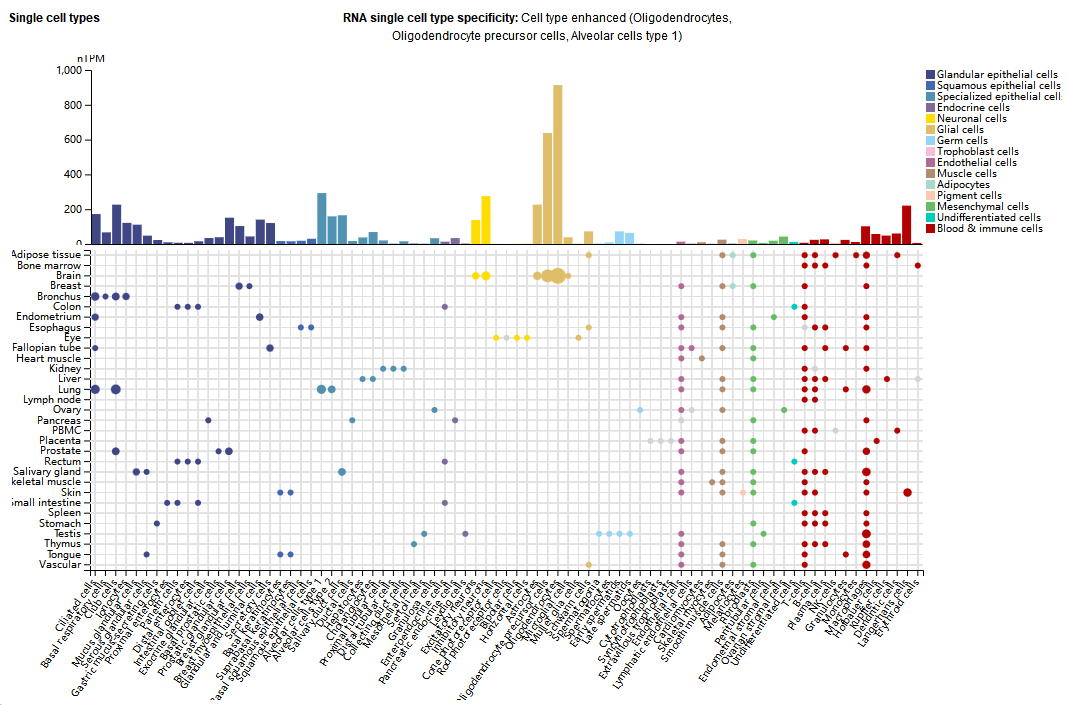
(Data source: uniprot)
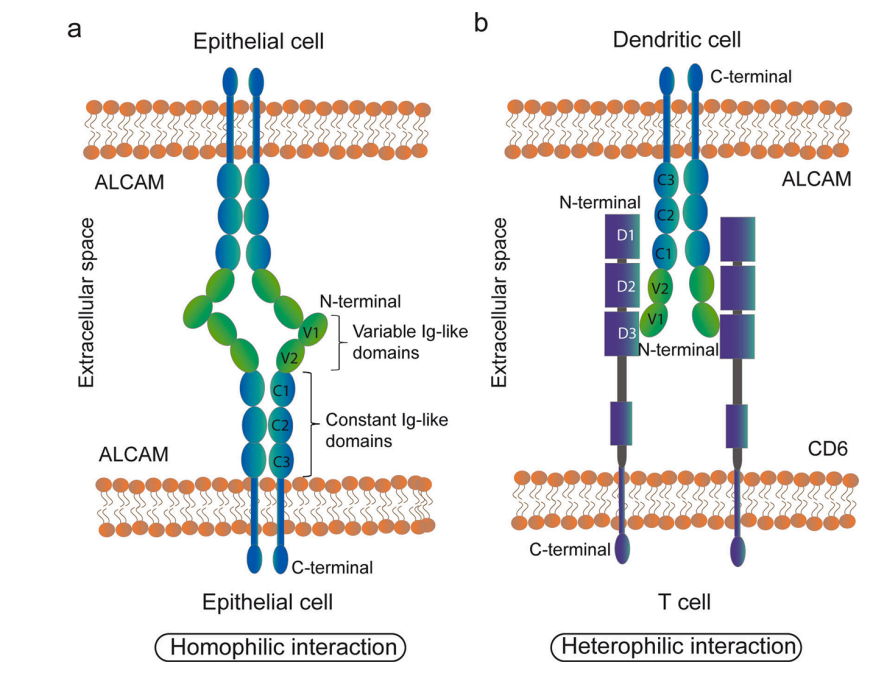
Structure of ALCAM and its ligands
ALCAM is a transmembrane protein and a cell surface glycoprotein related to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Its extracellular domain (ED) contains 10 potential N-glycosylation sites, a transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic domain. The ALCAM ED has five immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains (VVC2C2C2): two amino-terminal membrane-distal variable (V)-type domains and three membrane-proximal constant (C2)-type domains. ALCAM has been shown to have two alternatively spliced isoforms: ALCAM-Iso1 and Iso2. ALCAM-Iso1 is cleaved at the ED by the transmembrane metalloprotease ADAM17. ALCAM-Iso2 possesses a membrane-distal cleavage site that is dependent on MMP-14.

(Data source: Ferragut F, et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021)
ALCAM can undergo homophilic ALCAM-ALCAM interactions and heterophilic ALCAM-CD6 interactions. CD6 is the first ligand, and ALCAM and CD6 are recruited to the interface between T cells and antigen-presenting cells, contributing to the stabilization of the immune synapse and facilitating dendritic cell (DC)-induced T cell activation and proliferation.
Galectin-8 (Gal-8), a novel ALCAM/CD166 ligand, interacts with different glycosylated ligands (such as ALCAM) on the cell surface in a glycosylation-dependent manner.
CD9 is also a ligand for ALCAM, which induces enhanced adhesion of ALCAM-cognate cells and regulates ALCAM shedding. CD9 inhibits ADAM17 shedding enzyme activity, induces enhanced ALCAM aggregation, and increases ALCAM surface expression levels, both of which increase cell adhesion.
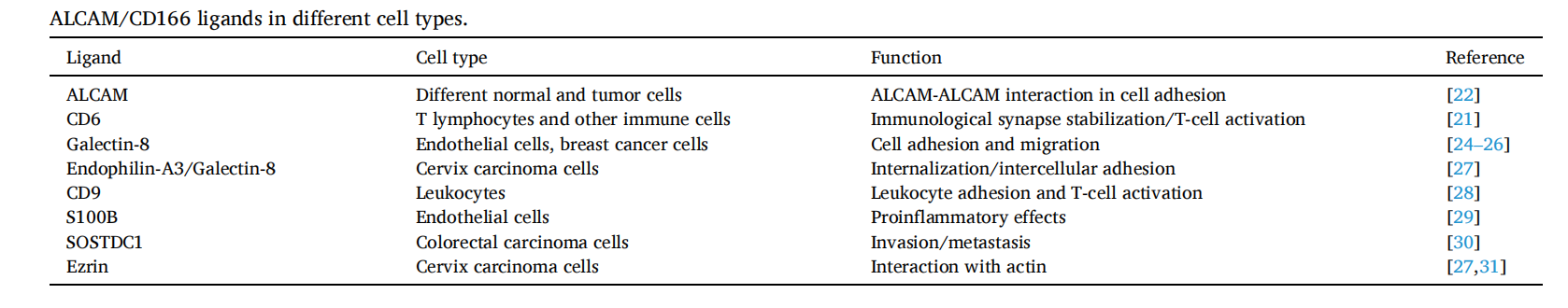
(Data source: Ferragut F, et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021)
Targeted therapy for ALCAM
Praluzatamab is a monoclonal antibody targeting ALCAM, developed by CytomX Therapeutics for the treatment of solid tumors. NCT04596150 is a Phase II open-label study evaluating the safety and antitumor activity of Praluzatamab Ravtansine (CX-2009) in advanced HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer, as well as the efficacy of Praluzatamab Ravtansine as monotherapy and in combination with Pacmilimab (CX-072) in advanced triple-negative breast cancer (CTMX-2009-002).
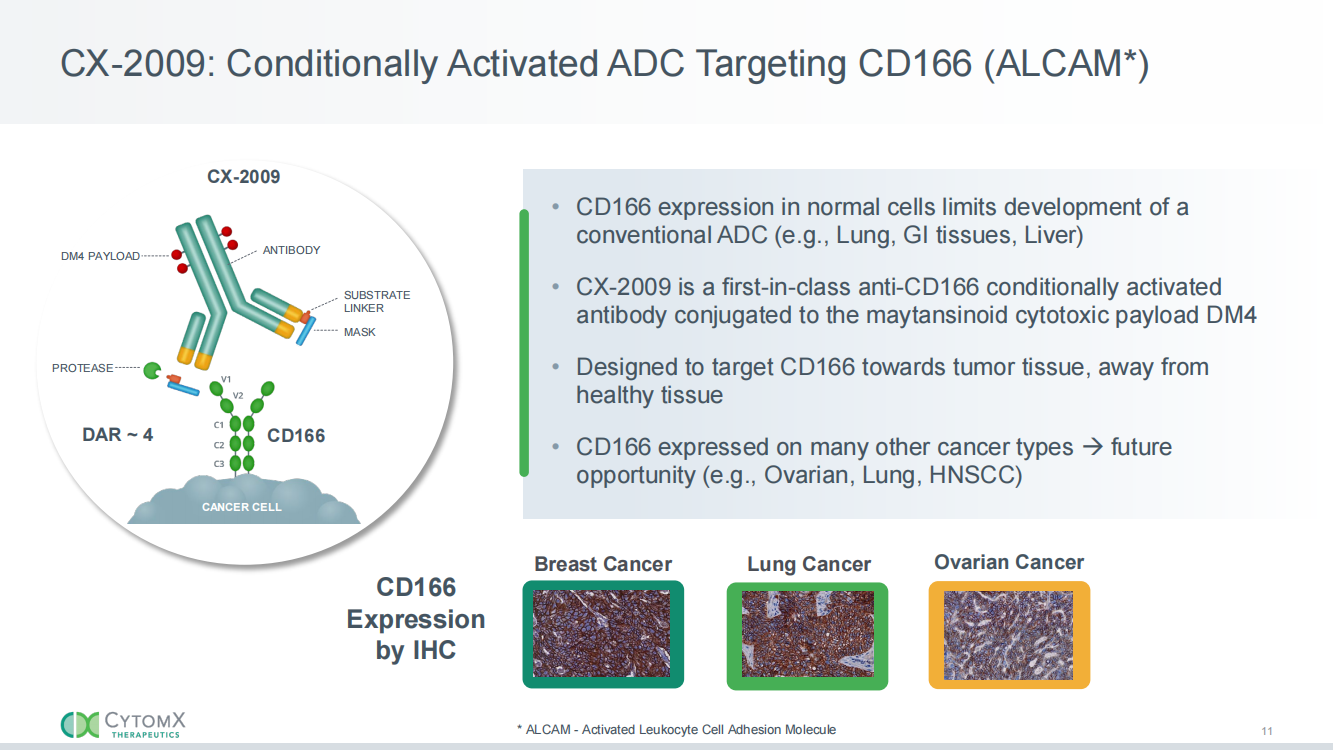
(Data source: CytomX Therapeutics)
